Targeting arid1a-mutant colorectal cancer: depletion of arid1b increases radiosensitivity and modulates dna damage response
Targeting arid1a-mutant colorectal cancer: depletion of arid1b increases radiosensitivity and modulates dna damage response"
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
ABSTRACT The SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex has been found mutated in a wide range of human cancers, causing alterations in gene expression patterns, proliferation and DNA damage
response that have been linked to poor clinical prognosis. Here, we investigated weather knockdown of ARID1B, one of two mutually exclusive subunits within the SWI/SNF complex, can sensitize
colorectal cancer cell lines mutated in the other subunit, ARID1A, to ionizing radiation (IR). ARID1A-mutated colorectal cancer (CRC) cell lines are selectively sensitized to IR after siRNA
mediated ARID1B depletion, as measured by clonogenic survival. This is characterized by a decrease in the surviving cell fraction to 87.3% ± 2.1%, 86.0% ± 1.1% and 77.2% ± 1.5% per 1 Gy
compared with control siRNA exposed cells in the dose range of 0–6 Gy for the LS180, RKO and SW48 lines, respectively (p < 0.0001, F-test). The magnitude of this dose modifying effect was
significantly larger in ARID1A mutated than in non-mutated cell lines (Spearman rank correlation rs = 0.88, p = 0.02). Furthermore, initial formation of RAD51 foci at 4 h after IR, as a
measure for homologous recombination repair, was significantly reduced in ARID1A-mutant CRC cell lines but not in the majority of wildtype lines nor in fibroblasts. These findings open up
perspectives for targeting ARID1B in combination with radiotherapy to improve outcomes of patients with ARID1A-mutant CRC. SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS THERAPEUTIC TARGETING OF
ARID1A-DEFICIENT CANCER CELLS WITH RITA (REACTIVATING P53 AND INDUCING TUMOR APOPTOSIS) Article Open access 29 May 2024 RATIONAL DESIGN OF ALTERNATIVE TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR RADIORESISTANT
RECTAL CANCER USING PATIENT-DERIVED ORGANOIDS Article Open access 10 April 2025 PRKCSH ENHANCES COLORECTAL CANCER RADIORESISTANCE VIA IRE1Α/XBP1S-MEDIATED DNA REPAIR Article Open access 06
April 2025 INTRODUCTION The multiprotein chromatin remodeling complex SWI/SNF plays a key role in the dynamic regulation of gene expression, and mutations of its subunits have repeatedly
been linked to human malignancies. Literature findings suggest a wide-spread role of alterations in the expression of SWI/SNF subunit genes in human cancer susceptibility and patient
survival times1. ARID1A and ARID1B are two mutually exclusive regulatory subunits of the SWI/SNF complex. Notably, mutations of ARID1A were found in several cancers. Wei and colleagues
described loss of ARID1A in colorectal cancer being associated with late TNM stage, poor pathological classification and distant metastasis, and concluded that patients with ARID1A-mutated
cancers may benefit from therapy targeting chromatin modifying enzymes2. Recent studies identified ARID1B as a potentially lethal target in ARID1A-mutant tumors, where depletion of ARID1B
selectively impaired proliferation and caused destabilization of the SWI/SNF complex3,4. Various publications have emphasized the importance of chromatin structure for DNA damage repair,
particularly highlighting the process of chromatin remodeling required to facilitate access of repair enzymes to DNA ends5. As a key member of the chromatin remodeling family, increasing
significance is attributed to the SWI/SNF complex in the processing of double strand breaks (DSB) especially during homologous recombination repair (HRR)6. Additionally to its involvement in
HRR, the SWI/SNF complex was also linked to the recruitment of several factors involved in non-homologous end joining (NHEJ)7. Targeting of chromatin remodeling, particularly of the SWI/SNF
complex8, may therefore prove to be a successful strategy for the sensitization of cancer cells to DNA-damaging therapy such as irradiation. Here, we investigated the effect of ARID1B
knockdown on radiosensitivity in colorectal cancer (CRC) cell lines by measuring clonogenic survival after irradiation of cells with and without ARID1A mutation. Additionally, formation of
DSB repair foci such as RAD51 and 53BP1 was evaluated to determine the mechanism of radiosensitization in ARID1A-mutant CRC cells. RESULTS ARID1B KNOCKDOWN AND ITS EFFECT ON RADIOSENSITIVITY
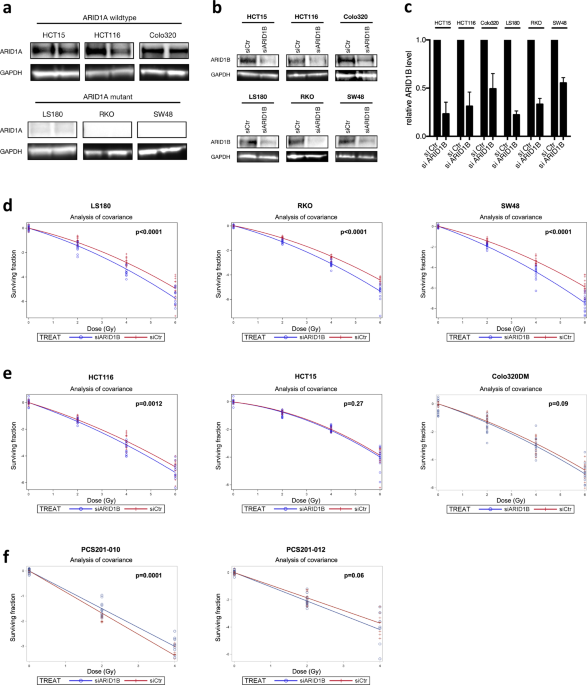
Colorectal carcinoma cell lines with wild type (HCT15, HCT116, Colo320DM) and mutant ARID1A (LS180, RKO, SW48) were investigated. As shown in Fig. 1a, immunoblotting of ARID1A confirmed the
mutation status of the CRC cell lines investigated in the present study. Mutations lead to loss of the full-length ARID1A protein, as also previously reported by Mouradov _et al_.9.
Treatment with ARID1B targeted siRNA reduced the expression levels to about 26%, 38%, 50%, 22%, 37% and 55% in HCT15, HCT116, Colo320DM, LS180, RKO, and SW48, respectively (Fig. 1b,c). To
evaluate the impact ARID1B knockdown has on radiation sensitivity, colony formation assays were performed in ARID1A-proficient and ARID1A-deficient CRC cell lines. ARID1B knockdown lead to a
significant reduction of the surviving fraction in CRC cells harboring ARID1A mutations (Fig. 1d). Radiation sensitivity of all ARID1A-deficient cell lines was increased over radiation dose
levels of 2–6 Gy as compared to control. The dose modifying factors by ARID1B knockdown are shown in Table 1. These dose-modifying factors correspond to a decrease in the survival fraction
to 87.3% ± 2.1%, 86.0% ± 1.1% and 77.2 ± 1.5% per 1 Gy in the dose range of 0–6 Gy for the ARID1A-mutant colorectal cell lines LS180, RKO and SW48, respectively (p < 0.0001, F-test). In
comparison, no significantly increased radiation sensitivity could be observed in ARID1A-proficient cell lines HCT15, Colo320 and primary human adult dermal fibroblasts (PCS201-010,
PCS201-012) (Fig. 1e,f). However, a small but significant sensitizing effect by ARID1B knockdown was observed in HCT116 with a dose-modifying factor of about half that observed in ARIAD1A
mutated lines. The dose-modifying factors due to ARID1B knockdown were significantly smaller in ARID1A-deficient than in ARID1A-wildtype cells (Table 1a). The Spearman rank-order correlation
between mutational status and dose-modifying factor reveals a significant correlation of ARID1A mutation and radiosensitizing effect of ARID1B knockdown (rs = 0.88, p = 0.02).
Radiosensitivity of all CRC cell lines after control transfection is given in Table 1b at the endpoint of the surviving fraction at 4 Gy (SF4) in comparison to unirradiated controls. ARID1A
mutated and non-muted cell lines had similar SF4 values. DEPLETION OF ARID1B INHIBITS INITIAL RAD51 FOCI FORMATION IN ARID1A-DEFICIENT CELLS To elucidate the mechanistic background of
radiosensitization in ARID1A-mutated cell lines, RAD51 foci formation as a marker of HRR was measured. Following ARID1B knockdown, cells were irradiated with 0 and 4 Gy and stained at 4 and
24 hours after irradiation. RAD51 foci formation was studied in cells counterstained with cyclin B1 as a marker for G2-phase cells, to only measure cells proficient in HRR as a pathway for
DNA damage repair (Fig. 2a). Depletion of ARID1B significantly reduced the number of RAD51 foci at 4 hours (maximum of initial level) after irradiation in all ARID1A-mutated cell lines, as
well as in the ARID1A-proficient cell line HCT116 (Fig. 2c), without an effect on RAD51 protein expression (Fig. 2b). RAD51 foci formation in the other investigated ARID1A-proficient cell
lines HCT15 and Colo320DM was not affected (Fig. 2d). Similarly, AIRD1B knockdown did not affect RAD51 foci formation in the human fibroblast cell lines PCS201-010 und PCS201-012 (Fig. 2e).
Additionally, we investigated 53BP1 foci formation as a marker of non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) activity following DNA damage. ARID1B knockdown did not affect 53BP1 foci formation in
either the ARID1A-mutated or the ARID1A-wildtype cell lines at 1, 4 and 24 hours following irradiation with 0, 0.5 and 4 Gy (Fig. 3a,b). Furthermore, to exclude changes in cell cycle
distribution following depletion of ARID1B as a reason for radiosensitization in ARID1B-mutated cell lines, we measured cell cycle distribution after transfection with siARID1B or siControl
exemplarily in RKO and HCT15. Cell cycle profiles did not reveal significant changes following ARID1B knockdown neither in ARID1A-proficient (RKO) and –deficient (HCT15) cell lines (Fig. 4).
DEPLETION OF ARID1B REDUCES PROLIFERATION AND PLATING EFFICIENCY IN ARID1A-PROFICIENT CRC CELL LINES To evaluate the effect of ARID1B knockdown on proliferation, we compared the short-term
proliferative potential of ARID1A-proficient and ARID1A-deficient cell lines after depletion of ARID1B. Knockdown of ARID1B significantly inhibited proliferation of ARID1A-proficient, but
not in ARID1A-deficient cell lines (Fig. 5). Colony formation assays were performed in ARID1A-proficient and ARID1A-deficient cells to evaluate the impact of ARID1B depletion on long-term
survival. Downregulation of ARID1B led to a significant decrease in plating efficiency in all cell lines except LS180, the most pronounced effect being observed in the ARID1A-proficient cell
lines Colo320DM and HCT116 (Table 2). The results from the short-term proliferation assay and the clonogenic survival assay reveal a significant inhibition of proliferation and clonogenic
ability after ARID1B knockdown especially in ARID1A-proficient CRC cell lines, but less in ARID1A-deficient cell lines. DISCUSSION Identifying new cancer-specific vulnerabilities arising in
the context of mutations within the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex can be of pronounced clinical significance, and can potentially give rise to more effective use of radiotherapy
through combination with chromatin-targeted therapy. In the present study, ARID1B knockdown in the context of ARID1A deficiency was evaluated for the effects on the radiosensitivity of CRC
cell lines. Our results demonstrate a novel approach to selectively increase radiation sensitivity in ARID1A-mutated cancers. The data from the colony formation assay reveal that ARID1B
knockdown sensitizes ARID1A-deficient cells without considerably affecting proliferation or plating efficiency, highlighting the specific effect on radiosensitivity. In comparison,
downregulation of ARID1B showed no sensitizing effect in the clonogenic assay for fibroblast cell lines and CRC lines with wild-type ARID1A, except for a minor sensitization of HCT116. While
alterations in SWI/SNF composition have wide-spread roles in tumor biology, these findings describe a very confined and specific vulnerability of the residual SWI/SNF complex in cancers
containing inactivating ARID1A mutations. In order to further investigate the mechanisms of radiosensitization, we investigated whether ARID1B knockdown affects formation of DSB repair foci.
Consistently with the data from the clonogenic survival assay, depletion of ARID1B had a significant impact on the radiation induced RAD51 foci formation in ARID1A-mutated cell lines. RAD51
foci formation in ARID1A-proficient colorectal carcinoma (CRC) cell lines was not affected, except for HTC116. In addition, siARID1B had no effect on RAD51 foci in two different normal skin
fibroblast cells. Rad51 foci were measured in cyclin B1-positive cells alone, since HRR is present in S/G2 phase cells only, further refining this assay to specifically represent HRR
activity. An altered interaction between members of the SWI/SNF complex and HRR enzymes following depletion of ARID1B might ultimately contribute to an increased radiosensitivity in
ARID1A-mutated cell lines. However, much of these possible interactions between SWI/SNF subunits and DSB repair enzymes remain elusive. ARID1A is recruited to double strand breaks mediated
by ATR10. In addition, ARID1B also accumulates at DNA-double strand breaks. Suppression of ARID1A or ARID1B could lead to reduced non-homologous end-joining4. While we did not find an effect
of ARID1B knockdown on 53BP1 foci formation, a marker of NHEJ, in any of the CRC cell line, this does not rule out a role of NEHJ on the observed radiosensitizing effect of ARID1B knock
down in ARID1A mutated CRC cell lines. Park _et al_. pointed out that in ARID1A deficient tumors, decreased accessibility of 53BP1 to DNA lesions leads to reduced NHEJ activity11. Comparing
ARID1A -proficient and -deficient cell lines, we found a broad overlap in the surviving fraction at 4 Gy as a measure for radiosensitivity. Taken together, evidence exists from different
studies that both NHEJ and HR can be affected by ARID1B knockdown. In ARID1A mutated cell lines, ARID1B knockdown led to a marked dose dependent radiosensitization, that was not dependent on
an anti-proliferative effect. Growth inhibition or reduction in platting efficiency was minor or not present in these cell lines and this highlights the selectivity of the radiosensitizing
effect. This radiosensitizing effect on the surviving fraction has the potential to be raised to high power during fractionated irradiation of colorectal carcinomas. In ARID1A-proficient CRC
cells, as well as in fibroblasts, depletion of ARID1B led to a significant inhibition of proliferation without DNA damage, but not to a dose dependent radiosensitization. However, several
of radiation dose-limiting normal tissues around a tumor are non-proliferating. Furthermore, the anti-proliferative effect of ARID1B knockdown in ARID1A proficient cells is consistent with
previous findings describing opposing roles of ARID1A and ARID1B in tumor biology12. Depletion of ARID1B may result in an overbalance of the tumor suppressing properties of ARID1A within the
SWI/SNF complexes, resulting in decreased proliferation of un-irradiated cells with wild-type ARID1A. Consistent with our study, Wang and colleagues demonstrated that ARID1B depletion
inhibits proliferation in bladder cancer cell lines without ARID1A mutation13. Additionally, high levels of ARID1B expression have been linked to poor clinical outcomes in bladder urothelial
carcinoma and breast carcinoma, while low ARID1A levels have been linked to poor clinical outcomes13,14,15,16,17. On the other hand, Helming and colleagues found a synthetic lethal
relationship of ARID1A and ARID1B in a subgroup but not in all of the analyzed ARID1A mutated cancer cell lines, describing ARID1B as a specific vulnerability in ARID1A-mutant cancers3.
