Highly conductive, stretchable and biocompatible ag–au core–sheath nanowire composite for wearable and implantable bioelectronics
Highly conductive, stretchable and biocompatible ag–au core–sheath nanowire composite for wearable and implantable bioelectronics"
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
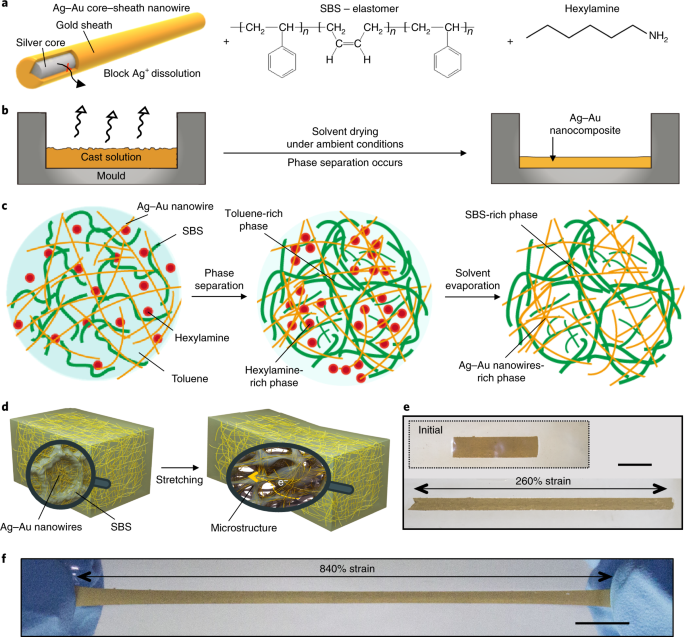
ABSTRACT Wearable and implantable devices require conductive, stretchable and biocompatible materials. However, obtaining composites that simultaneously fulfil these requirements is
challenging due to a trade-off between conductivity and stretchability. Here, we report on Ag–Au nanocomposites composed of ultralong gold-coated silver nanowires in an elastomeric
block-copolymer matrix. Owing to the high aspect ratio and percolation network of the Ag–Au nanowires, the nanocomposites exhibit an optimized conductivity of 41,850 S cm−1 (maximum of
72,600 S cm−1). Phase separation in the Ag–Au nanocomposite during the solvent-drying process generates a microstructure that yields an optimized stretchability of 266% (maximum of 840%).
The thick gold sheath deposited on the silver nanowire surface prevents oxidation and silver ion leaching, making the composite biocompatible and highly conductive. Using the nanocomposite,
we successfully fabricate wearable and implantable soft bioelectronic devices that can be conformally integrated with human skin and swine heart for continuous electrophysiological
recording, and electrical and thermal stimulation. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS
Access through your institution Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription $29.99 / 30 days cancel any time Learn more
Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print issues and online access $259.00 per year only $21.58 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full
article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs *
Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS EVAPORATION-INDUCED SELF-ASSEMBLED ULTRATHIN AGNW NETWORKS FOR HIGHLY CONFORMABLE WEARABLE ELECTRONICS Article Open access 07
May 2024 PHASE-SEPARATED STRETCHABLE CONDUCTIVE NANOCOMPOSITE TO REDUCE CONTACT RESISTANCE OF SKIN ELECTRONICS Article Open access 16 January 2024 HIGH-PERFORMANCE AG2SE-BASED
THERMOELECTRICS FOR WEARABLE ELECTRONICS Article Open access 29 May 2025 REFERENCES * Kim, Y. et al. Stretchable nanoparticle conductors with self-organized conductive pathways. _Nature_
500, 59–63 (2013). Article CAS Google Scholar * Park, M. et al. Highly stretchable electric circuits from a composite material of silver nanoparticles and elastomeric fibres. _Nat.
Nanotech._ 7, 803–809 (2012). Article CAS Google Scholar * Matsuhisa, N. et al. Printable elastic conductors by in situ formation of silver nanoparticles from silver flakes. _Nat. Mater._
16, 834–840 (2017). Article CAS Google Scholar * Kim, D. H. et al. Epidermal electronics. _Science_ 333, 838–843 (2011). Article CAS Google Scholar * Son, D. et al. Multifunctional
wearable devices for diagnosis and therapy of movement disorders. _Nat. Nanotech._ 9, 397–404 (2014). Article CAS Google Scholar * Choi, M. K. et al. Wearable red-green-blue quantum dot
light-emitting diode array using high-resolution intaglio transfer printing. _Nat. Commun._ 6, 7149 (2015). Article CAS Google Scholar * Lipomi, D. J. et al. Skin-like pressure and strain
sensors based on transparent elastic films of carbon nanotubes. _Nat. Nanotech._ 6, 788–792 (2011). Article CAS Google Scholar * Miyamoto, A. et al. Inflammation-free, gas-permeable,
lightweight, stretchable on-skin electronics with nanomeshes. _Nat. Nanotech._ 12, 907–913 (2017). Article CAS Google Scholar * You, I. et al. Stretchable E-skin apexcardiogram sensor.
