New directions for ocean nutrients
New directions for ocean nutrients"
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
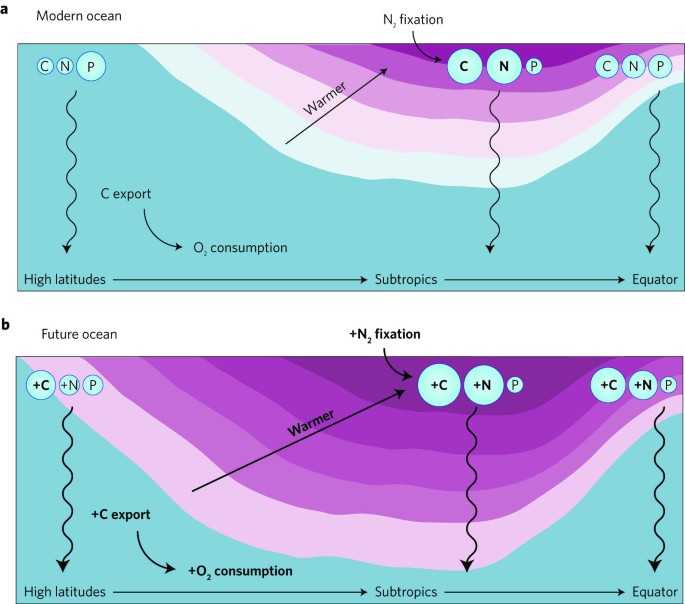
The elemental ratios of marine phytoplankton and organic matter vary widely across ocean biomes, according to a catalogue of biogeochemical data, suggesting that climate change may have
complex effects on the ocean’s elemental cycles. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access
through your institution Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription $29.99 / 30 days cancel any time Learn more Subscribe to
this journal Receive 12 print issues and online access $259.00 per year only $21.58 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy
now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact
customer support REFERENCES * Martiny, A. C. et al. _Nat. Geosci._ 6, 279–283 (2013). Article Google Scholar * Redfield, A. C. _On the Proportions of Organic Derivatives in Sea Water and
Their Relation_ _to the Composition of Plankton_ 176–192 (James Johnstone Memorial Volume, Liverpool Univ. Press, Liverpool, 1934). * Redfield, A. C. _Amer. Scientist_ 46, 205–221 (1958).
Google Scholar * Sarmiento, J. S. & Toggweiler, R. J. _Nature_ 308, 621–624 (1984). Article Google Scholar * Sarmiento, J. S., Hughes, T. M. C. & Manabe, S. _Nature_ 393, 245–249
(1998). Article Google Scholar * Copin-Montegut, C. & Copin-Montegut, G. _Deep-Sea Res._ 30, 31–46 (1983). Article Google Scholar * Karl, D., Letelier, R., Tupas, L., Dore, J.,
Christian, J. & Hebel, D. _Nature_ 38, 533–538 (1997). Article Google Scholar * Quigg, A. et al. _Nature_ 425, 291–294 (2003). Article Google Scholar * Geider, R. J. & La Roche,
J. _European J. Phycology_ 37, 1–17 (2002). Article Google Scholar * Klausmeier, C. A., Litchman, E., Dufresne, T. & Levin, S. A. _Nature_ 429, 171–174 (2004). Article Google Scholar
* Teng, Y.-C. et al. _Nat. Geosci._ 7, 895–898 (2014). Article Google Scholar * DeVries, T. & Deutsch, C. _Nat. Geosci._ 7, 890–895 (2014). Article Google Scholar * Weber, T. S.
& Deutsch, C. _Nature_ 467, 550–554 (2010). Article Google Scholar * Weber, T. S. & Deutsch, C. _Nature_ 467, 419–422 (2012). Article Google Scholar * Galbraith, E. D. &
Martiny, A. C. _Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA_ 112, 8199–8204 (2015). Article Google Scholar * Tanioka, T. & Matsumoto, K. _Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles_ 31, 1–15 (2017). Article Google
Scholar * Toseland, A. et al. _Nat. Clim. Change_ 3, 979–984 (2013). Article Google Scholar * Yvon-Durocher, G., Schaum, C.-E. & Trimmer, M. _Frontiers Microbiol._ 8, 1–14 (2017).
Article Google Scholar * Ayo, B. et al. _Global Change Biol._ 23, 4084–4093 (2017). Article Google Scholar * van de Wall, D. B., Vershoor, A. M. & Huisman, J. _Front. Ecol. Environ._
8, 145–212 (2010). Article Google Scholar Download references AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Department of Geography and Earth Research Institute, University of California,
Santa Barbara, CA, USA Tim DeVries Authors * Tim DeVries View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to Tim
DeVries. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE DeVries, T. New directions for ocean nutrients. _Nature Geosci_ 11, 15–16 (2018).
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41561-017-0042-z Download citation * Published: 02 January 2018 * Issue Date: January 2018 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41561-017-0042-z SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone
you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by
the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Trending News
Lucky habenero salsa - business of the week - newport beach newsWE ASKED THE SALSA LADY ABOUT HER AWARD WINNING LINE OF LUCKY HABANERO SALSAS Linda Saenz is passionate about every batc...
Intracellular bacterial growth is controlled by a kinase network around pkb/akt1ABSTRACT With the emergence of multidrug resistant (MDR) bacteria, it is imperative to develop new intervention strategi...
Biotech buy | NatureYou have full access to this article via your institution. Download PDF British drug company GlaxoSmithKline is to buy R...
Strange bedfellows | Nature PhysicsAccess through your institution Buy or subscribe Events will be taking place across the United Kingdom throughout 2015 t...
New directions for ocean nutrientsThe elemental ratios of marine phytoplankton and organic matter vary widely across ocean biomes, according to a catalogu...
Latests News
Rechallenge prior sildenafil nonrespondersABSTRACT To assess inappropriate use as a cause of sildenafil (Viagra™) failure and the feasibility of successfully rech...
New directions for ocean nutrientsThe elemental ratios of marine phytoplankton and organic matter vary widely across ocean biomes, according to a catalogu...
Strange bedfellows | Nature PhysicsAccess through your institution Buy or subscribe Events will be taking place across the United Kingdom throughout 2015 t...
Biotech buy | NatureYou have full access to this article via your institution. Download PDF British drug company GlaxoSmithKline is to buy R...
Intracellular bacterial growth is controlled by a kinase network around pkb/akt1ABSTRACT With the emergence of multidrug resistant (MDR) bacteria, it is imperative to develop new intervention strategi...