Here, we showed that independent from growth inhibition ARID1B knockdown can sensitize ARID1A mutated CRC cells to ionizing irradiation paralleled by a reduction of RAD51 foci induction
indicating reduced homologous recombination. Effective treatment with small molecular inhibitors targeting EZH2, ATR and PARP has already been demonstrated in ARID1A-deficient
tumors10,18,19. ARID1B is potentially drugable through its E3 ubiquitin ligase interaction20, and therefore similar approaches may be used in targeting ARID1B. In conclusion, our study shows
that radiosensitivity in ARID1A mutant CRC cell lines can selectively be increased through depletion of ARID1B, suggesting ARID1B as a potential therapeutic target to increase
radiosensitivity in ARID1A-deficient tumors. METHODS CELL LINES The human CRC cell lines LS180, RKO, SW48, HCT15, HCT116 and Colo320DM were obtained from ATCC (LGC Standards, Wesel,
Germany). LS180, RKO and SW48 were kept in MEM (Invitrogen) supplemented with 15% FBS, 1% essential amino acids and antibiotics. HCT15, HCT116 and Colo320DM were kept in RPMI (Invitrogen)
supplemented with 10% FBS plus antibiotics. Adult dermal fibroblasts (HDFa, PCS-201-012) and neonatal fibroblasts (HDFn, PCS-201-010) were obtained from ATCC. Fibroblasts were cultured with
fibroblast basal medium (FBM, PCS-201-030 from ATCC) supplemented with low serum fibroblast growth kit (ATCC, PCS-201-041). Cells were cultivated at 37 °C in 5% CO2. Irradiation was done
using the RS320 X-Ray machine by XStrahl Ltd. at 300 kV, 10 mA, dose rate 0,9 Gy/min. TRANSFECTION WITH SIRNA Cells were seeded in 6-well plates and incubated for 24 hours, obtaining a
70–80% confluent monolayer. Cells were then washed in HBSS and OptiMEM (both Gibco), and subsequently incubated with transfection reagent for 4 hours. We used 500 µl OptiMEM with 80 nM siRNA
and 6 µl Lipofectamine RNAiMAX (Invitrogen) for transfection reagent. To downregulate ARID1B, we established a mix of two siRNAs (Ambion s199170, Ambion s199168,) at 40 nM each for optimal
efficiency. As controls, we used non-targeting siRNA (Ambion 4390843) as well as H2O. After 4 hours of incubation with the transfection reagent, 500 µl of culture medium with double FBS was
added and cells incubated for 48 hours until harvesting for further experiments. Expression of targeted proteins was regularly checked by Western blots. IMMUNOBLOTTING Western blots were
performed with anti-ARID1A (CellSignalling, 12354P), anti-ARID1B (LS-Bio, LS-C382223), anti-RAD51 (Calbiochem, PC130-100UL) and anti-GAPDH (Abcam, ab8245). The secondary antibodies were
HRP-linked antibodies raised against mouse or rabbit IgG (GE Healthcare, NA931V and NA934V) and Alexa Fluor 488-linked antibodies against mouse (Invitrogen A11029). CELL PROLIFERATION ASSAY
48 hours after transfection, 0,5 × 106 cells were seeded per 25 cm2 flask. Cells were harvested and counted by automatic counting system Luna (Logos Biosystems) at day 1, 2, 3, 4, 7 after
seeding. CLONOGENIC SURVIVAL ASSAY 48 hours after transfection, cells were harvested and plated in triplicates in 9,6 cm2 culture dishes. After 4–6 hours in culture, cells were irradiated
and subsequently incubated for 10–14 days at 37 °C in 5% CO2. Cells were fixed and stained with 96% ethanol, 15% Giemsa and destained with distilled water. Colonies consisting of at least 50
cells were counted. Surviving fractions after the indicated treatments are presented as a fraction of the growth of non-irradiated colonies8. IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE ANALYSIS 48 hours after
siRNA transfection, cells were harvested, reseeded in chamber slides and irradiated 4 hours later. At indicated times after IR, cells were washed, fixed, permeabilized and incubated with
blocking buffer. Primary antibodies anti-RAD51 (Calbiochem, PC130-100UL), anti-cyclin B1 (EMD Millipore, 05-373) and anti-53BP1 (Abcam, ab21083) were added to the cells and incubated
