Cardiac tamponade | Nature Reviews Disease Primers
Cardiac tamponade | Nature Reviews Disease Primers"
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
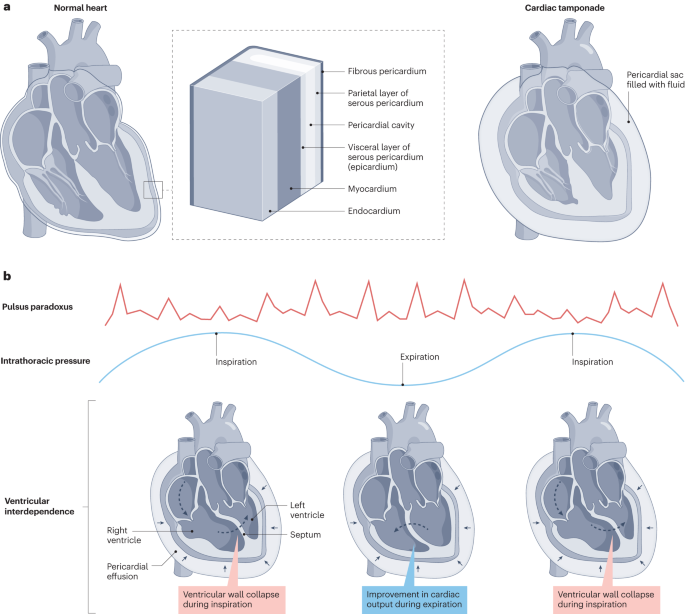
Cardiac tamponade is a medical emergency caused by the progressive accumulation of pericardial fluid (effusion), blood, pus or air in the pericardium, compressing the heart chambers and
leading to haemodynamic compromise, circulatory shock, cardiac arrest and death. Pericardial diseases of any aetiology as well as complications of interventional and surgical procedures or
chest trauma can cause cardiac tamponade. Tamponade can be precipitated in patients with pericardial effusion by dehydration or exposure to certain medications, particularly vasodilators or
intravenous diuretics. Key clinical findings in patients with cardiac tamponade are hypotension, increased jugular venous pressure and distant heart sounds (Beck triad). Dyspnoea can
progress to orthopnoea (with no rales on lung auscultation) accompanied by weakness, fatigue, tachycardia and oliguria. In tamponade caused by acute pericarditis, the patient can experience
fever and typical chest pain increasing on inspiration and radiating to the trapezius ridge. Generally, cardiac tamponade is a clinical diagnosis that can be confirmed using various imaging
modalities, principally echocardiography. Cardiac tamponade is preferably resolved by echocardiography-guided pericardiocentesis. In patients who have recently undergone cardiac surgery and
in those with neoplastic infiltration, effusive–constrictive pericarditis, or loculated effusions, fluoroscopic guidance can increase the feasibility and safety of the procedure. Surgical
management is indicated in patients with aortic dissection, chest trauma, bleeding or purulent infection that cannot be controlled percutaneously. After pericardiocentesis or pericardiotomy,
NSAIDs and colchicine can be considered to prevent recurrence and effusive–constrictive pericarditis.
The authors dedicate this Primer to the giants in the field of pericardial diseases: David H. Spodick, Ralph Shabetai and Bernhard Maisch.
Sackler Faculty of Medicine, Tel Aviv University, Bnei Brak, Israel
Department of Cardiology, University Clinical Centre of Serbia, Belgrade, Serbia
Cardiothoracic Department, Cardiology, University Hospital Santa Maria della Misericordia, Azienda Sanitaria Universitaria Friuli Centrale (ASUFC), Udine, Italy
Department of Biomedical and Clinical Sciences, Fatebenefratelli Hospital, The University of Milan, Milan, Italy
Department of Internal Medicine-Cardiology, Philipps University Marburg, Marburg, Germany
Institute for Cardiovascular Diseases “Dedinje“ and Belgrade University, Faculty of Medicine, Belgrade, Serbia
Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, USA
Introduction (Y.A., A.D.R. and I.B.); Epidemiology (Y.A., A.B., S.P. and I.B.); Mechanisms/pathophysiology (Y.A., M.I., S.P. and P.M.S.); Diagnosis, screening and prevention (Y.A. and M.I.);
Management (Y.A., A.D.R., M.I., A.B. and J.K.O.); Quality of life (Y.A., A.D.R. and P.M.S.); Outlook (A.B., Y.A. and I.B.). Y.A. and A.D.R. contributed equally to the Primer.
