Solvent-adaptive hydrogels with lamellar confinement cellular structure for programmable multimodal locomotion
Solvent-adaptive hydrogels with lamellar confinement cellular structure for programmable multimodal locomotion"
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
ABSTRACT Biological organisms can perform flexible and controllable multimodal motion under external stimuli owing to the hierarchical assembly of anisotropic structures across multiple
length scales. However, artificial soft actuators exhibit the limited response speed, deformation programmability and movement capability especially in harsh environments because of
insufficient anisotropic hierarchy and precision in structural design. Here, we report a programmed assembly directed confinement polymerization method for the fabrication of environmentally
tolerant and fast responsive hydrogels with lamellar assembly-confined cellular structure interpenetrated with highly aligned nanopillars by the directional freezing-assisted polymerization
in the predesigned anisotropic laminar scaffold. The obtained hydrogel exhibits ultrafast responsiveness and anisotropic deformation exposed to temperature/light/solvent stimulation,
maintaining highly consistent responsive deformation capability in all-polarity solvents over 100 days of soaking. Moreover, the hydrogels implement photoactive programmable multi-gait
locomotion whose amplitude and directionality are precisely regulated by the intrinsic structure, including controlled crawling and rotation in water and non-polar solvents, and 3D
self-propulsion floating and swimming in polar solvents. Thus, this hydrogel with hierarchically ordered structure and dexterous locomotion may be suitable for flexible intelligent actuators
serving in harsh solvent environments. SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS BIOINSPIRED HYDROPHOBIC PSEUDO-HYDROGEL FOR PROGRAMMABLE SHAPE-MORPHING Article Open access 21 January 2025
SELF-REGULATED REVERSAL DEFORMATION AND LOCOMOTION OF STRUCTURALLY HOMOGENOUS HYDROGELS SUBJECTED TO CONSTANT LIGHT ILLUMINATION Article Open access 24 February 2024 HIGH SPEED UNDERWATER
HYDROGEL ROBOTS WITH PROGRAMMABLE MOTIONS POWERED BY LIGHT Article Open access 23 November 2023 INTRODUCTION The living organisms with elaborate hierarchical architecture that perform
fascinating stimuli-responsive morphing behaviors have long been a source of inspiration for the design and manufacture of soft actuators1,2,3. Hydrogels with a crosslinked polymer network
in water are of growing attention as soft smart actuation materials in the fields of moving robotics4,5, haptic device6 and biomedical engineering7, owing to their biological tissue
similarity, good flexibility and high degree of freedom triggered by ambient stimuli. Based on the osmotic pressure-driven de-swelling/swelling8, isotropic contraction/expansion is generally
performed for the hydrogels with homogeneous network structure under the global stimulation9,10. Furthermore, conventional hydrogels usually suffer from weak environmental adaptability and
stability when exposed to a liquid arising from the mutually exclusive mechanism of loose crosslinking of polymer network for fast response to stimuli11. Inspired by high arrangement of
collagen fibers enabling the skeletal muscles to implement anisotropic movements under heavy loading cycles12, great efforts have been devoted to constructing the intricate yet programmable
anisotropic architectures through the introduction of highly aligned nanounits into polymeric hydrogel network by applying electric/magnetic/acoustic fields or shear force to orient
nanomaterials before or during the gelation process13,14,15,16. However, because the hierarchy and precision of the assembly structure in the reported anisotropic hydrogels are far lagging
behind that of natural biological tissues, they behave the limited three-dimensional (3D) configurational changes and bionic movements17,18. Especially, their actuating speeds are limited to
several minutes by sluggish deswelling and swelling processes determined by the diffusion of water molecules upon exposure to stimuli9,19,20,21. Cellular architectures with high mechanical
robustness having aligned open porous interconnected network to provide fast liquid transport channels may resolve the conflict between fast actuating speed and long-term actuation
stability22,23,24. Introducing cellular network structure into stimuli-responsive hydrogels has shown effectiveness in improving responsive speed and environmental tolerance owing to strong
capillary effect, large water diffusion coefficient, low liquid flow resistance and mechanical stability as well as facile wet-shaping fabrication technique25,26. Unfortunately, only
isotropic deformations are shown for the reported cellular hydrogels under stimuli as their thickness is reduced to micrometer to millimeter scales along the pore direction when serving as
the actuators26,27,28. Therefore, it is highly desired to exert hierarchical anisotropy and robust constituents into cellular structure across multiple length scales if anisotropic hydrogel
actuators are advanced with simultaneously rapid actuation speed and high environmental adaptability, but remains challenging. Here, we demonstrate a programmed assembly directed confinement
polymerization strategy for the fabrication of environmentally tolerant and multi-responsive hydrogels with lamellar assembly-confined cellular structure interpenetrated with highly aligned
nanopillars by the directional freezing-assisted polymerization of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAM) in the predesigned anisotropic laminar silver nanowire (AgNW)/sodium alginate (SA)
aerogel (ASAA) scaffold. Benefiting from hierarchically anisotropic and robust structure with low-tortuosity mass transport channels, the obtained hydrogel exhibits fast anisotropic
stimuli-responsive deformation in harsh environments, outperforming the reported thermally active hydrogel actuators, and high long-term stability with nearly unchanged responsive rates in
all polarity solvents over 100 days. Furthermore, photoactive programmable multi-gait motions, including steered crawling and rotation in water and nonpolar solvents, and 3D self-propulsion
floating and swimming in polar solvents are realized, whose magnitude and directionality are precisely pre-coded in inherent structural orientation of the hydrogel actuator. This work
provides useful insights into the design and construction of flexible smart actuators for steady application in extreme environments. RESULTS FABRICATION OF HIERARCHICALLY ANISOTROPIC
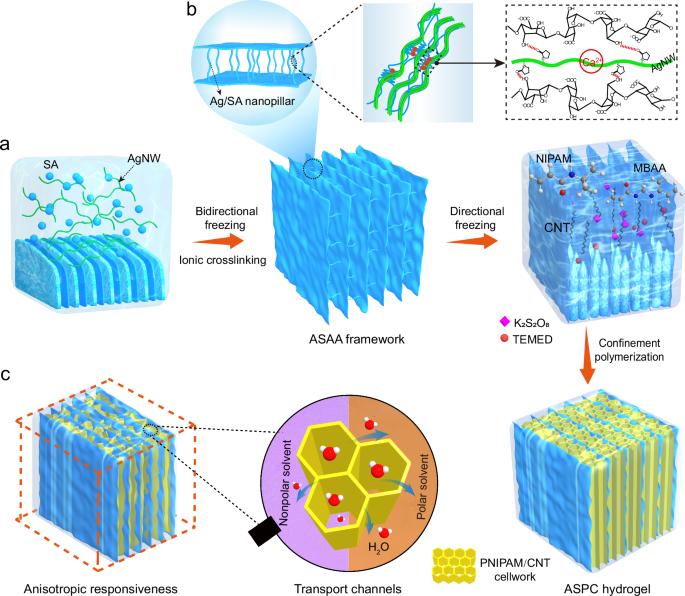
STRUCTURE A lamellar assembly confined-cellular architecture design strategy was developed to fabricate a fast responsive and environmentally tolerant hydrogel integrated with hierarchically
anisotropic structure by a consecutive freezing-induced assembly and freezing-assisted confinement polymerization process. As illustrated in Fig. 1a, the mixture of 25 mg mL−1 of AgNWs
(diameter: 60–100 nm, length: ~15 μm) and 20 mg mL−1 of SA was first dropped onto a silicone mold placing in a self-made bidirectional freezing device (Supplementary Figs. 1 and 2). After
the bidirectional freezing assembly and the subsequent freeze-drying, the ASAA scaffold was obtained and further ionically crosslinked for mechanical enhancement by immersing in ethanol
solution of CaCl2 (20 mg mL−1) for 10 min followed by solvent exchange with deionized water. The ASAA exhibited a typical lamellar structure consisting of 2 μm-thick lamellae with the
spacing of ∼50 μm (Fig. 2a, b). High-magnification SEM image captured that abundant of highly oriented AgNW/SA nanopillars were interpenetrated between the adjacent lamellae (Fig. 2c). Based
on the inherent 1D geometric anisotropy of hydrophilic AgNWs, the nanopillar configuration among the lamellae in ASAA scaffold was regulated by the content of AgNWs29. At a low content of
10 mg mL−1, the nanounits tended to be repelled into the gap by the growing ice branches, forming a layered microstructure parallel to the direction of freezing front movement with the
sporadically-distributed nanopillars among 30 µm-spaced lamellae (A10SAA) (Supplementary Fig. 3a–c). As the AgNW content increasing to 25 mg mL−1, the enhanced interactions between the AgNWs
and SA restricted the movement of nanofillers and strengthened linear arrangement of the AgNWs. A small fraction of AgNWs and SA was entrapped within the ice crystals by tip-splitting and
subsequent healing, leading to the formation of the nanopillars between adjacent layers. At a 45 mg mL−1 of AgNW, the spacing between lamellae was increased to ∼70 µm, and the microwalls
were formed among the adjacent layers, leading to the decrease in structural anisotropy (A45SAA) (Supplementary Fig. 3d–f). Subsequently, the polymerizable precursor solution containing
N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAM) and carbon nanotubes (CNTs) was filled into the predesigned ASAA matrix and unidirectionally frozen in the direction parallel to the ASAA lamellae by an ice
templating assembly technique at −30 °C (Fig. 1a). Noted that to prevent the polymerization of the precursor solution before directional freezing assembly, the temperature of above mixture
was controlled at ∼5 °C in the filling process. After two-stage confinement polymerization at −18 °C for 18 h and 25 °C for 5 h, a PNIPAM/CNT hydrogel network was confined within the ASAA
scaffold. Thus, a hierarchically anisotropic hydrogel was finally fabricated, denoted as ASPC hydrogel. The obtained hydrogel inherited the laminated architecture from the ASAA with the
lamellar spacing slightly expanded to ∼60 µm (Fig. 2d and Supplementary Fig. 4). Enlarged top-view SEM image showed that 3D interconnected open porous honeycomb network with the pore size of
10–25 µm was homogeneously distributed within layered framework of the ASPC hydrogel (Fig. 2e). Parallel to the growth direction of ice crystals, a secondary interconnected lamellar network
with low tortuosity having the spacing of 6–10 μm was uniformly arranged in the neighboring AgNW/SA layers (Fig. 2f, g). Uniform distributions of Ag, C, O and N elements in elemental
mappings confirmed the incorporation of PNIPAM/CNT gel within the ASAA scaffold (Supplementary Fig. 5). Similarly, the A10SPC and A45SPC hydrogels prepared by the assembly of PNIPAM/CNT
network within A10SAA and A45SAA scaffolds showed cellular network structure with different pore sizes confined in the layered framework (Supplementary Fig. 6a–f). Another control hydrogel
by the polymerization of PNIPAM/CNT network in the ASAA framework displayed a closed cell network, defined as the ASAA-PC (Supplementary Fig. 6g–i). X-ray microcomputed tomography (micro-CT)
was further utilized for nondestructive visualization of full image of the ASPC based on X-ray sensitive to the materials density30. An anisotropic lamellar structure aligned on the
macroscale was reconstructed (Fig. 2h). Cross-sectional images stemming from 3D stereogram showed aligned pores within the network, wherein abundant nanopillars perpendicular to the thin
layer were observed in _xy_ plane of the ASPC (Fig. 2i and Supplementary Fig. 7). SEM images, high-angle annular dark field scanning transmission electron microscope (HAADF-STEM) images and
elemental mappings were conducted on ultrathin slices of the hydrogel parallel to the lamellae. Abundant Ag species were demonstrated at the cross sections of the slice, which inherited from
the cut-off tips of AgNW/SA nanopillars interpenetrated among the ASAA lamellae (Supplementary Figs. 8 and 9). In Raman scattering mappings, no obvious Raman signal was observed between
the AgNW/SA lamellae of the A10SPC hydrogel at a low AgNW content (Supplementary Fig. 10a, b). With increasing the AgNW content, the enhanced Raman signal with a pillar configuration
resulting from surface plasmon resonance of AgNWs was recorded in-between the lamellae of the ASPC hydrogel (Fig. 2j–l)31. Comparatively, a microwall-shaped image with the greatly-enhanced
Raman intensity was scanned between the A45SPC lamellae at a high AgNW content (Supplementary Figs. 10c, d). These results indicated that the ASPC held the architecture of AgNW/SA
nanopillars interpenetrated across the PNIPAM/CNT network between the AgNW/SA lamellae, which not only ensured the material integrity, but also stored more elastic energy for elastic
deformation and recovery of the hydrogel network. Distinctive from traditional cellular structure, a four-level anisotropic hierarchy was built in the ASPC hydrogel by the predesigned
matrix-directed and space-confined polymerization strategy: the nanosized AgNWs were assembled into anisotropic AgNW/SA lamellae (first level); the directionally-frozen assembled PNIPAM/CNT
compartmental units (second level) were then interconnected to form anisotropic honeycomb network, which was confined within the lamellar framework with the AgNW/SA nanopillars
perpendicularly interpenetrated at tens of micrometers (third level) (Fig. 1b); following with long-range interlamination of AgNW/SA lamellae by PNIPAM/CNT cellular network, a macroscopic
anisotropic assembly with fast transport channels was finally created (fourth level), showing great potentials in anisotropic responsive deformation (Fig. 1c). ANISOTROPIC DEFORMATIONS IN
ALL SOLVENTS Owing to highly anisotropic lamella confinement honeycomb architecture, the ASPC hydrogel exhibited anisotropic deformation behaviors in liquids exposed to external stimuli,
including temperature, light and solvent (Fig. 3a, Supplementary Movie 1). When dipped in a 45 °C water bath, that was higher than the LCST of PNIPAM, the ASPC hydrogel abruptly contracted
by 41.6% perpendicular to the AgNW/SA lamellae within 1.1 s with the unchanged length in the orthogonal direction (Fig. 3b and Supplementary Fig. 11a). Once transferred into a water bath at
25 °C, the shrunk hydrogel immediately expanded to the original shape within 1.05 s. The average deformation and recovery rates were measured to be 1.97 mm s−1 and 2.06 mm s−1, respectively,
which were faster than the reported thermally actuating hydrogels13,14,17,25,27,28. Furthermore, no apparent fatigue was observed after 100 deformation-recovery cycles (Supplementary Fig.
11b). Such notable anisotropic deformation benefitted from reinforced-concrete ASAA with ordered layered structure, which resisted strain along the parallel direction and allowed transverse
strain (Supplementary Fig. 12). When the temperature was switched, the PNIPAM/CNT network stretched like a muscle, generating an anisotropic extension in the ASPC hydrogel. Even when placed
in 45 °C water for 100 h, the hydrogel recovered rapidly within 5 s of cooling (Supplementary Fig. 13). Furthermore, the influences of the temperature of unidirectional freezing and the
content of crosslinker on the thermal responsiveness of ASPC hydrogels were explored (Supplementary Fig. 14). With the freezing temperature decreasing from −30 °C to −120 °C, the contraction
ratio of the obtained hydrogels perpendicular to the lamella decreased from 42% to 13% in 1.1–1.9 s, while the recovery time of the shrunk gels increased from 1.1 s to 2.5 s (Supplementary
Fig. 14a, b), indicating the sluggish transport of water and the limited shrinkage of the network by a denser network when decreasing the freezing temperature. Similarly, as the crosslinker
content increased, the increased crosslinking density of the polymer chains led to a decrease in both the shrinkage and actuation rate of the hydrogel (Supplementary Fig. 14c, d). In
contrast, the control A10SPC and A45SPC hydrogels showed decreased anisotropic deformations of 0.32 and 0.18 at slower deformation rates of 0.70 mm s−1 and 0.31 mm s−1, respectively
(Supplementary Fig. 15a, b). Because of lacking free channels for rapid water transportation, the recovery of the contracted ASAA-PC hydrogel was high up to 14 min (Supplementary Fig. 15c).
The control hydrogel prepared by in-situ polymerization of PNIPAM and CNTs showed isotropic volume changes with a contraction of 58.1% after immersing in the hot water for 23 s and a
sluggish recovery process up to 12 min in a water bath at 25 °C (Supplementary Fig. 15d). Besides hot water, NIR irradiation triggered an anisotropic underwater deformation at a speed of
1.02 mm s−1 with a shrinkage of 40.7% perpendicular to the lamellae occurred in 2 s at a laser intensity of 1.5 W cm−2 arising from notable optical-to-mechanical energy conversion capacity
of the assembled AgNWs and CNTs in the ASPC hydrogel (Fig. 3b and Supplementary Fig. 16a). Once turning off the light, the hydrogel recovered to original shape at a rapid speed of 0.68 mm
s−1 (within 3 s). Noted that the temperature of the control hydrogel without the CNTs only achieved 49.6 °C in 3 s, much lower than 72.5 °C of the ASPC hydrogel under the irradiation at 1.5
W cm−2 (Supplementary Fig. 16b), and shrunk by 22% perpendicular to the lamellae at a speed of 0.48 mm s−1 in 2 s (Supplementary Fig. 16c), suggesting important roles of CNTs in high
actuation performance. With the merits of porous cellular network confined in lamellar structure providing highly free channels, the hydrogel afforded rapid and reversible photo-driven
deformation in non-polar solvents including petroleum ether, _n_-hexane, toluene, liquid paraffin and vegetable oil, by quickly repelling/absorbing water through the channels under the
action of siphon when on/off switching the light (Supplementary Fig. 17). After 100 deformation cycles, no obvious deterioration in responsiveness was detected. Even in high-viscosity liquid
paraffin over 100 cycles, its deformation and recovery speeds decreased slightly from 0.94 to 0.86 mm s−1, and 0.21 to 0.11 mm s−1, respectively (Supplementary Fig. 18). Impressively, the
ASPC hydrogel exhibited cyclically anisotropic deformation when alternatively exposed to a polar solvent-cosolvent of PNIPAM, and water. For example, benefitting from the open low-tortuosity
honeycomb network channels, ethanol quickly entered in the hydrogel network and competed with the amide groups on PNIPAM to form hydrogen bonds with water when the ASPC hydrogel was
transferred from water to ethanol32. This destroyed the hydration structure between hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions, resulting in the shrinkage of PNIPAM network33. After soaking in
ethanol for 30 s, the PNIPAM network reached a hydrophobic equilibrium in accompany with more ethanol molecules interacting with water molecules, and the hydrogel piece was shrunk by 39%
along the direction vertical to the lamellae (Fig. 3a, c). With continually exchanging with ethanol molecules, PNIPAM network recovered under the synergy of hydrophobic interaction between
isopropyl groups and hydrophobic domain of ethanol, and the increased number of hydrogen bonds between the amide bonds and hydroxyl of ethanol33. In the next 50 s, the shrunk gel was
expanded to original shape with the molar ratio of ethanol increased from 0.15 to 0.30 (Supplementary Fig. 19a). Notably, such deformations were reversible with the decrease of ethanol
content to 0.11 and 0.02 when soaking the above gel in water for 40 s and 90 s (Fig. 3c). The periodic exchange of ethanol and water was confirmed by reversible changes of intensity of ʋ(CH)
peaks in Raman spectra at different deformation stages (Supplementary Fig. 19b)32. Under the cosolvency mechanism that controlled the interactions of solvent-water and
solvent-hydrophilic/hydrophobic groups of PNIPAM chains, the hydrogel displayed a phase-separation network in the co-solvent environment with ethanol content ranging from 0.02 to 0.15,
leading to anisotropic shrinkage33,34. With ethanol or water content increased, the conformation of polymer network got extended, leading to an appearance of shape recovery. Furthermore, the
polar solvents of dimethyl formamide (DMF), acetonitrile, acetone and tetrahydrofuran (THF) also stimulated the ASPC hydrogel with anisotropic deformation in a reversible manner
(Supplementary Fig. 20). Notably, stable and repeatable shape deformations without significant response hysteresis were observed by cycling a gel piece in different solvents and water for 50
cycles (Supplementary Fig. 21). To evaluate long-term responsive stability of the ASPC hydrogel in liquids, the anti-swelling behavior was investigated by monitoring the changes in geometry
over time. Swelling equilibrium was rapidly achieved within 3 s in water, due to capillary siphon effect and anisotropic structure, accompanied by an expansion of 25% perpendicular to the
AgNW/SA lamellae and negligible changes in lamellar dimensions (Fig. 3d). For the subsequent 180 days of soaking in water, the morphology of the ASPC hydrogel almost kept unchanged. This
strong water-resistant performance was attributed to anisotropic cellular PNIPAM/CNT network with free channels fixed into rigid, anisotropic ASAA framework, which significantly restrained
the swelling of polymer network caused by osmotic pressure. Furthermore, the ASPC hydrogel displayed high adaptability in a variety of solvents with a wide polarity range (Low row in Fig.
3e). Soaking in polar solvents, the hydrogel first underwent anisotropic shrinkage-recovery deformation, and then expanded 18%–22% to achieve swelling equilibrium in the following 10–15 s
(Supplementary Fig. 22a–e). Afterwards, it was stable over 180 days. Non-swollen performance was also observed during 180 days of soaking in non-polar solvents (Supplementary Fig. 22f). In
contrast, the A10SAA hydrogel exhibited a larger swelling ratio with an expansion of 37% perpendicular to the lamella after 10 days of immersion in water resulting from the layered structure
with the fewer interconnections (Supplementary Fig. 23a). The weakened anisotropic swelling behavior of the A45SPC was delivered with 20.4% and 3.2% of expansion perpendicular to the
lamella and along the lamella, respectively, after soaking in water for 10 days (Supplementary Fig. 23b). The ASAA-PC hydrogel experienced the sluggish swelling equilibrium in accompany with
a swelling ratio of 138% after 80 h (Supplementary Fig. 23c), resulting from slow water diffusion and poor mechanical robustness of the closed cell network. Relying on strong adaptability
in harsh liquid environments, the ASPC hydrogel maintained rapid, highly consistent photo/solvent-responsive capability without obvious deterioration in deformation and recovery rates even
after soaking in various solvents over 100 days (Upper row in Fig. 3e and Supplementary Figs. 24 and 25), indicating its excellent long-term stability. After soaking in these solvents for
100 days, no apparent fatigue was observed over 100 actuating cycles stimulated by NIR or polar solvents (Fig. 3g). These results fully suggested the ASPC hydrogel having strong
environmental tolerance and excellent stimuli-responsiveness in all solvents, outperforming the previously reported hydrogels (Fig. 3f, h), which confirmed its great potentials as flexible
smart drives with anisotropic responses in extreme environments. PROGRAMMABLE MULTIMODAL MOTIONS IN WATER AND NONPOLAR SOLVENTS Hydrogel system has been widely developed in the design of
bionic robotics owing to high mobility, high degree of freedom of deformation and high programmability35. Especially, the stimuli-responsive hydrogels containing active units can directly
transform stimulation into macroscopic deformation and movements under the force/torque generated by physical/chemical reactions. With the help of an asymmetric shape design or a customized
substrate, various locomotion gaits, including walking, crawling, rolling, jumping and swimming are achieved36. Benefitting from highly anisotropic hierarchical structure and cellular
network with fast mass transport capability, the ASPC hydrogels could actualize rapid and stable anisotropic deformations in solvent environments, and further implement programmable
locomotion exposed to periodic scanning of NIR light. The fundamental motion mechanism was that photo-induced contractile strain caused the friction competition between the head and tail of
hydrogel, which mimicked the movements of the larvae relying on the synergistic effects between cyclic contraction and expansion of the body and asymmetric friction of the body and
substrate37. When the NIR light scanned the gel under the water from right to left (Fig. 4a), a pair of contractile forces _F_c1 and _F_c2 rapidly generated on the head and tail by the
contraction of polymer network with rising temperature, which sought to induce slip between the gel and substrate (polytetrafluoroethylene). The corresponding frictional resistances _f_1 and
_f_2 were opposite to the directions of contraction forces. Note that the head slid slightly towards the tail at the beginning due to the speedy dehydration of the cell network. Arising
from the hydrophilic-to-hydrophobic conversion of polymer chains, the friction coefficient _µ_1 between the head and substrate increased correspondingly, leading to _µ_1 > _µ_238. With
persistent energy accumulation under continuous light exposure until the tail conquered static friction, where _F_c2 > _f_2, and _F_c1 = _f_1, the tail moved towards the stationary head.
Once the light stimulating the tail, the shrunk head expanded rapidly with the help of low-tortuosity open cell network accelerating the transport of water, producing a pair of expansion
forces _F_e1 and _F_e2. The recovery of hydrophilic polymer network at the head enabled _µ_1 < _µ_2, leading the head to slide forward (_F_e1 > _f_1, and _F_e2 = _f_2). Therefore, by
cyclically scanning the hydrogel sheet, the telescoping peristaltic movements were generated following with continuous contraction and expansion deformations. The influences of gel
dimensions including length and width, and power intensity of NIR on the crawling velocity of ASPC hydrogel in water were explored. As for a short gel, the small energy accumulation and
release of the deformable cell network resulted in a low crawling velocity. The crawling velocity increased accordingly to achieve a maximum velocity of 0.07 mm s−1 at the length of 7 mm
(Supplementary Fig. 26a). Additionally, a gel with a long length also exhibited the decreased crawling velocity, which arose from the increased friction force that limited the movement of
the gel. Upon increasing the width of the gel from 1 mm to 3 mm, the instability of the centroid under light caused by size effect was gradually overcome, resulting in an increase in
crawling velocity (Supplementary Fig. 26b). But further increasing the width reduced the velocity because of the increased friction. Moreover, with increasing the intensity, the head of the
gel could accumulate more energy in a short period of time, enabling the tail to overcome static friction and slid towards the head, ultimately leading to an increase in crawling velocity
(Supplementary Fig. 26c). Notably, the decisive force for the mobility, _F_c, was always perpendicular to the AgNW/SA lamellas, due to deformable anisotropic cellular network confined to a
rigid layered scaffold. Thus, the directionality of motion could be facilely regulated by altering inherent structural parameter α of the hydrogel sheet, which was defined as the orientation
angle between the AgNW/SA lamellae and long axis direction of the cut sheet (Fig. 4b). At a fixed α except for 90°, a torque (_τ_) was generated by the component force of _F_c in vertical
direction (_F_⊥ = _F_c2 × cos α), whereas the component in horizontal direction (_F_// = _F_c2 × sin α) drove for horizontal locomotion, enabling the hydrogel to achieve steered crawling in
a controllable direction (Fig. 4c). The hydrogel sheet rotated anticlockwise while crawling when 0° < α < 90° (defined as positive angle) and rotated clockwise while crawling when 90°
< α < 180° (Supplementary Fig. 27a). Due to the disappearance of the _F_⊥ at α = 90°, the rightward crawling was produced at a speed of 0.075 mm s−1 under cyclic light scanning from
right to left. The cooperation of deformation and friction force was manifested by the discrete displacements of the head and tail at distinct periods of time (Fig. 4d). At α = 45° or 135°,
a steered crawling in anticlockwise or clockwise direction was delivered with a total of 60° rotating angle and cumulative displacement of 4 mm over 13 scanning cycles (Fig. 4e,
Supplementary Fig. 27b and Supplementary Movie 2). The detailed relationship between the α and crawling trajectory (motion angle and horizontal displacement) of gel was illustrated (Fig.
4f). When the α increased from 0° to 90°, the _F_// was gradually enhanced, and therefore, the horizontal displacement of anticlockwise crawling was increased to 0.6 mm after a NIR scanning,
which conformed to the sine function. On the other hand, at a larger α, it was faster to achieve energy accumulation threshold that conquered the friction force and triggered the tail to
move forward, which produced the head with a smaller irradiated area (Supplementary Fig. 28). Thereby, a larger force arm _L_ for the rotating motion was yielded that defined as the distance
between the center of tail and the anchor (head) and was proportional to sinα. Meanwhile, the _F_⊥ proportional to cosα was gradually decreased. Therefore, the torque that caused the tail
to rotate around the anchor reached its maximum value at α = 45°, enabling a largest motion angle of 6.5° per scanning cycle. At 90° < α < 180°, the gel sheet moved clockwise in
similar movement magnitude. Noted that the crawling direction was always opposite to the scanning direction (defined as positive displacement). For example, when changing the scanning
direction from left to right, the gel crawled leftwards at a speed of 0.073 mm s−1 at α = 90° (Supplementary Fig. 29a, b). Furthermore, it steered anticlockwise at 0° < α < 90°, and
clockwise at 90° < α < 180°, respectively, while maintaining positive displacements (Supplementary Fig. 29c, d). To this end, both the direction and magnitude of crawling motion were
preprogrammed into the internal structural parameter of hydrogel irrespective of external conditions like the irradiation direction and complex macroscopic geometry of gel (Fig. 4f and
Supplementary Fig. 30). In addition to the steerable crawling, the rotating motion with controllable direction could be realized by changing the scanning mode of NIR light (Supplementary
Movie 3). When the light scanned the gel diagonally, the rotational contraction force _F__R_ perpendicular to the lamellas generated in the irradiation area was decomposed along the diagonal
(Fig. 4g). The component force perpendicular to the diagonal (_F__R_⊥) propelled the generation of a torque to rotate around the centroid, while the static friction force arising from the
component force parallel to the diagonal (_F__R_//) prevented a shift along the light scanning path. With the energy accumulation, a rotation was generated. Specifically, for the hydrogel at
α = 90°, when exerting 26 scanning cycles from the upper left to lower right, it rotated clockwise around its center of gravity to 180° in an increment of about 7° per cycle (Fig. 4g).