_Adv. Mater._ 28, 6359–6364 (2016). Article CAS Google Scholar * Gong, S. et al. Highly stretchy black gold E-skin nanopatches as highly sensitive wearable biomedical sensors. _Adv.
Electron. Mater._ 1, 1400063 (2015). Article Google Scholar * Park, J. et al. Electromechanical cardioplasty using a wrapped elasto-conductive epicardial mesh. _Sci. Transl. Med._ 8,
344ra386 (2016). Google Scholar * Lu, C. et al. Flexible and stretchable nanowire-coated fibers for optoelectronic probing of spinal cord circuits. _Sci. Adv._ 3, e1600955 (2017). Article
Google Scholar * Lee, P. et al. Highly stretchable and highly conductive metal electrode by very long metal nanowire percolation network. _Adv. Mater._ 24, 3326–3332 (2012). Article CAS
Google Scholar * Choi, S. et al. Stretchable heater using ligand-exchanged silver nanowire nanocomposite for wearable articular thermotherapy. _ACS Nano_ 9, 6626–6633 (2015). Article CAS
Google Scholar * McShan, D., Ray, P. C. & Yu, H. Molecular toxicity mechanism of nanosilver. _J. Food Drug Anal._ 22, 116–127 (2014). Article CAS Google Scholar * Yang, M., Hood, Z.
D., Yang, X., Chi, M. & Xia, Y. Facile synthesis of Ag@Au core–sheath nanowires with greatly improved stability against oxidation. _Chem. Commun._ 53, 1965–1968 (2017). Article CAS
Google Scholar * Gong, S. et al. A wearable and highly sensitive pressure sensor with ultrathin gold nanowires. _Nat. Commun._ 5, 3132 (2014). Article Google Scholar * Chen, Y., Ouyang,
Z., Gu, M. & Cheng, W. Mechanically strong, optically transparent, giant metal superlattice nanomembranes from ultrathin gold nanowires. _Adv. Mater._ 25, 80–85 (2013). Article CAS
Google Scholar * Andres, L. J. et al. Rapid synthesis of ultra-long silver nanowires for tailor-made transparent conductive electrodes: proof of concept in organic solar cells.
_Nanotechnology_ 26, 265201 (2015). Article Google Scholar * Sun, Y., Yin, Y., Mayers, B. T., Herricks, T. & Xia, Y. Uniform silver nanowires synthesis by reducing AgNO3 with ethylene
glycol in the presence of seeds and poly(vinyl pyrrolidone). _Chem. Mater._ 14, 4736–4745 (2002). Article CAS Google Scholar * Liu, H. et al. Etching-free epitaxial growth of gold on
silver nanostructures for high chemical stability and plasmonic activity. _Adv. Funct. Mater._ 25, 5435–5443 (2015). Article CAS Google Scholar * Yang, Y., Liu, J., Fu, Z. W. & Qin,
D. Galvanic replacement-free deposition of Au on Ag for core–shell nanocubes with enhanced chemical stability and SERS activity. _J. Am. Chem. Soc._ 136, 8153–8156 (2014). Article CAS
Google Scholar * Dong, A. et al. A generalized ligand-exchange strategy enabling sequential surface functionalization of colloidal nanocrystals. _J. Am. Chem. Soc._ 133, 998–1006 (2011).
