A potent antibiotic-loaded bone-cement implant against staphylococcal bone infections
A potent antibiotic-loaded bone-cement implant against staphylococcal bone infections"
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
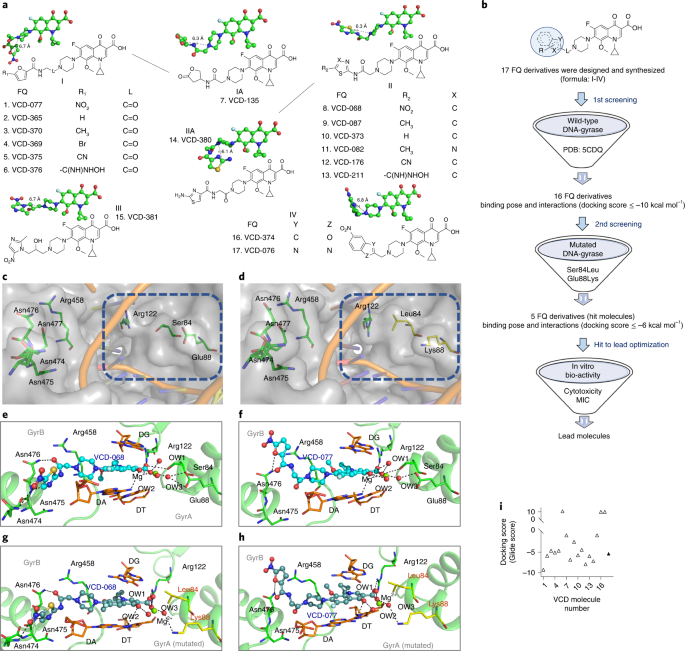
ABSTRACT New antibiotics should ideally exhibit activity against drug-resistant bacteria, delay the development of bacterial resistance to them and be suitable for local delivery at desired
sites of infection. Here, we report the rational design, via molecular-docking simulations, of a library of 17 candidate antibiotics against bone infection by wild-type and mutated bacterial
targets. We screened this library for activity against multidrug-resistant clinical isolates and identified an antibiotic that exhibits potent activity against resistant strains and the
formation of biofilms, decreases the chances of bacterial resistance and is compatible with local delivery via a bone-cement matrix. The antibiotic-loaded bone cement exhibited greater
efficacy than currently used antibiotic-loaded bone cements against staphylococcal bone infections in rats. Potent and locally delivered antibiotic-eluting polymers may help address
antimicrobial resistance. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your
institution Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription $29.99 / 30 days cancel any time Learn more Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles $119.00 per year only $9.92 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy
now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer
support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS EVIDENCE OF BISPHOSPHONATE-CONJUGATED SITAFLOXACIN ERADICATION OF ESTABLISHED METHICILLIN-RESISTANT _S. AUREUS_ INFECTION WITH
OSSEOINTEGRATION IN MURINE MODELS OF IMPLANT-ASSOCIATED OSTEOMYELITIS Article Open access 18 October 2023 COMBINATION OF BACTERIOPHAGES AND VANCOMYCIN IN A CO-DELIVERY HYDROGEL FOR LOCALIZED
TREATMENT OF FRACTURE-RELATED INFECTIONS Article Open access 29 August 2024 EVALUATION OF A BONE FILLER SCAFFOLD FOR LOCAL ANTIBIOTIC DELIVERY TO PREVENT _STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS_ INFECTION
IN A CONTAMINATED BONE DEFECT Article Open access 13 May 2021 DATA AVAILABILITY The main data supporting the results in this study are available within the paper and its Supplementary
Information. The raw and analysed datasets generated during the study are available for research purposes from the corresponding authors on reasonable request. Source data for the figures
are provided with this paper. REFERENCES * Morris, K. Battle against antibiotic resistance is being lost. _Lancet Infect. Dis._ 7, 509 (2007). Article Google Scholar * Bush, K. et al.
Tackling antibiotic resistance. _Nat. Rev. Microbiol_. 9, 894–896 (2011). Article CAS Google Scholar * Teillant, A., Gandra, S., Barter, D., Morgan, D. J. & Laxminarayan, R. Potential
burden of antibiotic resistance on surgery and cancer chemotherapy antibiotic prophylaxis in the USA: a literature review and modelling study. _Lancet Infect. Dis._ 15, 1429–1437 (2015).