However, When the light was applied for 30 scanning cycles from the top right corner along the diagonal of the gel, it rotated anticlockwise around the centroid to 180°, with an average
increase of about 6° for each cycle. (Supplementary Fig. 31). In addition, it was measured that the optimal length (_l_) and width (_w_) of the gel for the rotation were 7 mm and 3.5 mm,
respectively (Supplementary Fig. 32). When the light scanned the gel diagonally from the upper left, as the driving force of the rotation, _F__R_⊥, was expressed by the equation: _F__R_⊥ =
_F__R_ × cos (α + φ), where φ was defined as the angle between the diagonal and long axis of the gel (Supplementary Fig. 33a). When the light scanned the gel diagonally from the top right
corner, _F__R_⊥ was expressed by the equation: _F__R_⊥ = _F__R_ × cos (α − φ) (Supplementary Fig. 33b). Based on _l_ = 7 mm and _w_ = 3.5 mm, the φ was calculated to be ∼27°. When the _F__R_
was generated along the diagonal, where α + φ = 90° or α − φ = 90°, the gel could not rotate as the _F__R_⊥ was equal to zero. Thus, the critical value of α was ∼63° for the light scanning
from the upper left and ∼117° for the light scanning from the upper right. Taking light scanning gel diagonally from the upper left corner as an example, at 0° ≤ α < 63° and 153° < α
< 180°, the gel rotated anticlockwise and the rotation angle gradually decreased with the increase of α. Contrarily, the clockwise rotation was occurred when 63° < α ≤ 153°. The
experimental results were highly consistent with the above analyses where a critical α of 60° was measured, indicating good motion controllability (Fig. 4h). Furthermore, the ASPC hydrogel
exhibited excellent adaptability including steerable crawling and rotation in non-polar solvents such as petroleum ether, _n_-hexane, toluene, paraffin and vegetable oil. Notably, the gel
behaved phototropic motion in non-polar solvents (Supplementary Movie 4). Taking _n_-hexane as an example, because the water released by the polymer network of the irradiated area formed a
lubrication layer between the gel and substrate, the friction was reduced correspondingly39. As a result, when light irradiated on the head, the contracted head moved towards the tail under
the effect of _F_c1 > _f_1, and _F_c2 = _f_2. Since the light removed away the head and irradiated on the tail, the synergy of the expansion of the head and shrinkage of the tail led to
_F_e2 > _f_2, and _F_e1 = _f_1, driving the tail to move towards the light (Supplementary Fig. 34a). Typically, the sheet at α = 90° could crawl phototropically at a speed of ∼0.04 mm
s−1 (Supplementary Fig. 34b,c). Besides, at 0° < α < 90°, the gel rotated anticlockwise while crawling, and crawled clockwise at 90° < α < 180° (Supplementary Fig. 35). For
example, at α = 45°, a counterclockwise crawling was delivered with a displacement of 3 mm and motion angle of 17.5° over 60 s of cyclic scanning (Supplementary Fig. 35b). Additionally, the
gel at α = 90° could rotate clockwise by 360° under 100 cycles of the diagonal scanning from the upper left (Supplementary Fig. 36 and Supplementary Movie 5). For clear demonstration,
different locomotion modes in different solvents were summarized (Fig. 4i and Supplementary Fig. 37). Even in the paraffin with high viscosity, the controllable movements at a displacement
velocity of 0.024 mm s−1 and a rotating velocity of 1.75° s−1 were achieved for the crawling and rotation, respectively. Thus, the fabricated hydrogel robots implemented multi-gait
locomotion whose amplitude and directionality were accurately regulated by the intrinsic structure. As for both the crawling and rotation motions, their driving force that determined the
motion trajectory was the contraction force perpendicular to the lamellar structure. By decomposing the contraction force along the light scanning direction, the component of force in the
parallel direction contributed to the displacement, while the vertical direction created torque to change the motion direction. CONTROLLABLE 3D SELF-PROPULSION LOCOMOTION IN POLAR SOLVENTS
Besides programmable crawling and rotating motions in water and non-polar solvents, the ASPC hydrogel that reached the solvent exchange equilibrium in polar organic solvents could perform a
manageable 3D self-propulsion locomotion under the stimulation of NIR light (Fig. 5a, Supplementary Fig. 38 and Supplementary Movie 6). Typically, when illuminated in ethanol, the gel
spontaneously assumed an optimal posture for floating with low resistance under the asymmetry of temperature and flow fields induced by the photothermal effect (Supplementary Fig. 39a). With
quickly repelling the ethanol through the unimpeded cell network, the robot rapidly floated up to the liquid-air interface with a depth of 50 mm within 3 s of illumination (Fig. 5b and
Supplementary Fig. 39b). After reaching the interface, it could float stably on the liquid surface for several seconds under the action of surface tension. To examine the floating mechanism,
multiphysics model based on the finite-element method (FEM) was employed to calculate the flow velocity and temperature distribution at different times (Supplementary Fig. 40 and
Supplementary Note 1). The irradiated surface of the gel was regarded as a heat source, from which heat was transmitted to the fluid, forming a temperature gradient along the illumination
direction. With increasing temperature under the continual irradiation, the upward liquid produced a buoyant flow40. It was simulated that the maximum buoyancy velocity reached 21.7 mm s−1
at 1.6 s when the temperature difference was set to be 10 K (Fig. 5b). Upon increasing the temperature gradient, the velocity of the induced convection was greatly improved (Supplementary
Fig. 40c, d). The experimental results validated that the time of the hydrogel floating to a height of 30 mm decreased from 3.1 s to 1.1 s as the power intensity increased from 1.5 to 2.5 W
cm−2 (Supplementary Fig. 41a). Furthermore, no obvious fatigue was recorded after floating for 100 cycles, indicating its excellent stability (Supplementary Fig. 41b). Notably, the gel
achieved a maximum floating height of 400 mm at a floating speed of 13.2 mm s−1 (Supplementary Fig. 42a), outperforming the previously-reported soft floating robots (Supplementary Fig. 42b).
After arrival at the liquid-air interface, the continued illumination raised the local temperature and decreased the surface tension of the liquid around the gel correspondingly. A partial
surface tension gradient was therefore produced, along which an impetus was generated to propel the hydrogel swimming navigation on the solvent surface under the Marangoni effect. The
temperature and swimming velocity were monitored by changing the power intensity (Supplementary Fig. 43a). When the light power increased from 1.5 to 2.5 W cm−2, the surface tension of the
liquid surrounding the gel was decreased with the temperature of the gel increased, leading to an increased surface tension gradient in the solution and an enhanced Marangoni effect. The
swimming velocity was therefore improved. Moreover, when decreasing surface tension of the solution, for example, decreasing the volume fraction of ethanol, the swimming velocity would
decrease resulting from the weakened Marangoni effect (Supplementary Fig. 43b). These results indicated a swimming propulsion of the photothermal Marangoni effect. Noted that the navigation
direction could be precisely controlled by the α of the gel rather than a complex shape design. At α = 0°, the hydrogel performed linear swimming along the direction of Marangoni propulsion
(Fig. 5c, Supplementary Fig. 44 and Supplementary Movie 7). When changing the α, the locomotion mode transformed accordingly. This was because when the gel was heated, the contraction force
_F_S was generated by the shrinkage of the polymer network, causing the gel to deviate from the direction of the Marangoni propulsion. The resultant force _F_, originated from the Marangoni
propulsive force _F_M and reacting force of contraction force _F_S’, generated a rotational torque _τ_s, resulting in a rotational motion of gel around the centroid under the balance of
buoyancy and gravity (Supplementary Fig. 45). The clockwise and anticlockwise rotational swimming were attained by regulating the α. Specifically, when α = 45°, the swimmer rotated clockwise
at an angular velocity of ω = 1.57 rad s−1 and took on anticlockwise rotation at ω = 1.05 rad s−1 at α = 135° (Fig. 5d and Supplementary Movie 8). The time-dependent angular displacement θ
was conformed to a sinusoidal curve (Fig. 5e). It was observed that the swimmer could rotate steadily for 845 s upon continuous irradiation (Supplementary Fig. 46). Furthermore, the
floating-swimming movements worked smoothly under NIR stimulation in other polar solvents with the density less than water including DMF, acetonitrile, acetone and THF (Fig. 5f). To this
end, the 3D self-propulsion motion with the controllable directionality on the liquid surface was easily actualized by taking advantage of high structural anisotropy. This was different from
the traditional Marangoni swimmers41,42. Traditionally, because of unsatisfactory heat transfer efficiency during convection, the floating height was limited. Furthermore, to control the
swimming trajectory, it was necessary to selectively focus light on different regions of the absorber to affect the direction of the applied force or provide a specific direction of
light-absorbing materials within the device43,44. This greatly reduced the programmability and efficiency of motion, making it impossible to satisfy the requirements of multifunctional soft
robots. In sharp contrast, the ASPC robot demonstrated potentials to navigate across unstructured environments including the interface of different solvents without complex accessories (Fig.
5g). It was observed that the robot at α = 135° reached the interface of _n_-hexane and acetonitrile through floating motion induced by NIR light, and then crossed the set maze through
changing the swimming mode of anticlockwise rotation under the synergy of the Marangoni effect and structure-guided shrinkage (Supplementary Movie 9). DISCUSSION In conclusion, we reported a
strategy of confined assembly polymerization of oriented porous channels into a highly ordered nanoassembly framework to fabricate environmentally tolerant and multi-stimuli responsive ASPC
hydrogels with hierarchically anisotropic cellular structure by programmable directional freezing assisted two-stage in situ polymerization. Benefitting from highly anisotropic layered
scaffold structure and low-tortuous open mass transfer channels, the ASPC hydrogel exhibited ultrafast anisotropic deformation under the stimulation of heat, light and solvent. With the help
of the reinforced-concrete components and robust structure, the gel could stably adapt in all-polarity solvent environments with highly consistent responsive capability after 100 days of
aging. These prominent performances enabled the gels to perform photoactivated programmable locomotion in various solvents that encoded in their internal anisotropic structures, including
steered crawling in water and non-polar solvents, and controllable 3D self-propulsion swimming motion in polar solvents. The design concept and fabrication method in this work will open an
effective avenue to access rapid responsive and stable hydrogel materials with controllable movements in complex solvents by regulating hierarchy and precision of assembly structure, and may
broaden the application scope of flexible intelligent actuators in unusual harsh environments. METHODS FABRICATION OF ASPC HYDROGEL Firstly, a self-made bidirectional freezing device was
built for the assembly of the lamellar architecture, which was made of a foam box containing liquid nitrogen, a steel plate with high thermal conductivity and a silicone mold with adjustable
shape. The mixture consisting of AgNW suspension (25 mg mL−1) and SA solution (20 mg mL−1) was dropped onto a silicone mold placing in a specific position that was 1 cm away from the cold
source on the steel plate. Then, liquid nitrogen was continuously and slowly added to maintain the desired height during the freezing process. After completely frozen in 30 min, the sample
was freeze dried using a Labconco FreeZone freeze-dryer (pressure: 10 Pa, temperature: −56 °C) for 48 h. To enhance the robustness of the scaffold, the obtained ASAA network was further
ionically crosslinked by immersing in ethanol solution of CaCl2 (20 mg mL−1) for 10 min followed by solvent exchange with deionized water. In the following, the predesigned ASAA matrix was
immersed in 5 mL solution (viscosity: 3.37 mPa s) containing 1 g of NIPAM as monomer, 2 mg of MBAA as crosslinker, 25 mg of K2S2O8 as initiator and 800 µL of CNTs (2 wt%) for 1 min. To
ensure full filling of the scaffold with the precursors, the vacuum dryer (pressure: −0.1 MPa) was applied to continuously press the PNIPAM solution into the ASAA scaffold until no obvious
bubbles emerged from the scaffold (1 min). Noted that to prevent the precursor solution from polymerizing before freezing assembly, the above mixture was placed in an ice bath which was
controlled at ∼5 °C in the filling process. By quickly adding 20 µL of TEMED as accelerator, the polymerizable mixture was transferred to a cold plate at −30 °C and unidirectionally frozen
in the direction parallel to the ASAA lamella for 5 min. Following with the cryopolymerization in the refrigerator (−18 °C) for 18 h and room temperature polymerization for 5 h, the ASPC
hydrogel was finally fabricated. Similarly, the A10SAA and A45SAA scaffolds were prepared by controlling the contents of AgNWs at 10 and 45 mg mL−1, respectively. By directional freezing
assisted polymerization of the NIPAM-CNT solution in the A10SAA and A45SAA scaffolds as that of ASPC, the A10SPC and A45SPC hydrogels were fabricated. Another comparative hydrogel was
fabricated through in-situ polymerization of the PNIPAM-CNT network in the ASAA scaffold without the directional freezing assembly, defined as ASAA-PC hydrogel. MATERIALS CHARACTERIZATION
Structural and compositional analyses of the samples were performed by SEM images and elemental mappings on a Zeiss Merlin Compact field-emission scanning electron microscope equipped with
an Oxford Inca energy instrument at an acceleration voltage of 5 kV. Optical microscope image was measured on a microscope MV3000. The freeze-dried hydrogel embedding resin was used to
obtain ultrathin slices parallel to the Ag/SA lamellae by Leica EM UC7 cryo microtome, and deposited on silicon wafer and copper mesh for subsequent observation. The morphology,
microstructure and elemental mapping of the AgNW nanopillars were observed using EDS-SEM and HAADF-STEM (JEM1400FLASH). The internal morphology of the ASPC hydrogel was 3D visualized by
X-ray computed microtomography (Xray-Zeiss-Xradia-520-Versa) operating at an accelerating voltage of 100 kV. Raman spectroscopy and spatial Raman mapping were recorded on a LabRAM-HR (Horiba
JY) confocal laser micro-Raman spectrometer. The temperature change under NIR (808 nm) irradiation was monitored by a Fluke Ti400 infrared imager. The mechanical properties of ASPC
hydrogels in the equilibrated state were measured at room temperature by using an Instron 5965 A testing instrument with the stretch speed of 100 mm min−1. The stimuli-responsive deformation
of the hydrogel was recorded by a camera and then analyzed by measuring the variations of gel dimensions. The relative dimensional change was calculated as Lt/L0, where L0 was initial
dimension and Lt was the dimension after deformation. The swelling ratio was calculated as Lt/L0. The deformation and recovery rates were calculated as (L0-Lt)/t, where t was deformation or
recovery time. DATA AVAILABILITY The data supporting the findings of this study are included in the paper and its Supplementary Information. All data are available from the corresponding
author on request. Source data are provided with this paper. REFERENCES * Nepal, D. et al. Hierarchically structured bioinspired nanocomposites. _Nat. Mater._ 22, 18–35 (2023). Article ADS
CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Dawson, C., Vincent, J. & Rocca, A.-M. How pine cones open. _Nature_ 390, 668 (1997). Article ADS CAS Google Scholar * Wu, S., Hong, Y., Zhao, Y.,
Yin, J. & Zhu, Y. Caterpillar-inspired soft crawling robot with distributed programmable thermal actuation. _Sci. Adv._ 9, eadf8014 (2023). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google
Scholar * Zhu, Q. L. et al. Animating hydrogel knotbots with topology-invoked self-regulation. _Nat. Commun._ 15, 300 (2024). Article ADS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Guo,
K., Yang, X., Zhou, C. & Li, C. Self-regulated reversal deformation and locomotion of structurally homogenous hydrogels subjected to constant light illumination. _Nat. Commun._ 15, 1694
(2024). Article ADS CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Zhou, Y. H. et al. A multimodal magnetoelastic artificial skin for underwater haptic sensing. _Sci. Adv._ 10, eadj8567
(2024). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Zheng, Z. et al. Programmable aniso-electrodeposited modular hydrogel microrobots. _Sci. Adv._ 8, eade6135 (2022). Article CAS
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Jiang, Z. & Song, P. Strong and fast hydrogel actuators. _Science_ 376, 245 (2022). Article ADS CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Du, X. et al.
Fast transport and transformation of biomacromolecular substances via thermo-stimulated active “inhalation-exhalation” cycles of hierarchically structured smart PNIPAM-DNA hydrogels. _Adv.
Mater._ 35, 2206302 (2023). Article CAS Google Scholar * Chen, Z. et al. Paper‐structure inspired multiresponsive hydrogels with solvent‐induced reversible information recording,
self‐encryption, and multidecryption. _Adv. Funct. Mater._ 32, 2201009 (2022). Article CAS Google Scholar * Kamata, H., Akagi, Y., Kayasuga-Kariya, Y., Chung, U. I. & Sakai, T.
“Nonswellable” hydrogel without mechanical hysteresis. _Science_ 343, 873–875 (2014). Article ADS CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Reed, R., Houston, T. W. & Todd, P. M. Structure and
function of the sarcolemma of skeletal muscle. _Nature_ 211, 534–536 (1966). Article ADS CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Zhu, Q. L. et al. Light-steered locomotion of muscle-like hydrogel
by self-coordinated shape change and friction modulation. _Nat. Commun._ 11, 5166 (2020). Article ADS CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Zhu, Q. L. et al. Distributed electric
field induces orientations of nanosheets to prepare hydrogels with elaborate ordered structures and programmed deformations. _Adv. Mater._ 32, 2005567 (2020). Article CAS Google Scholar *
Li, M., Mei, J., Friend, J. & Bae, J. Acousto-photolithography for programmable shape deformation of composite hydrogel sheets. _Small_ 18, 2204288 (2022). Article CAS Google Scholar
* Nasseri, R. et al. Programmable nanocomposites of cellulose nanocrystals and zwitterionic hydrogels for soft robotics. _Nat. Commun._ 14, 6108 (2023). Article ADS CAS PubMed PubMed
Central Google Scholar * Chen, L. et al. Anisotropic thermoresponsive hydrogels by mechanical force orientation of clay nanosheets. _Polymer_ 192, 122309 (2020). Article Google Scholar *
Li, C. et al. Fast and programmable locomotion of hydrogel-metal hybrids under light and magnetic fields. _Sci. Robot._ 5, eabb9822 (2020). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Itahara, T.,
Tsuchida, T. & Morimoto, M. Solvent-driven swelling and shrinking of poly(NIPAM) gels crosslinked by tris-methacrylated phloroglucinol derivatives. _Polym. Chem._ 1, 1062–1066 (2010).
Article CAS Google Scholar * Huang, J., Liao, J., Wang, T., Sun, W. & Tong, Z. Super strong dopamine hydrogels with shape memory and bioinspired actuating behaviours modulated by
solvent exchange. _Soft Matter_ 14, 2500–2507 (2018). Article ADS CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Wei, S. et al. Bioinspired synergistic fluorescence-color-switchable polymeric hydrogel
actuators. _Angew. Chem. Int. Ed._ 58, 16243–16251 (2019). Article CAS Google Scholar * Wang, Y. et al. Highly compressible and environmentally adaptive conductors with high-tortuosity
interconnected cellular architecture. _Nat. Synth._ 1, 975–986 (2022). Article ADS Google Scholar * Cui, Y. et al. Smart sponge for fast liquid absorption and thermal responsive
self-squeezing. _Adv. Mater._ 32, 1908249 (2020). Article CAS Google Scholar * Yan, Q. et al. Bio‐inspired stimuli‐responsive Ti3C2Tx/PNIPAM anisotropic hydrogels for high‐performance
actuators. _Adv. Funct. Mater._ 33, 2301982 (2023). Article CAS Google Scholar * Jian, Y. et al. Stimuli-responsive hydrogel sponge for ultrafast responsive actuator. _Supramol. Mater._
1, 100002 (2022). Google Scholar * Liu, J. et al. Two-step freezing polymerization method for efficient synthesis of high-performance stimuli-responsive hydrogels. _ACS Omega_ 5, 5921–5930
(2020). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Zhao, Y. et al. Somatosensory actuator based on stretchable conductive photothermally responsive hydrogel. _Sci. Robot._ 6,
eabd5483 (2021). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Zong, L. et al. Activation of actuating hydrogels with WS2 nanosheets for biomimetic cellular structures and steerable prompt deformation.
_ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces_ 9, 32280–32289 (2017). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Zhao, H. et al. Cloning nacre’s 3D interlocking skeleton in engineering composites to achieve
exceptional mechanical properties. _Adv. Mater._ 28, 5099–5105 (2016). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Song, L. et al. Visualizing the toughening mechanism of nanofiller with 3D
X-ray Nano-CT: Stress-induced phase separation of silica nanofiller and silicone polymer double networks. _Macromolecules_ 50, 7249–7257 (2017). Article ADS CAS Google Scholar * Wang,
Y., Seebald, J. L., Szeto, D. P. & Irudayaraj, J. Biocompatibility and biodistribution of surface-enhanced Raman scattering nanoprobes in zebrafish embryos: In vivo and multiplex
imaging. _ACS Nano_ 4, 4039–4053 (2010). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Bharadwaj, S. et al. Cononsolvency of thermoresponsive polymers: Where we are now and where we are going.
_Soft Matter_ 18, 2884–2909 (2022). Article ADS CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Zhu, P. W. & Napper, D. H. Coil-to-globule type transitions and swelling of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)
and poly(acrylamide) at latex interfaces in alcohol–water mixtures. _J. Colloid Interface Sci._ 177, 343–352 (1996). Article ADS CAS Google Scholar * Wang, F., Shi, Y., Luo, S., Chen, Y.
& Zhao, J. Conformational transition of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) single chains in its cononsolvency process: A study by fluorescence correlation spectroscopy and scaling analysis.
_Macromolecules_ 45, 9196–9204 (2012). Article ADS CAS Google Scholar * Chen, L. et al. Multi-stimuli responsive, shape deformation, and synergetic biomimetic actuator. _Chem. Eng. J._
480, 148205 (2024). Article CAS Google Scholar * Wei, X. et al. Remotely controlled light/electric/magnetic multiresponsive hydrogel for fast actuations. _ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces_ 15,
10030–10043 (2023). Article CAS Google Scholar * Shen, T. et al. Remotely triggered locomotion of hydrogel mag-bots in confined spaces. _Sci. Rep._ 7, 16178 (2017). Article ADS PubMed
PubMed Central Google Scholar * Chang, D. P., Dolbow, J. E. & Zauscher, S. Switchable friction of stimulus-responsive hydrogels. _Langmuir_ 23, 250–257 (2007). Article CAS PubMed
Google Scholar * Vernerey, F. & Shen, T. The mechanics of hydrogel crawlers in confined environment. _J. R. Soc. Interface_ 14, 20170242 (2017). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google
Scholar * Hou, G. et al. Self-regulated underwater phototaxis of a photoresponsive hydrogel-based phototactic vehicle. _Nat. Nanotechnol._ 19, 77–84 (2024). Article ADS CAS PubMed
Google Scholar * Wang, W. et al. Direct laser writing of superhydrophobic PDMS elastomers for controllable manipulation via marangoni effect. _Adv. Funct. Mater._ 27, 1702946 (2017).
