Edible mrna vaccine in lettuce chloroplasts
Edible mrna vaccine in lettuce chloroplasts"
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
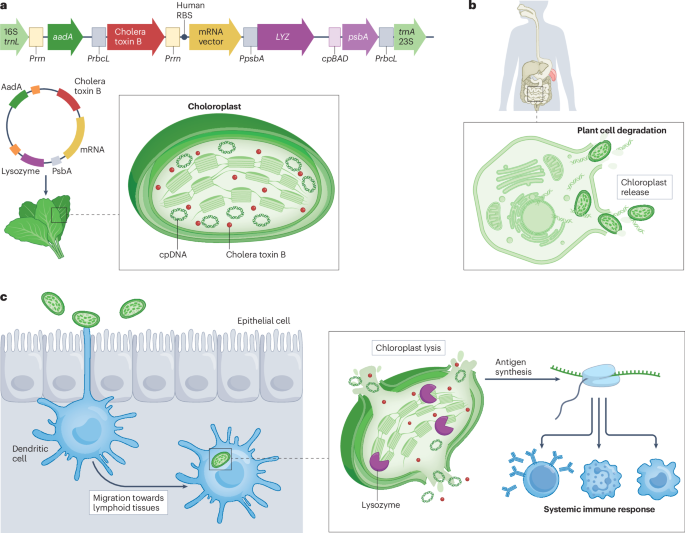
Messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccines hold promise for creating new and improved immunizations; however, their delivery is challenging in terms of compliance, reactogenicity, cost and scalability.
In response to ‘the ultimate bioengineering challenge’ competition, we propose an edible mRNA vaccine platform using lettuce chloroplasts. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 digital issues and online access to
articles $119.00 per year only $9.92 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which
are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support REFERENCES * Han, J. et al.
Chloroplast display of subunit vaccines and their efficacy via oral administration. _Int. J. Biol. Macromol._ 258, 129125 (2024). Article MATH Google Scholar * Kanagaraj, A. P., Verma, D.
& Daniell, H. Expression of dengue-3 premembrane and envelope polyprotein in lettuce chloroplasts. _Plant Mol. Biol._ 76, 323–333 (2011). Article Google Scholar * Jawalagatti, V.,
Kirthika, P. & Lee, J. H. Oral mRNA vaccines against infectious diseases- a bacterial perspective [invited]. _Front. Immunol._ 13, 884862 (2022). Article Google Scholar * Ruhlman, T.,
Verma, D., Samson, N. & Daniell, H. The role of heterologous chloroplast sequence elements in transgene integration and expression. _Plant Physiol._ 152, 2088–2104 (2010). Article
Google Scholar * Ruhlman, T., Ahangari, R., Devine, A., Samsam, M. & Daniell, H. Expression of cholera toxin B–proinsulin fusion protein in lettuce and tobacco chloroplasts – oral
administration protects against development of insulitis in non‐obese diabetic mice. _Plant Biotechnol. J._ 5, 495–510 (2007). Article Google Scholar * Immethun, C. M. et al. Physical,
chemical, and metabolic state sensors expand the synthetic biology toolbox for _Synechocystis_ sp. PCC 6803. _Biotechnol. Bioeng._ 114, 1561–1569 (2017). Article MATH Google Scholar *
Mulo, P., Sicora, C. & Aro, E.-M. Cyanobacterial _psbA_ gene family: optimization of oxygenic photosynthesis. _Cell. Mol. Life Sci._ 66, 3697–3710 (2009). Article Google Scholar *
Stelljes, C. & Koenig, F. Specific binding of D1 protein degradation products to the _psbAI_ promoter in _Synechococcus_ sp. strain PCC 7942. _J. Bacteriol._ 189, 1722–1726 (2007).
Article Google Scholar * Stratmann, T. Cholera toxin subunit B as adjuvant — an accelerator in protective immunity and a break in autoimmunity. _Vaccines_ 3, 579–596 (2015). Article MATH
Google Scholar * Farache, J. et al. Luminal bacteria recruit CD103+ dendritic cells into the intestinal epithelium to sample bacterial antigens for presentation. _Immunity_ 38, 581–595
(2013). Article Google Scholar * Nawaz, N. et al. Lysozyme and its application as antibacterial agent in food industry. _Molecules_ 27, 6305 (2022). Article MATH Google Scholar * Svab,
Z. & Maliga, P. High-frequency plastid transformation in tobacco by selection for a chimeric aadA gene. _Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA_ 90, 913–917 (1993). Article MATH Google Scholar
Download references AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Westlake University, Hangzhou, China Carson Campbell * University of Chicago, Chicago, IL, USA Esteban Azagra Authors *
Carson Campbell View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Esteban Azagra View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed
Google Scholar CONTRIBUTIONS The authors contributed equally to the preparation of this manuscript. CORRESPONDING AUTHORS Correspondence to Carson Campbell or Esteban Azagra. ETHICS
DECLARATIONS COMPETING INTERESTS The authors declare no competing interests. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Campbell, C., Azagra, E.
Edible mRNA vaccine in lettuce chloroplasts. _Nat Rev Bioeng_ 3, 264–266 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s44222-025-00299-1 Download citation * Published: 14 April 2025 * Issue Date: April
2025 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s44222-025-00299-1 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable
link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative