Mechanisms of radiotherapy-associated cognitive disability in patients with brain tumours
Mechanisms of radiotherapy-associated cognitive disability in patients with brain tumours"
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
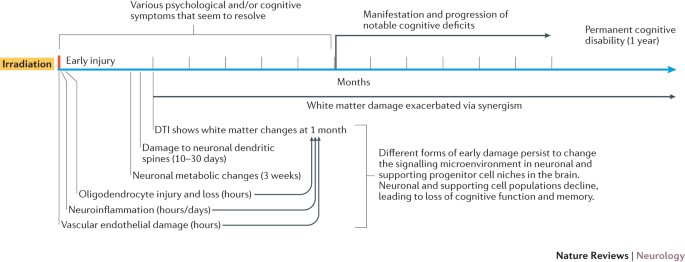
KEY POINTS * Intracranial radiotherapy leads to permanent and substantial cognitive disability in 50–90% of patients * The pathophysiology of radiotherapy-associated cognitive disability
remains poorly understood and there are no effective preventive measures or long-term treatments * Historically, most research has addressed markers of damage and the cognitive decline that
appears 6 months to 1 year or more after irradiation * More-sensitive imaging techniques have revealed subtle evidence of CNS damage much sooner than 6 months after radiation * These early
forms of CNS damage can persist and synergize over time to cause long-term, irreversible deficits in neurons and supporting cell lineages that are vital to cognition * Consideration of early
forms of radiation-induced CNS damage could help to identify early treatments that can reverse degenerative processes before they cause permanent disability ABSTRACT Standard treatment of
primary and metastatic brain tumours includes high-dose megavoltage-range radiation to the cranial vault. About half of patients survive >6 months, and many attain long-term control or
cure. However, 50–90% of survivors exhibit disabling cognitive dysfunction. The radiation-associated cognitive syndrome is poorly understood and has no effective prevention or long-term
treatment. Attention has primarily focused on mechanisms of disability that appear at 6 months to 1 year after radiotherapy. However, recent studies show that CNS alterations and dysfunction
develop much earlier following radiation exposure. This finding has prompted the hypothesis that subtle early forms of radiation-induced CNS damage could drive chronic pathophysiological
processes that lead to permanent cognitive decline. This Review presents evidence of acute radiation-triggered CNS inflammation, injury to neuronal lineages, accessory cells and their
progenitors, and loss of supporting structure integrity. Moreover, injury-related processes initiated soon after irradiation could synergistically alter the signalling microenvironment in
progenitor cell niches in the brain and the hippocampus, which is a structure critical to memory and cognition. Progenitor cell niche degradation could cause progressive neuronal loss and
cognitive disability. The concluding discussion addresses future directions and potential early treatments that might reverse degenerative processes before they can cause permanent cognitive
disability. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe
to this journal Receive 12 print issues and online access $209.00 per year only $17.42 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF
Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact
customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS ASSESSMENT OF COGNITIVE AND NEURAL RECOVERY IN SURVIVORS OF PEDIATRIC BRAIN TUMORS IN A PILOT CLINICAL TRIAL USING METFORMIN Article
27 July 2020 INVESTIGATION OF HIGH-DOSE RADIOTHERAPY'S EFFECT ON BRAIN STRUCTURE AGGRAVATED COGNITIVE IMPAIRMENT AND DETERIORATED PATIENT PSYCHOLOGICAL STATUS IN BRAIN TUMOR TREATMENT
Article Open access 02 May 2024 IRRADIATION AND LITHIUM TREATMENT ALTER THE GLOBAL DNA METHYLATION PATTERN AND GENE EXPRESSION UNDERLYING A SHIFT FROM GLIOGENESIS TOWARDS NEUROGENESIS IN
HUMAN NEURAL PROGENITORS Article Open access 13 July 2023 REFERENCES * Chi, A. & Komaki, R. Treatment of brain metastasis from lung cancer. _Cancers (Basel)_ 2, 2100–2137 (2010). Article
CAS Google Scholar * Shi, L. _ et al_. Aging masks detection of radiation-induced brain injury. _Brain Res._ 1385, 307–316 (2011). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar *
Greene-Schloesser, D., Moore, E. & Robbins, M. E. Molecular pathways: radiation-induced cognitive impairment. _Clin. Cancer Res._ 19, 2294–2300 (2013). Article CAS PubMed PubMed
Central Google Scholar * Moore, E. D., Kooshki, M., Wheeler, K. T., Metheny-Barlow, L. J. & Robbins, M. E. Differential expression of Homer1a in the hippocampus and cortex likely plays
a role in radiation-induced brain injury. _Radiat. Res._ 181, 21–32 (2014). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Wu, P. H. _ et al_. Radiation induces acute alterations in neuronal
function. _PLoS ONE_ 7, e37677 (2012). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * McTyre, E., Scott, J. & Chinnaiyan, P. Whole brain radiotherapy for brain metastasis.