The institution of A.B. received funding from Kiniksa Pharmaceuticals as an investigative site. A.B. also received an unrestricted research grant from Swedish Orphan Biovitrum AB (SOBI) and
ACARPIA as well as travel and accommodation to attend an advisory committee organized by SOBI and an advisory board organized by Kiniksa Pharmaceuticals. The other authors declare no
competing interests.
Nature Reviews Disease Primers thanks A. Abbate, M. Chetrit, C. L. Jellis, M. M. Lewinter and J.-L. Vincent for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Video 1. Echocardiography in the diagnosis of cardiac tamponade. Two-dimensional echocardiographic apical long-axis view showing a large pericardial effusion with
characteristic right atrial and right ventricular collapse in real time.
Supplementary Video 2. Echocardiography in the diagnosis of cardiac tamponade. Two-dimensional echocardiographic subxiphoid view showing the swinging heart in the large effusion.
Supplementary Video 3. Echocardiography in the diagnosis of cardiac tamponade. Two-dimensional echocardiographic parasternal long-axis view showing a large pericardial effusion with
characteristic ventricular septal motion in real time.
Supplementary Video 4. Echocardiography in the diagnosis of cardiac tamponade. M-mode echocardiography of a large pericardial effusion with characteristic ventricular septal motion in real
time.
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author
self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Trending News
Playlist 48 | playlist 48 teaser | season 1Preview: Season 1 | 30s Hear from musicians of all genres with connections to Arizona, the 48th state. “Playlist 48” hig...
Deaths of mom and ex-pro hockey player in newport beach condo were not murder-suicide: copsPolice in Newport Beach, California, are investigating the deaths of a former pro hockey player and a mother-of-two foun...
Don't stand so close to me ... | Nature Reviews NeuroscienceAccess through your institution Buy or subscribe Oxytocin has been dubbed the 'social hormone' for its ability...
Why companies are still failing to protect our personal dataWhy companies are still failing to protect our personal dataClip: 11/30/2018 | 6m 48sVideo has Closed Captions | CCWhy c...
WATCH: Brad Pitt Wants Joint Custody of Kids, Source Says: 'It's What Is Best for Them'WATCH: Brad Pitt Wants Joint Custody of Kids, Source Says: 'It's What Is Best for Them'ByPeople StaffUpdated on December...
Latests News
Cardiac tamponade | Nature Reviews Disease PrimersCardiac tamponade is a medical emergency caused by the progressive accumulation of pericardial fluid (effusion), blood, ...
Political tremors in istanbul: the rise of turkey's new left------------------------- * * X.com * Facebook * E-Mail * * * X.com * Facebook * E-Mail * Messenger * WhatsApp * Dieser ...
Beliefs and counseling practices among dermatologists regarding sexual and other adverse effects of finasterideABSTRACT Finasteride may cause low libido and erectile dysfunction and the product label of finasteride also includes po...
Bret Michaels Treated By Paramedics After Concert Health ScareBret Michaels faced a medical emergency on Thursday, cutting short a concert in Manchester, New Hampshire after sufferin...
Reduction in inflammatory markers expression in serum is related to improvement in renal functions in intrauterine undernourished ratsABSTRACT BACKGROUND AND AIMS: Maternal undernutrition can induce a range of fetal adaptations, which can lead to permane...