Article CAS Google Scholar * Lee, H. et al. A graphene-based electrochemical device with thermoresponsive microneedles for diabetes monitoring and therapy. _Nat. Nanotech._ 11, 566–572
(2016). Article Google Scholar * Lee, H., Hong, Y. J., Baik, S., Hyeon, T. & Kim, D. H. Enzyme-based glucose sensor: from invasive to wearable device. _Adv. Healthc. Mater._ 7,
e1701150 (2018). Article Google Scholar * Li, J. et al. Correlations between percolation threshold, dispersion state, and aspect ratio of carbon nanotubes. _Adv. Funct. Mater._ 17,
3207–3215 (2007). Article CAS Google Scholar * Knite, M., Hill, A. J., Pas, S. J., Teteris, V. & Zavickis, J. Effects of plasticizer and strain on the percolation threshold in
polyisoprene–carbon nanocomposites: positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopy and electrical resistance measurements. _Mater. Sci. Eng. C_ 26, 771–775 (2006). Article CAS Google Scholar
* Sun, J. Y. et al. Highly stretchable and tough hydrogels. _Nature_ 489, 133–136 (2012). Article CAS Google Scholar * Dong, J., Abukhdeir, N. M. & Goldthorpe, I. A. Simple assembly
of long nanowires through substrate stretching. _Nanotechnology_ 26, 485302 (2015). Article Google Scholar * Wang, L.-F., Liu, J.-Q., Yang, B. & Yang, C.-S. PDMS-based low cost
flexible dry electrode for long-term EEG measurement. _IEEE Sens. J._ 12, 2898–2904 (2012). Article Google Scholar * Hurley, M. V. & Bearne, L. M. Non-exercise physical therapies for
musculoskeletal conditions. _Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol._ 22, 419–433 (2008). Article Google Scholar * Sarzi-Puttini, P. et al. Osteoarthritis: an overview of the disease and its
treatment strategies. _Semin. Arthritis Rheum._ 35 (SUPPL. 1), 1–10 (2005). Article Google Scholar * Xu, B. et al. An epidermal stimulation and sensing platform for sensorimotor prosthetic
control, management of lower back exertion, and electrical muscle activation. _Adv. Mater._ 28, 4462–4471 (2016). Article CAS Google Scholar * Lim, S. et al. Transparent and stretchable
interactive human machine interface based on patterned graphene heterostructures. _Adv. Funct. Mater._ 25, 375–383 (2015). Article CAS Google Scholar * Kuiken, T. A., Marasco, P. D.,
Lock, B. A., Harden, R. N. & Dewald, J. P. Redirection of cutaneous sensation from the hand to the chest skin of human amputees with targeted reinnervation. _Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA_
104, 20061–20066 (2007). Article CAS Google Scholar * Lee, S. et al. A strain-absorbing design for tissue–machine interfaces using a tunable adhesive gel. _Nat. Commun._ 5, 5898 (2014).
Article CAS Google Scholar * Xu, L. et al. 3D multifunctional integumentary membranes for spatiotemporal cardiac measurements and stimulation across the entire epicardium. _Nat. Commun._
5, 3329 (2014). Article Google Scholar * Lelovas, P. P., Kostomitsopoulos, N. G. & Xanthos, T. T. A comparative anatomic and physiologic overview of the porcine heart. _J. Am. Assoc.
Lab. Anim. Sci._ 53, 432–438 (2014). CAS Google Scholar * Pham, T. & Sun, W. Comparison of biaxial mechanical properties of coronary sinus tissues from porcine, ovine and aged human
species. _J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater._ 6, 21–29 (2012). Article CAS Google Scholar * Smits, F. M. Measurement of sheet resistivities with the four-point probe. _Bell Syst. Tech. J._
37, 711–718 (1958). Article Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This work was supported by the Institute for Basic Science (grant numbers IBS-R006-D1 and IBS-R006-A1). The
authors thank the staff of the National Center for Inter-university Research Facilities (NCIRF) and the Research Institute of Advanced Materials (RIAM) in Seoul National University. The
authors also thank M. Josephson for material and intellectual support of the animal research. AUTHOR INFORMATION Author notes * These authors contributed equally: Suji Choi, Sang Ihn Han,
Dongjun Jung, Hye Jin Hwang. AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Center for Nanoparticle Research, Institute for Basic Science (IBS), Seoul, Republic of Korea Suji Choi, Sang Ihn Han, Dongjun Jung,
Chaehong Lim, Ok Kyu Park, Mincheol Lee, Taeghwan Hyeon & Dae-Hyeong Kim * School of Chemical and Biological Engineering, Institute of Chemical Processes, Seoul National University,
Seoul, Republic of Korea Suji Choi, Sang Ihn Han, Dongjun Jung, Chaehong Lim, Ok Kyu Park, Mincheol Lee, Ji Woong Yu, Ji Ho Ryu, Won Bo Lee, Taeghwan Hyeon & Dae-Hyeong Kim *
Cardiovascular Division, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA Hye Jin Hwang, Soochan Bae, Cory M. Tschabrunn, Sun Youn Bae, Peter M. Kang & Reza
Nezafat * Department of Physiology, School of Dentistry, Seoul National University, Seoul, Republic of Korea Sang-Woo Lee & Kyungpyo Park Authors * Suji Choi View author publications You