_Surg. Neurol. Int._ 4, S236–S244 (2013). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Owonikoko, T. K. _ et al_. Current approaches to the treatment of metastatic brain tumours. _Nat.
Rev. Clin. Oncol._ 11, 203–222 (2014). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * McDuff, S. G. _ et al_. Neurocognitive assessment following whole brain radiation therapy and
radiosurgery for patients with cerebral metastases. _J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry_ 84, 1384–1391 (2013). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Marsh, J. C., Gielda, B. T., Herskovic, A. M.
& Abrams, R. A. Cognitive sparing during the administration of whole brain radiotherapy and prophylactic cranial irradiation: current concepts and approaches. _J. Oncol._ 2010, 198208
(2010). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Jenrow, K. A. _ et al_. Selective inhibition of microglia-mediated neuroinflammation mitigates radiation-induced cognitive
impairment. _Radiat. Res._ 179, 549–556 (2013). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Lippitz, B. _ et al_. Stereotactic radiosurgery in the treatment of brain metastases:
the current evidence. _Cancer Treat. Rev._ 40, 48–59 (2014). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Phillips, M. H., Stelzer, K. J., Griffin, T. W., Mayberg, M. R. & Winn, H. R. Stereotactic
radiosurgery: a review and comparison of methods. _J. Clin. Oncol._ 12, 1085–1099 (1994). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Bilimagga, R. S. _ et al_. Role of palliative radiotherapy
in brain metastases. _Indian J. Palliat. Care_ 15, 71–75 (2009). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Wadasadawala, T., Gupta, S., Bagul, V. & Patil, N. Brain metastases
from breast cancer: management approach. _J. Cancer Res. Ther._ 3, 157–165 (2007). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Packer, R. J. _ et al_. Treatment of children with medulloblastomas with
reduced-dose craniospinal radiation therapy and adjuvant chemotherapy: a Children's Cancer Group study. _J. Clin. Oncol._ 17, 2127–2136 (1999). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar *
Davis, C. M. _ et al_. Effects of X-ray radiation on complex visual discrimination learning and social recognition memory in rats. _PLoS ONE_ 9, e104393 (2014). Article CAS PubMed PubMed
Central Google Scholar * Shi, L., Molina, D. P., Robbins, M. E., Wheeler, K. T. & Brunso-Bechtold, J. K. Hippocampal neuron number is unchanged 1 year after fractionated whole-brain
irradiation at middle age. _Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys._ 71, 526–532 (2008). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Greene-Schloesser, D. _ et al_. Radiation-induced brain
injury: a review. _Front. Oncol._ 2, 73 (2012). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Palmer, S. L., Reddick, W. E. & Gajjar, A. Understanding the cognitive impact on
children who are treated for medulloblastoma. _J. Pediatr. Psychol._ 32, 1040–1049 (2007). Article PubMed Google Scholar * [No authors listed.] Outcomes of cancer treatment for technology
assessment and cancer treatment guidelines. American Society of Clinical Oncology. _J. Clin. Oncol._ 14, 671–679 (1996). * Gustafsson, M., Edvardsson, T. & Ahlstrom, G. The relationship
between function, quality of life and coping in patients with low-grade gliomas. _Support. Care Cancer_ 14, 1205–1212 (2006). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Frost, M. H. & Sloan, J.
A. Quality of life measurements: a soft outcome — or is it? _Am. J. Manag. Care_ 8, S574–S579 (2002). PubMed Google Scholar * Lin, N. U. _ et al_. Challenges relating to solid tumour
brain metastases in clinical trials, part 2: neurocognitive, neurological, and quality-of-life outcomes. A report from the RANO group. _Lancet Oncol._ 14, e407–e416 (2013). Article PubMed
Google Scholar * Lee, Y. W., Cho, H. J., Lee, W. H. & Sonntag, W. E. Whole brain radiation-induced cognitive impairment: pathophysiological mechanisms and therapeutic targets. _Biomol.
Ther. (Seoul)_ 20, 357–370 (2012). Article CAS Google Scholar * Attia, A., Page, B. R., Lesser, G. J. & Chan, M. Treatment of radiation-induced cognitive decline. _Curr. Treat.
Options Oncol._ 15, 539–550 (2014). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Rooney, J. W. & Laack, N. N. Pharmacological interventions to treat or prevent neurocognitive decline after brain
radiation. _CNS Oncol._ 2, 531–541 (2013). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Connor, M. _ et al_. Dose-dependent white matter damage after brain radiotherapy.
_Radiother. Oncol._ http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2016.10.003 (2016). * Armstrong, C. L., Gyato, K., Awadalla, A. W., Lustig, R. & Tochner, Z. A. A critical review of the clinical
effects of therapeutic irradiation damage to the brain: the roots of controversy. _Neuropsychol. Rev._ 14, 65–86 (2004). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Shi, L. _ et al_. Maintenance of
white matter integrity in a rat model of radiation-induced cognitive impairment. _J. Neurol. Sci._ 285, 178–184 (2009). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Parihar, V. K. _ et
al_. Persistent changes in neuronal structure and synaptic plasticity caused by proton irradiation. _Brain Struct. Funct._ 220, 1161–1171 (2015). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar *
Ljubimova, N. V., Levitman, M. K., Plotnikova, E. D. & Eidus, L. Endothelial cell population dynamics in rat brain after local irradiation. _Br. J. Radiol._ 64, 934–940 (1991). Article
CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Palmer, T. D., Willhoite, A. R. & Gage, F. H. Vascular niche for adult hippocampal neurogenesis. _J. Comp. Neurol._ 425, 479–494 (2000). Article CAS
PubMed Google Scholar * Peiffer, A. M. _ et al_. Neuroanatomical target theory as a predictive model for radiation-induced cognitive decline. _Neurology_ 80, 747–753 (2013). Article
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Parihar, V. K. & Limoli, C. L. Cranial irradiation compromises neuronal architecture in the hippocampus. _Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA_ 110,
12822–12827 (2013). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Agarwal, S., Manchanda, P., Vogelbaum, M. A., Ohlfest, J. R. & Elmquist, W. F. Function of the blood–brain barrier and
restriction of drug delivery to invasive glioma cells: findings in an orthotopic rat xenograft model of glioma. _Drug Metab. Dispos._ 41, 33–39 (2013). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central
Google Scholar * Furnari, F. B. _ et al_. Malignant astrocytic glioma: genetics, biology, and paths to treatment. _Genes Dev._ 21, 2683–2710 (2007). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar *
Puhalla, S. _ et al_. Unsanctifying the sanctuary: challenges and opportunities with brain metastases. _Neuro Oncol._ 17, 639–651 (2015). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar *
Packer, R. J., Zhou, T., Holmes, E., Vezina, G. & Gajjar, A. Survival and secondary tumors in children with medulloblastoma receiving radiotherapy and adjuvant chemotherapy: results of
Children's Oncology Group trial A9961. _Neuro Oncol._ 15, 97–103 (2013). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Ruben, J. D. _ et al_. Cerebral radiation necrosis: incidence, outcomes,
and risk factors with emphasis on radiation parameters and chemotherapy. _Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys._ 65, 499–508 (2006). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Chen, J. _ et al_.
Radiation induced temporal lobe necrosis in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a review of new avenues in its management. _Radiat. Oncol._ 6, 128 (2011). Article PubMed PubMed Central
Google Scholar * Dropcho, E. J. Neurotoxicity of radiation therapy. _Neurol. Clin._ 28, 217–234 (2010). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Sheline, G. E., Wara, W. M. & Smith, V.
Therapeutic irradiation and brain injury. _Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys._ 6, 1215–1228 (1980). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Saury, J. M. & Emanuelson, I. Cognitive
consequences of the treatment of medulloblastoma among children. _Pediatr. Neurol._ 44, 21–30 (2011). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Deng, W., Aimone, J. B. & Gage, F. H. New neurons
and new memories: how does adult hippocampal neurogenesis affect learning and memory? _Nat. Rev. Neurosci._ 11, 339–350 (2010). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar *
Hoffmann, M. The human frontal lobes and frontal network systems: an evolutionary, clinical, and treatment perspective. _ISRN Neurol._ 2013, 892459 (2013). Article PubMed PubMed Central
Google Scholar * Parihar, V. K. _ et al_. What happens to your brain on the way to Mars. _Sci. Adv._ 1, e1400256 (2015). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Fuster, J.