overnight. Secondary antibodies anti-mouse Alexa Fluor 488 (Invitrogen, A11017) and anti-rabbit Cyanine Cy3 (Jackson, 111-165-008) were applied together with 1 µg/ml DAPI (Invitrogen)
nuclear counterstain for 1,5 hours at room temperature. Slides were examined on the fluorescent microscope imager Z1 (Zeiss). STATISTICAL ANALYSIS Colony data were analyzed using a
linear-quadratic model describing the dependence of the logarithm of cellular survival on dose. The interaction between ARID1B knock down and the radiation dose response was described as a
slope modifying effect of the linear term of the linear-quadratic model (Procedure GLM, SAS/STAT 14.1, SAS Institute Inc. Version, Cary, NC, USA). Higher order effects were considered if
significant at alpha = 0.01. DATA AVAILABILITY All relevant data not presenting in the main figures is available from the authors. REFERENCES * Savas, S. & Skardasi, G. Critical Reviews
in Oncology/Hematology The SWI/SNF complex subunit genes: Their functions, variations, and links to risk and survival outcomes in human cancers. _Crit. Rev. Oncol./Hematol._ 123, 114–131
(2018). Article Google Scholar * Wei, X.-L. _et al_. Clinicopathologic and prognostic relevance of ARID1A protein loss in colorectal cancer. _World J. Gastroenterol._ 20, 18404–18412
(2014). Article Google Scholar * Helming, K. C. _et al_. ARID1B is a specific vulnerability in ARID1A-mutant cancers. _Nat. Med._ 20, 251–254 (2014). Article CAS Google Scholar *
Watanabe, R. _et al_. SWI/SNF Factors Required for Cellular Resistance to DNA Damage Include ARID1A and ARID1B and Show Interdependent Protein Stability. _Cancer Res._ 74, 2465 LP–2475
(2014). Article Google Scholar * Price, B. D. & D’Andrea, A. D. Chromatin remodeling at DNA double-strand breaks. _Cell_ 152, 1344–1354 (2013). Article CAS Google Scholar * Chai,
B., Huang, J., Cairns, B. R. & Laurent, B. C. Distinct roles for the RSC and Swi/Snf ATP-dependent chromatin remodelers in DNA double-strand break repair. _Genes Dev._ 19, 1656–1661
(2005). Article CAS Google Scholar * Vélez-Cruz, R. _et al_. RB localizes to DNA double-strand breaks and promotes DNA end resection and homologous recombination through the recruitment
of BRG1. _Genes Dev._ 30, 2500–2512 (2016). Article Google Scholar * Zernickel, E. _et al_. Targeting of BRM Sensitizes BRG1 -Mutant Lung Cancer Cell Lines to Radiotherapy. 18, 656–667
(2019). * Mouradov, D. _et al_. Colorectal cancer cell lines are representative models of the main molecular subtypes of primary cancer. _Cancer Res._ 74, 3238–3247 (2014). Article CAS
Google Scholar * Bitler, B. G. _et al_. Synthetic lethality by targeting EZH2 methyltransferase activity in ARID1A-mutated cancers. _Nat. Med._ 21, 231–238 (2015). Article CAS Google
Scholar * Park, Y. _et al_. Loss of ARID1A in Tumor Cells Renders Selective Vulnerability to Combined Ionizing Radiation and PARP Inhibitor Therapy. 25, 5584–5595 (2019). * Nagl, N. G.,
Wang, X., Patsialou, A., Van Scoy, M. & Moran, E. Distinct mammalian SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complexes with opposing roles in cell-cycle control. _EMBO J._ 26, 752–763 (2007).
Article CAS Google Scholar * Wang, B. _et al_. Expression of ARID1B Is Associated With Poor Outcomes and Predicts the Benefit from Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma.
_J. Cancer_ 8, 3490–3497 (2017). Article Google Scholar * Xu, N. _et al_. Low Arid1a Expression Correlates with Poor Prognosis and Promotes Cell Proliferation and Metastasis in
Osteosarcoma (2017). * Shao, F. _et al_. Clinicopathological significance of ARID1B in breast invasive ductal carcinoma. _Histopathology_ 67, 709–718 (2015). Article Google Scholar * Chou,
A. _et al_. Loss of ARID1A expression in colorectal carcinoma is strongly associated with mismatch repair deficiency. _Hum. Pathol._ 45, 1697–1703 (2014). Article CAS Google Scholar *
Yan, H. B. _et al_. Reduced expression of the chromatin remodeling gene ARID1A enhances gastric cancer cell migration and invasion via downregulation of E-cadherin transcription.