Article Google Scholar * Hou, K. et al. Programmable light-driven swimming actuators via wavelength signal switching. _Sci. Adv._ 7, eabh3051 (2021). Article ADS CAS PubMed PubMed
Central Google Scholar * Wang, W. et al. Laser‐induced graphene tapes as origami and stick‐on labels for photothermal manipulation via marangoni effect. _Adv. Funct. Mater._ 31, 2006179
(2020). Article Google Scholar * Okawa, D., Pastine, S. J., Zettl, A. & Fréchet, J. M. Surface tension mediated conversion of light to work. _J. Am. Chem. Soc._ 131, 5396–5398 (2009).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Pi, M. et al. Rapid gelation of tough and anti‐swelling hydrogels under mild conditions for underwater communication. _Adv. Funct.
Mater._ 33, 2210188 (2022). Article Google Scholar * Ren, J. et al. An anti‐swellable hydrogel strain sensor for underwater motion detection. _Adv. Funct. Mater._ 32, 2107404 (2021).
Article Google Scholar * Li, F. et al. Bioinspired nonswellable ultrastrong nanocomposite hydrogels with long-term underwater superoleophobic behavior. _Chem. Eng. J._ 375, 122047 (2019).
Article ADS CAS Google Scholar * Dou, X. et al. One-step soaking strategy toward anti-swelling hydrogels with a stiff “armor”. _Adv. Sci._ 10, 2206242 (2023). Article CAS Google
Scholar * He, S. et al. Non‐swelling and anti‐fouling MXene nanocomposite hydrogels for underwater strain sensing. _Adv. Mater. Technol._ 7, 2101343 (2021). Article Google Scholar * Fan,
H., Wang, J. & Jin, Z. Tough, swelling-resistant, self-healing, and adhesive dual-cross-linked hydrogels based on polymer–tannic acid multiple hydrogen bonds. _Macromolecules_ 51,
1696–1705 (2018). Article ADS CAS Google Scholar * Xu, P. et al. A nonswellable gradient hydrogel with tunable mechanical properties. _J. Mater. Chem. B_ 8, 2702–2708 (2020). Article
CAS PubMed Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22471052, 22171066, 21922104 (H.P.C.), and
22293044 (S.H.Y).), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2021YFA0715700 and 2018YFE0202201 (S.H.Y.)) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities
(JZ2023YQTD0074 (H.P.C.), and JZ2021HGPA0064 (H.Q.)). AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Anhui Province Engineering Research Center of Flexible and Intelligent Materials, School
of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei, P. R. China Xin Yao, Hong Chen, Haili Qin, Qi-Hang Wu & Huai-Ping Cong * Institute of Innovative Materials,
Department of Chemistry, College of Science, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, P. R. China Shu-Hong Yu * New Cornerstone Science Laboratory, Division of Nanomaterials
& Chemistry, Hefei National Research Center for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, Department of Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, P. R. China Shu-Hong
Yu Authors * Xin Yao View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Hong Chen View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed
Google Scholar * Haili Qin View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Qi-Hang Wu View author publications You can also search for this author
inPubMed Google Scholar * Huai-Ping Cong View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Shu-Hong Yu View author publications You can also search for
this author inPubMed Google Scholar CONTRIBUTIONS H.P.C. and S.H.Y. supervised the project, conceived the idea and designed the experiments. X.Y. planned and performed the experiments,
collected and analyzed the data. H.C. and H.Q. contributed to the structural analyses. Q.H.W. helped with the materials synthesis. X.Y., H.P.C. and S.H.Y. wrote the paper, and all authors
discussed the results and commented on the manuscript. CORRESPONDING AUTHORS Correspondence to Huai-Ping Cong or Shu-Hong Yu. ETHICS DECLARATIONS COMPETING INTERESTS The authors declare no
competing interests. PEER REVIEW PEER REVIEW INFORMATION _Nature Communications_ thanks Junjie Yang and the other, anonymous, reviewers for their contribution to the peer review of this
work. A peer review file is available. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION PUBLISHER’S NOTE Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional
affiliations. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DESCRIPTION OF ADDITIONAL SUPPLEMENTARY FILES SUPPLEMENTARY MOVIE 1 SUPPLEMENTARY MOVIE 2 SUPPLEMENTARY MOVIE 3
SUPPLEMENTARY MOVIE 4 SUPPLEMENTARY MOVIE 5 SUPPLEMENTARY MOVIE 6 SUPPLEMENTARY MOVIE 7 SUPPLEMENTARY MOVIE 8 SUPPLEMENTARY MOVIE 9 SOURCE DATA TRANSPARENT PEER REVIEW FILE SOURCE DATA
RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS OPEN ACCESS This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use,
sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons
licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or
other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in
the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the
copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/. Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Yao, X., Chen, H.,
Qin, H. _et al._ Solvent-adaptive hydrogels with lamellar confinement cellular structure for programmable multimodal locomotion. _Nat Commun_ 15, 9254 (2024).
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-53549-y Download citation * Received: 17 June 2024 * Accepted: 16 October 2024 * Published: 26 October 2024 * DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-53549-y SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not
currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Trending News
7 Questions on the Daily Impact of the CoronavirusFrom how we work, socialize, and even pray, the coronavirus has upturned American life. The Pew Research Center’s Claudi...
Malignant tumors arising in patients with congenital bone diseases —investigation by a questionnaireSUMMARY We have collected data on 111 cases of malignant tumors arising in patients with congenital, mostly hereditary b...
Frank SMITH | Premiere.frBiographie News Photos Vidéos Films Séries Nom de naissance SMITH Avis PoorNot so pooraveragegoodvery good Filmographie ...
Frequent allelic loss of the rb, d13s319 and d13s25 locus in myeloid malignancies with deletion/translocation at 13q14 of chromosome 13, but not in lyABSTRACT In order to identify a commonly deleted region of 13q14 on chromosome 13, we performed fluorescence _in situ_ h...
Latest East Bay news and more | East Bay TimesBrentwood police chief to retire in SeptemberBrentwood Police Chief Tim Herbert will officially retire on Sept.5 after o...
Latests News
Solvent-adaptive hydrogels with lamellar confinement cellular structure for programmable multimodal locomotionABSTRACT Biological organisms can perform flexible and controllable multimodal motion under external stimuli owing to th...
Martin lewis explains whether help to buy or lifetime isa is bestMartin Lewis, 47, offered advice in ISAs to a caller on the BBC radio show yesterday. Angus, 23, asked the money saving ...
A single-cell comparison of adult and fetal human epicardium defines the age-associated changes in epicardial activityABSTRACT Re-activating quiescent adult epicardium represents a potential therapeutic approach for human cardiac regenera...
Islam 'shocked' by concert backlashThe musician, formerly known as Cat Stevens, kicked off his first trek in 33 years in Dublin, Ireland on Sunday (15Nov09...
Following replicative dna synthesis by time-resolved x-ray crystallographyABSTRACT The mechanism of DNA synthesis has been inferred from static structures, but the absence of temporal informatio...