M. Frontal lobe and cognitive development. _J. Neurocytol._ 31, 373–385 (2002). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Braun, U. _ et al_. Dynamic reconfiguration of frontal brain networks
during executive cognition in humans. _Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA_ 112, 11678–11683 (2015). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Murphy, E. S. _ et al_. Review of cranial
radiotherapy-induced vasculopathy. _J. Neurooncol._ 122, 421–429 (2015). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Pellmar, T. C., Schauer, D. A. & Zeman, G. H. Time- and dose-dependent
changes in neuronal activity produced by X radiation in brain slices. _Radiat. Res._ 122, 209–214 (1990). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Padovani, L., Andre, N., Constine, L. S.
& Muracciole, X. Neurocognitive function after radiotherapy for paediatric brain tumours. _Nat. Rev. Neurol._ 8, 578–588 (2012). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Panagiotakos, G.
_ et al_. Long-term impact of radiation on the stem cell and oligodendrocyte precursors in the brain. _PLoS ONE_ 2, e588 (2007). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar *
Gangloff, H. & Haley, T. J. Effects of X-irradiation on spontaneous and evoked brain electrical activity in cats. _Radiat. Res._ 12, 694–704 (1960). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
* Bassant, M. H. & Court, L. Effects of whole-body gamma irradiation on the activity of rabbit hippocampal neurons. _Radiat. Res._ 75, 593–606 (1978). Article CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Pellmar, T. C. & Lepinski, D. L. Gamma radiation (5–10 Gy) impairs neuronal function in the guinea pig hippocampus. _Radiat. Res._ 136, 255–261 (1993). Article CAS PubMed
Google Scholar * Gerstner, H. B., Brooks, P. M. & Smith, S. A. Effect of X-radiation on the flow of perfusion fluid through the isolated rabbit's ear. _Am. J. Physiol._ 182,
459–461 (1955). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Krueger, H., Wagelie, E. G. & Bogart, R. Radiation and responses of rabbit ear artery to xylene, alcohol, and epinephrine.
_Radiat. Res._ 30, 420–430 (1967). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Li, Y. Q., Chen, P., Haimovitz-Friedman, A., Reilly, R. M. & Wong, C. S. Endothelial apoptosis initiates acute
blood–brain barrier disruption after ionizing radiation. _Cancer Res._ 63, 5950–5956 (2003). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Brown, W. R., Thore, C. R., Moody, D. M., Robbins, M. E. &
Wheeler, K. T. Vascular damage after fractionated whole-brain irradiation in rats. _Radiat. Res._ 164, 662–668 (2005). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Finet, P., Rooijakkers, H.,
Godfraind, C. & Raftopoulos, C. Delayed compressive angiomatous degeneration in a case of mesial temporal lobe epilepsy treated by γ knife radiosurgery: case report. _Neurosurgery_ 67,
218–220 (2010). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Desai, S. S., Paulino, A. C., Mai, W. Y. & Teh, B. S. Radiation-induced moyamoya syndrome. _Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys._ 65,
1222–1227 (2006). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Ullrich, N. J. _ et al_. Moyamoya following cranial irradiation for primary brain tumors in children. _Neurology_ 68, 932–938 (2007).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Hahn, C. A. _ et al_. Dose-dependent effects of radiation therapy on cerebral blood flow, metabolism, and neurocognitive dysfunction. _Int. J. Radiat.
Oncol. Biol. Phys._ 73, 1082–1087 (2009). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Abayomi, O. K. Pathogenesis of cognitive decline following therapeutic irradiation for head and neck
tumors. _Acta Oncol._ 41, 346–351 (2002). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Calvo, W., Hopewell, J. W., Reinhold, H. S. & Yeung, T. K. Time- and dose-related changes in the white matter
of the rat brain after single doses of X rays. _Br. J. Radiol._ 61, 1043–1052 (1988). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Filley, C. M. White matter dementia. _Ther. Adv. Neurol.
Disord._ 5, 267–277 (2012). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Zhao, W. _ et al_. Administration of the peroxisomal proliferator-activated receptor gamma agonist pioglitazone
during fractionated brain irradiation prevents radiation-induced cognitive impairment. _Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys._ 67, 6–9 (2007). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Lee, T.
C. _ et al_. Chronic administration of the angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, ramipril, prevents fractionated whole-brain irradiation-induced perirhinal cortex-dependent cognitive
impairment. _Radiat. Res._ 178, 46–56 (2012). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Hansson, E. Astroglia from defined brain regions as studied with primary cultures.
_Prog. Neurobiol._ 30, 369–397 (1988). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Pal, B. Astrocytic actions on extrasynaptic neuronal currents. _Front. Cell. Neurosci._ 9, 474 (2015). Article
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Hamilton, N. B. & Attwell, D. Do astrocytes really exocytose neurotransmitters? _Nat. Rev. Neurosci._ 11, 227–238 (2010). Article CAS
PubMed Google Scholar * Hwang, S. Y. _ et al_. Ionizing radiation induces astrocyte gliosis through microglia activation. _Neurobiol. Dis._ 21, 457–467 (2006). Article CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Ho, G., Zhang, C. & Zhuo, L. Non-invasive fluorescent imaging of gliosis in transgenic mice for profiling developmental neurotoxicity. _Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol._ 221, 76–85
(2007). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Chiang, C. S., McBride, W. H. & Withers, H. R. Radiation-induced astrocytic and microglial responses in mouse brain. _Radiother. Oncol._
29, 60–68 (1993). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Moore, E. D., Kooshki, M., Metheny-Barlow, L. J., Gallagher, P. E. & Robbins, M. E. Angiotensin-(1–7) prevents radiation-induced
inflammation in rat primary astrocytes through regulation of MAP kinase signaling. _Free Radic. Biol. Med._ 65, 1060–1068 (2013). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Li, Y. Q., Jay, V.
& Wong, C. S. Oligodendrocytes in the adult rat spinal cord undergo radiation-induced apoptosis. _Cancer Res._ 56, 5417–5422 (1996). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kurita, H. _ et al_.
Radiation-induced apoptosis of oligodendrocytes in the adult rat brain. _Neurol. Res._ 23, 869–874 (2001). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Tsuruda, J. S. _ et al_. Radiation effects
on cerebral white matter: MR evaluation. _AJR Am. J. Roentgenol._ 149, 165–171 (1987). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Wang, S. _ et al_. Radiation induced brain injury: assessment
of white matter tracts in a pre-clinical animal model using diffusion tensor MR imaging. _J. Neurooncol._ 112, 9–14 (2013). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Hellstrom, N. A.,
Bjork-Eriksson, T., Blomgren, K. & Kuhn, H. G. Differential recovery of neural stem cells in the subventricular zone and dentate gyrus after ionizing radiation. _Stem Cells_ 27, 634–641
(2009). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Ming, G. L. & Song, H. Adult neurogenesis in the mammalian brain: significant answers and significant questions. _Neuron_ 70, 687–702
(2011). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Mizumatsu, S. _ et al_. Extreme sensitivity of adult neurogenesis to low doses of X-irradiation. _Cancer Res._ 63, 4021–4027
(2003). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kalm, M., Karlsson, N., Nilsson, M. K. & Blomgren, K. Loss of hippocampal neurogenesis, increased novelty-induced activity, decreased home cage
activity, and impaired reversal learning one year after irradiation of the young mouse brain. _Exp. Neurol._ 247, 402–409 (2013). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Manda, K., Ueno, M. &
Anzai, K. Cranial irradiation-induced inhibition of neurogenesis in hippocampal dentate gyrus of adult mice: attenuation by melatonin pretreatment. _J. Pineal Res._ 46, 71–78 (2009).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Tada, E., Parent, J. M., Lowenstein, D. H. & Fike, J. R. X-Irradiation causes a prolonged reduction in cell proliferation in the dentate gyrus of
adult rats. _Neuroscience_ 99, 33–41 (2000). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Rola, R. _ et al_. Radiation-induced impairment of hippocampal neurogenesis is associated with cognitive
deficits in young mice. _Exp. Neurol._ 188, 316–330 (2004). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Raber, J. _ et al_. Radiation-induced cognitive impairments are associated with changes in
indicators of hippocampal neurogenesis. _Radiat. Res._ 162, 39–47 (2004). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Chen, H. _ et al_. Ionizing radiation perturbs cell cycle progression of
neural precursors in the subventricular zone without affecting their long-term self-renewal. _ASN Neuro_ http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/1759091415578026 (2015). * Monje, M. L., Mizumatsu, S.,
Fike, J. R. & Palmer, T. D. Irradiation induces neural precursor-cell dysfunction. _Nat. Med._ 8, 955–962 (2002). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Tofilon, P. J. & Fike, J. R.