Article Google Scholar * Willyard, C. The drug-resistant bacteria that pose the greatest health threats. _Nature_ 543, 15 (2017). Article CAS Google Scholar * Wanted: a reward for
antibiotic development. _Nat. Biotechnol._ 36, 555, (2018). * Doron, S. & Davidson, L. E. Antimicrobial stewardship. _Mayo Clin. Proc._ 86, 1113–1123 (2011). Article Google Scholar *
Trampuz, A. & Widmer, A. F. Infections associated with orthopedic implants. _Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis._ 19, 349–356 (2006). Article CAS Google Scholar * Sloan, M., Premkumar, A. &
Sheth, N. P. Projected volume of primary total joint arthroplasty in the U.S., 2014 to 2030. _J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am._ 100, 1455–1460 (2018). Article Google Scholar * Moriarty, T. F. et al.
Orthopaedic device-related infection: current and future interventions for improved prevention and treatment. _EFORT Open Rev._ 1, 89–99 (2016). Article Google Scholar * Li, B. &
Webster, T. J. Bacteria antibiotic resistance: new challenges and opportunities for implant-associated orthopedic infections. _J. Orthop. Res._ 36, 22–32 (2018). PubMed Google Scholar *
Arciola, C. R., Campoccia, D. & Montanaro, L. Implant infections: adhesion, biofilm formation and immune evasion. _Nat. Rev. Microbiol_.16, 397–409 (2018). Article CAS Google Scholar
* Gogia, J. S., Meehan, J. P., Di Cesare, P. E. & Jamali, A. A. Local antibiotic therapy in osteomyelitis. _Semin. Plast. Surg._ 23, 100–107 (2009). Article Google Scholar * Wright, J.
A. & Nair, S. P. Interaction of staphylococci with bone. _Int. J. Med. Microbiol._ 300, 193–204 (2010). Article CAS Google Scholar * Suhardi, V. J. et al. A fully functional
drug-eluting joint implant. _Nat. Biomed. Eng._ 1, 0080 (2017). Article CAS Google Scholar * Dowding, J. E. Mechanisms of gentamicin resistance in _Staphylococcus aureus_. _Antimicrob.
Agents Chemother._ 11, 47–50 (1977). Article CAS Google Scholar * Gardete, S. & Tomasz, A. Mechanisms of vancomycin resistance in _Staphylococcus aureus_. _J. Clin. Invest_. 124,
2836–2840 (2014). Article Google Scholar * Landersdorfer, C. B. et al. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Antibiotics in Bone. In _Bone and Joint Infections_ (Ed. Zimmerli, W.) 81–98
(Wiley, 2021). * Hooper, D. C. Mode of action of fluoroquinolones. _Drugs_ 58, 6–10 (1999). Article CAS Google Scholar * Acar, J. F. & Goldstein, F. W. Trends in bacterial resistance
to fluoroquinolones. _Clin. Infect. Dis._ 24, S67–S73 (1997). Article CAS Google Scholar * Kampranis, S. C. & Maxwell, A. The DNA gyrase-quinolone complex. ATP hydrolysis and the
mechanism of DNA cleavage. _J. Biol. Chem._ 273, 22615–22626 (1998). Article CAS Google Scholar * Aldred, K. J., Kerns, R. J. & Osheroff, N. Mechanism of quinolone action and
resistance. _Biochemistry_ 53, 1565–1574 (2014). Article CAS Google Scholar * Hooper, D. C. & Jacoby, G. A. Mechanisms of drug resistance: quinolone resistance. _Ann. N. Y. Acad.