_Carcinogenesis_ 35, 867–876 (2014). Article CAS Google Scholar * Williamson, C. T. _et al_. ATR inhibitors as a synthetic lethal therapy for tumours deficient in ARID1A. _Nat. Commun._
7, 13837 (2016). Article CAS ADS Google Scholar * Shen, J. _et al_. ARID1A Deficiency Impairs the DNA Damage Checkpoint and Sensitizes Cells to PARP Inhibitors. _Cancer Discov._ 5,
752–767 (2015). Article CAS Google Scholar * Li, X. S., Trojer, P., Matsumura, T., Treisman, J. E. & Tanese, N. Mammalian SWI/SNF-A Subunit BAF250/ARID1 Is an E3 Ubiquitin Ligase That
Targets Histone H2B. 30, 1673–1688 (2010). Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This work is funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) as part of the Graduate School (GRK1739/2).
AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Department of Radiotherapy, University of Duisburg-Essen, University Hospital, Essen, Germany B. Niedermaier, A. Sak, E. Zernickel, Shan Xu, M.
Groneberg & M. Stuschke Authors * B. Niedermaier View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * A. Sak View author publications You can also
search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * E. Zernickel View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Shan Xu View author publications You can
also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * M. Groneberg View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * M. Stuschke View author publications
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CONTRIBUTIONS M.S. directed the study. B.N., A.S., S.X. and E.Z. designed and performed experiments. M.G. performed experiments.
B.N., A.S., E.Z. and M.S. analyzed and interpreted the data. M.S., B.N. and A.S. wrote the manuscript. CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to B. Niedermaier. ETHICS DECLARATIONS COMPETING
INTERESTS The authors declare no competing interests. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION PUBLISHER’S NOTE Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and
institutional affiliations. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS OPEN ACCESS This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing,
adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons
license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a
credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted
use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. Reprints and permissions ABOUT
THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Niedermaier, B., Sak, A., Zernickel, E. _et al._ Targeting ARID1A-mutant colorectal cancer: depletion of ARID1B increases radiosensitivity and modulates DNA
damage response. _Sci Rep_ 9, 18207 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-54757-z Download citation * Received: 15 August 2019 * Accepted: 13 November 2019 * Published: 03 December 2019
* DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-54757-z SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link
is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Trending News
Finance: learn more about aarp membership benefitsYour AARP membership empowers you to take control of your financial future and career goals. Explore valuable tools and ...
Jeannie's life spent serving the senior communityFor Jeannie Rubero, working with older adults is more than a job. It’s a calling. Jeannie, 61, tended to both her gran...
Launch: unizon timelock adminUnizon has launched the Unizon Timelock Admin version1.0 . Timelock, as the name suggests, is a mechanism of locking and...
Per2 induction limits lymphoid-biased haematopoietic stem cells and lymphopoiesis in the context of dna damage and ageingABSTRACT Ageing-associated impairments in haemato-lymphopoiesis are associated with DNA damage accumulation and reduced ...
187 hypothermia decreases intrapulmonary shunt in dogsABSTRACT The effect of hypothermia on respiratory failure has not been studied. One possible advantage of hypothermia in...
Latests News
Targeting arid1a-mutant colorectal cancer: depletion of arid1b increases radiosensitivity and modulates dna damage responseABSTRACT The SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex has been found mutated in a wide range of human cancers, causing alter...
Katie price huge transformation includes a 'shopping list of plastic surgeries'KATIE PRICE IS ONLY JUST BACK FROM TURKEY, BUT A SOURCE SAYS SHE HAS MANY MORE PROCEDURES PLANNED FOR THE FUTURE. 14:00,...
Will steve jobs’ resignation shake apple to its core?“God dammit, Gil,” shouted Bill Gates. “Why are you spending $400 million on this junk? Steve knows nothing about techno...
A lifetime of service: josie’s dedication to helping kidsAt a time when many of her friends are living a quiet life, Josephine “Josie” Watson’s days can get busy and loud. She l...
The best places to start a second careerMemorial Day Sale! Join AARP for just $11 per year with a 5-year membership Join now and get a FREE gift. Expires 6/4 G...