can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Sang Ihn Han View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Dongjun Jung View author
publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Hye Jin Hwang View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Chaehong Lim
View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Soochan Bae View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Ok
Kyu Park View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Cory M. Tschabrunn View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed
Google Scholar * Mincheol Lee View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Sun Youn Bae View author publications You can also search for this author
inPubMed Google Scholar * Ji Woong Yu View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Ji Ho Ryu View author publications You can also search for this
author inPubMed Google Scholar * Sang-Woo Lee View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Kyungpyo Park View author publications You can also
search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Peter M. Kang View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Won Bo Lee View author publications You
can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Reza Nezafat View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Taeghwan Hyeon View author
publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Dae-Hyeong Kim View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CONTRIBUTIONS
S.C., S.I.H., D.J., H.J.H., T.H. and D.-H.K. designed the experiments. S.C., S.I.H., D.J., C.L., M.L., H.J.H., T.H. and D.-H.K. performed experiments and analysis. S.C., S.I.H., D.J.,
H.J.H., C.L., S.B., O.K.P., C.M.T., S.Y.B., S.-W.L., K.P., P.M.K. and R.N. performed in vivo animal experiments and data analysis. S.I.H., S.-W.L. and K.P. performed in vitro experiments and
analysis. J.W.Y., J.H.R. and W.B.L. performed computer simulations. S.C., S.I.H., D.J., H.J.H., S.B., T.H. and D.-H.K. wrote the paper. CORRESPONDING AUTHORS Correspondence to Taeghwan
Hyeon or Dae-Hyeong Kim. ETHICS DECLARATIONS COMPETING INTERESTS The authors declare no competing interests. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION PUBLISHER’S NOTE: Springer Nature remains neutral with
regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary figures 1–15, Supplementary References
SUPPLEMENTARY VIDEO The heat rolling-pressed Ag–Au nanocomposite was stretched to 200%, 400% and 840% RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE
Choi, S., Han, S.I., Jung, D. _et al._ Highly conductive, stretchable and biocompatible Ag–Au core–sheath nanowire composite for wearable and implantable bioelectronics. _Nature Nanotech_
13, 1048–1056 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-018-0226-8 Download citation * Received: 19 February 2018 * Accepted: 10 July 2018 * Published: 13 August 2018 * Issue Date: November
2018 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-018-0226-8 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable
link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Trending News
Tragic tale of malegaon’s supermanBY: GARIMA SHUKLA | Updated Date: Fri, 12 Aug 2011 12:55:00 (IST) इतने साल से हमने सुना कि कई सुपरमेन की जिंदगी का ट्रेज...
The policy ask with mark girolami: “computer science should be compulsory at gcse level”Mark Girolami is chief scientist at the Alan Turing Institute, the UK’s national institute for data science and artifici...
How to Fight Back Against Age DiscriminationAARP Facebook Twitter LinkedIn Workers who believe their age has cost them — whether it's a job, a promotion, a raise — ...
Farming pays tribute to duke of edinburgh - farmers weekly© ITV/Shutterstock Tributes are pouring in from across the farming world to Prince Philip, who died aged 99 on Friday (9...
Us president donald trump to ban tiktok today - times of indiaUS President Donald Trump has said that he will act to ban TikTok as soon as on Saturday, amidst reports of American tec...
Latests News
Highly conductive, stretchable and biocompatible ag–au core–sheath nanowire composite for wearable and implantable bioelectronicsABSTRACT Wearable and implantable devices require conductive, stretchable and biocompatible materials. However, obtainin...
Pellets victims protestPellets victims protest Debi Dhar February 19, 2018 8:27 am No Comments A pellet victim holds a placard during a protes...
Kate hudson flaunts her incredibly toned bodyKate Hudson has really sprung back into top shape since welcoming her third child, daughter Rani Rose, over two years ag...
How to set up and market a broiler unit - farmers weekly© Tim Scrivener A prospective broiler farmer faces a large initial investment. A development worth its salt will cost up...
[pdf] download ayuh, another downeast cookbook: recipes from maine by virginia wrightLast access: 16105 user Last server checked: 11 Minutes ago! Click Here => https://gowatermarkmedia.blogspot.com/medi...