Sci._ 1354, 12–31 (2015). Article CAS Google Scholar * Blower, T. R., Williamson, B. H., Kerns, R. J. & Berger, J. M. Crystal structure and stability of gyrase–fluoroquinolone cleaved
complexes from _Mycobacterium tuberculosis_. _Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA_ 113, 1706–1713 (2016). Article CAS Google Scholar * Conrad, S. et al. gyrA mutations in high-level
fluoroquinolone-resistant clinical isolates of _Escherichia coli_. _J. Antimicrob. Chemother._ 38, 443–455 (1996). Article CAS Google Scholar * Chan, P. F. et al. Structural basis of DNA
gyrase inhibition by antibacterial QPT-1, anticancer drug etoposide and moxifloxacin. _Nat. Commun._ 6, 10048 (2015). * Diekema, D. J. et al. Survey of infections due to _Staphylococcus_
species: frequency of occurrence and antimicrobial susceptibility of isolates collected in the United States, Canada, Latin America, Europe, and the Western Pacific region for the SENTRY
Antimicrobial Surveillance Program, 1997–1999. _Clin. Infect. Dis._ 32, S114–S132 (2001). Article CAS Google Scholar * Zimmerli, W. Clinical presentation and treatment of orthopaedic
implant-associated infection. _J. Intern. Med._ 276, 111–119 (2014). Article CAS Google Scholar * Kim, W. et al. A new class of synthetic retinoid antibiotics effective against bacterial
persisters. _Nature_ 556, 103–107 (2018). Article CAS Google Scholar * Peeters, E. et al. Modulation of the substitution pattern of 5-aryl-2-aminoimidazoles allows fine-tuning of their
antibiofilm activity spectrum and toxicity. _Antimicrob. Agents Chemother._ 60, 6483–6497 (2016). Article CAS Google Scholar * Cramariuc, O. et al. Mechanism for translocation of
fluoroquinolones across lipid membranes. _Biochim. Biophys. Acta_ 1818, 2563–2571 (2012). Article CAS Google Scholar * Vroom, J. M. et al. Depth penetration and detection of pH gradients
in biofilms by two-photon excitation microscopy. _Appl. Environ. Microbiol._ 65, 3502–3511 (1999). Article CAS Google Scholar * Lebeaux, D., Leflon-Guibout, V., Ghigo, J. M. & Beloin,
C. In vitro activity of gentamicin, vancomycin or amikacin combined with EDTA or l-arginine as lock therapy against a wide spectrum of biofilm-forming clinical strains isolated from
catheter-related infections. _J. Antimicrob. Chemother._ 70, 1704–1712 (2015). Article CAS Google Scholar * McMahon. S. et al. Thermal necrosis and PMMA – a cause for concern? _Orthop.
Proc._ 94-B, 64 (2012). * Hussain, S. et al. Antibiotic-loaded nanoparticles targeted to the site of infection enhance antibacterial efficacy. _Nat. Biomed. Eng._ 2, 95–103 (2018). Article
CAS Google Scholar * ASTM Standard, ASTM F451. in _Annual Book of ASTM Standards_ Vol. 13.01 55–61 (ASTM International, 2000). https://www.astm.org * Kurtz, S., Ong, K., Lau, E., Mowat, F.
& Halpern, M. Projections of primary and revision hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 2005 to 2030. _J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am._ 89, 780–785 (2007). Article Google Scholar
* Bryan, A. J. et al. Irrigation and debridement with component retention for acute infection after hip arthroplasty: improved results with contemporary management. _J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am._
99, 2011–2018 (2017). Article Google Scholar * https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/early-development-considerations-innovative-combination-products (US
FDA, 2020). * Bistolfi, A., Ferracini, R., Albanese, C., Vernè, E. & Miola, M. PMMA-based bone cements and the problem of joint arthroplasty infections: status and new perspectives.
_Materials_ 12, 4002 (2019). Article CAS Google Scholar * Stokes, J. M. et al. A deep learning approach to antibiotic discovery. _Cell_ 181, 475–483 (2020). Article CAS Google Scholar
* FDA. (ed https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/principles-premarket-pathways-combination-products) (US FDA, 2022). * Entenza, J. M., Giddey, M.,
Vouillamoz, J. & Moreillon, P. In vitro prevention of the emergence of daptomycin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus and enterococci following combination with amoxicillin/clavulanic
acid or ampicillin. _Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents_ 35, 451–456 (2010). Article CAS Google Scholar * Metzler, K., Drlica, K. & Blondeau, J. M. Minimal inhibitory and mutant prevention
concentrations of azithromycin, clarithromycin and erythromycin for clinical isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae. _J. Antimicrob. Chemother._ 68, 631–635 (2013). Article CAS Google
Scholar * Guy, R. H. H. & On, J. The determination of drug release rates from topical dosage forms. _Int. J. Pharm._ 60, R1–R3 (1990). Article CAS Google Scholar * Rissing, J. P.,
Buxton, T. B., Weinstein, R. S. & Shockley, R. K. Model of experimental chronic osteomyelitis in rats. _Infect. Immun._ 47, 581–586 (1985). Article CAS Google Scholar * Rouse, M. S.
et al. Daptomycin treatment of _Staphylococcus aureus_ experimental chronic osteomyelitis. _J. Antimicrob. Chemother._ 57, 301–305 (2006). Article CAS Google Scholar Download references
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We thank S. Bandopadhayaya for his dedication in providing us with clinical perspectives and detailed explanations while conceiving the project. The authors from Vyome
Therapeutics Limited acknowledge the funding support from the Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council, Department of Biotechnology (DBT), India, under a Small Business Innovation
Research Initiative grant. H.L.J. discloses support for the publication of this study from the National Institutes of Health (grant numbers AR073135 and CA236702) and the Department of
Defense (grant numbers PC180355 and CA201065). AUTHOR INFORMATION Author notes * These authors contributed equally: Sumana Ghosh, Mau Sinha. AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Vyome Therapeutics
Inc., Princeton, NJ, USA Sumana Ghosh, Mau Sinha, Ritwik Samanta, Suresh Sadhasivam, Anamika Bhattacharyya, Ashis Nandy, Swamini Saini, Nupur Tandon, Himanshi Singh, Swati Gupta, Anjali
Chauhan, Keerthi Kumar Aavula, Mukesh Kumar Garg & Shamik Ghosh * Vyome Therapeutics Limited, New Delhi, India Sumana Ghosh, Mau Sinha, Ritwik Samanta, Suresh Sadhasivam, Anamika
Bhattacharyya, Ashis Nandy, Swamini Saini, Nupur Tandon, Himanshi Singh, Swati Gupta, Anjali Chauhan, Keerthi Kumar Aavula, Mukesh Kumar Garg & Shamik Ghosh * Department of
Biotechnology, Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur, India Sneha Susan Varghese & Sudip Ghosh * Center for Engineered Therapeutics, Department of Medicine, Brigham and Women’s
Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA Pujie Shi, Tanmoy Saha, Aparna Padhye, Hae Lin Jang & Shiladitya Sengupta * Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology,
Cambridge, MA, USA Pujie Shi, Tanmoy Saha, Aparna Padhye & Shiladitya Sengupta * Division of Rheumatology, Inflammation, and Immunity, Department of Medicine, Brigham and Women’s
Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA Pujie Shi, Aparna Padhye & Hae Lin Jang * Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School,
Boston, MA, USA Pujie Shi, Aparna Padhye & Hae Lin Jang Authors * Sumana Ghosh View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Mau Sinha View
author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Ritwik Samanta View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Suresh
Sadhasivam View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Anamika Bhattacharyya View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed
Google Scholar * Ashis Nandy View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Swamini Saini View author publications You can also search for this
author inPubMed Google Scholar * Nupur Tandon View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Himanshi Singh View author publications You can also
search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Swati Gupta View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Anjali Chauhan View author publications
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Keerthi Kumar Aavula View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Sneha Susan Varghese
View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Pujie Shi View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Sudip
Ghosh View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Mukesh Kumar Garg View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google
Scholar * Tanmoy Saha View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Aparna Padhye View author publications You can also search for this author
inPubMed Google Scholar * Shamik Ghosh View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Hae Lin Jang View author publications You can also search for
this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Shiladitya Sengupta View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CONTRIBUTIONS Sumana Ghosh and M.S. designed
and performed the experiments, and contributed to the analysis of the results and the writing of the manuscript. R.S., S. Sadhasivam, A.B., A.N., S. Saini, N.T., H.S., S. Gupta, A.C.,
K.K.A., S.S.V., P.S., M.K.G., T.S. and A.P. contributed to the design and experimentation, and to the analysis of the results. Sudip Ghosh provided resources. Shamik Ghosh, H.L.J. and S.
Sengupta designed and supervised the study, and contributed to the analysis of the results and the writing of the paper. CORRESPONDING AUTHORS Correspondence to Shamik Ghosh, Hae Lin Jang or
Shiladitya Sengupta. ETHICS DECLARATIONS COMPETING INTERESTS Sumana Ghosh, M.S., R.S., S. Sadhasivam, A.N., A.B., S. Saini, N.T., H.S., S. Gupta, A.C., M.K.G. and Shamik Ghosh are employees
of Vyome Therapeutics Limited. Sumana Ghosh and Shamik Ghosh hold equity in Vyome Therapeutics Inc. S. Sengupta is a co-founder and board member of Vyome Therapeutics Limited, and owns
equity in Vyome Therapeutics Inc. H.L.J. is a founder of Curer Inc. and holds equity in the company. S.S.V. and Sudip Ghosh declare no competing interests. PEER REVIEW PEER REVIEW
INFORMATION _Nature Biomedical Engineering_ thanks Ebru Oral, Liam Grover and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
PUBLISHER’S NOTE Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. EXTENDED DATA EXTENDED DATA FIG. 1 PHYSICOCHEMICAL
CHARACTERIZATION OF VCD-077 IMPREGNATED PMMA BEADS. (A-C) FT-IR spectrum of different groups (a) VCD-077, (b) PMMA, (c) VCD-077 impregnated PMMA at (40:1) with VCD-077 peaks 1 (3352.75
cm−1), 2 (3114.27 cm−1), 3 (1643.82 cm−1), 4 (1615.48 cm−1), 5 (1595.79 cm−1), 6 (1550.68 cm−1), 7 (1352.31 cm−1), 8 (1313.02 cm−1).(D) Release of VCD-077 from Smartset HV® (PMMA) bead at
different drug:polymer ratio (1:40, 2:40 and 3:40) in pH 7.4 buffer. Data is represented as mean ± SD (n = 3). (E) Release of VCD-077 from Smartset HV® (PMMA) bead at different particle size
from drug:polymer ratio (1:40) or (F) at different temperatures, in pH 7.4 buffer. Data is represented as mean ± SD (n = 3). Source data SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION MAIN SUPPLEMENTARY
INFORMATION Supplementary figures, tables and methods. REPORTING SUMMARY SOURCE DATA SOURCE DATA FOR FIGS. 3, 5, 6 AND EXTENDED DATA FIG. 1 Source data. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Springer
Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript
version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law. Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Ghosh, S., Sinha, M.,
Samanta, R. _et al._ A potent antibiotic-loaded bone-cement implant against staphylococcal bone infections. _Nat. Biomed. Eng_ 6, 1180–1195 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-022-00950-x
Download citation * Received: 10 May 2020 * Accepted: 08 September 2022 * Published: 13 October 2022 * Issue Date: October 2022 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-022-00950-x SHARE THIS
ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Trending News
EVs to account for 12-15% of India's total car sales by 2030: Moody’sElectric vehicles will account for 12%-15% of total car sales in India by the end of the decade, falling short of the go...
Stadiums to staycations: How IPL 2025 is powering a silent travel movementSummer cricket fever aside, the Indian Premier League (IPL) 2025 has led a silent movement–reshaping India’s travel and ...
All changes to Income Tax Returns you need to know for FY 2024-25The revised Income Tax Returns (ITRs) for the AY26 are in place as a prerequisite. As anticipated, there are major chang...
Hollywood, Bollywood, YouTube-wood? Talking to Zerodha’s Nikhil Kamath, YouTube CEO Neal Mohan charts a new path for cinemaKamath, reflecting on his own media journey growing up in India, recalled, how he grew up in the city of Bangalore (now ...
Why AkzoNobel is a strategic requirement for JSW’s expansion dreamsJSW Paints is reportedly close to acquiring a 74.76% stake in AkzoNobel India from its Dutch parent, potentially marking...
Latests News
A potent antibiotic-loaded bone-cement implant against staphylococcal bone infectionsABSTRACT New antibiotics should ideally exhibit activity against drug-resistant bacteria, delay the development of bacte...
Two immersive experiences at la villetteHow about a laser game? Set a stone's throw from the Cité des Sciences, and formerly known as Yoo Moov, discover La...
Trade rules are deeply flawed but trump’s tariff fixation is hurting america and the rest of the worldFree trade has been very, very good to the U.S., but it is yielding diminishing returns. By all accounts, the era of cor...
Make an appointment | veterans affairsFOR MENTAL HEALTH CARE APPOINTMENTS Call the Mental Health Clinic. PHONE: 734-845-3471 or 800-361-8387, ext. 53471 FOR D...
Dispose unused medications and prescription (dump) opioids act take back event | va saginaw health care | veterans affairsSaginaw , MI — On Saturday, April 22, 2023 from 10:00 a.m. to 2:00 p.m., the Aleda E. Lutz VAMC, located at 1500 Weiss S...