The radioresponse of the central nervous system: a dynamic process. _Radiat. Res._ 153, 357–370 (2000). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Acharya, M. M. _ et al_. Human neural stem
cell transplantation ameliorates radiation-induced cognitive dysfunction. _Cancer Res._ 71, 4834–4845 (2011). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Acharya, M. M., Roa, D.
E., Bosch, O., Lan, M. L. & Limoli, C. L. Stem cell transplantation strategies for the restoration of cognitive dysfunction caused by cranial radiotherapy. _J. Vis. Exp._
http://dx.doi.org/10.3791/3107 (2011). * Warrington, J. P., Csiszar, A., Mitschelen, M., Lee, Y. W. & Sonntag, W. E. Whole brain radiation-induced impairments in learning and memory are
time-sensitive and reversible by systemic hypoxia. _PLoS ONE_ 7, e30444 (2012). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Monje, M. L., Toda, H. & Palmer, T. D.
Inflammatory blockade restores adult hippocampal neurogenesis. _Science_ 302, 1760–1765 (2003). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Lee, W. H., Sonntag, W. E., Mitschelen, M., Yan, H.
& Lee, Y. W. Irradiation induces regionally specific alterations in pro-inflammatory environments in rat brain. _Int. J. Radiat. Biol._ 86, 132–144 (2010). Article PubMed PubMed
Central Google Scholar * Ballesteros-Zebadua, P., Chavarria, A., Celis, M. A., Paz, C. & Franco-Perez, J. Radiation-induced neuroinflammation and radiation somnolence syndrome. _CNS
Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets_ 11, 937–949 (2012). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kyrkanides, S. _ et al_. Cyclooxygenase-2 modulates brain inflammation-related gene expression in
central nervous system radiation injury. _Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res._ 104, 159–169 (2002). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Monje, M. L. _ et al_. Impaired human hippocampal
neurogenesis after treatment for central nervous system malignancies. _Ann. Neurol._ 62, 515–520 (2007). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Ekdahl, C. T., Claasen, J. H., Bonde, S., Kokaia,
Z. & Lindvall, O. Inflammation is detrimental for neurogenesis in adult brain. _Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA_ 100, 13632–13637 (2003). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Ingraham, J.
P., Forbes, M. E., Riddle, D. R. & Sonntag, W. E. Aging reduces hypoxia-induced microvascular growth in the rodent hippocampus. _J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci._ 63, 12–20 (2008).
Article PubMed Google Scholar * Park, J. A., Choi, K. S., Kim, S. Y. & Kim, K. W. Coordinated interaction of the vascular and nervous systems: from molecule- to cell-based approaches.
_Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun._ 311, 247–253 (2003). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Licht, T. _ et al_. Reversible modulations of neuronal plasticity by VEGF. _Proc. Natl Acad.
Sci. USA_ 108, 5081–5086 (2011). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kang, S. G. _ et al_. Isolation and perivascular localization of mesenchymal stem cells from mouse brain.
_Neurosurgery_ 67, 711–720 (2010). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Kim, J. H., Jenrow, K. A. & Brown, S. L. Mechanisms of radiation-induced normal tissue toxicity and
implications for future clinical trials. _Radiat. Oncol. J._ 32, 103–115 (2014). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Robbins, M. E., Bourland, J. D., Cline, J. M., Wheeler, K.
T. & Deadwyler, S. A. A model for assessing cognitive impairment after fractionated whole-brain irradiation in nonhuman primates. _Radiat. Res._ 175, 519–525 (2011). Article CAS
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Gonzalez Burgos, I., Nikonenko, I. & Korz, V. Dendritic spine plasticity and cognition. _Neural Plast._ 2012, 875156 (2012). PubMed PubMed
Central Google Scholar * Frankfurt, M. & Luine, V. The evolving role of dendritic spines and memory: interaction(s) with estradiol. _Horm. Behav._ 74, 28–36 (2015). Article CAS
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Yuste, R. & Bonhoeffer, T. Morphological changes in dendritic spines associated with long-term synaptic plasticity. _Annu. Rev. Neurosci._ 24,
1071–1089 (2001). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Schwechter, B. & Tolias, K. F. Cytoskeletal mechanisms for synaptic potentiation. _Commun. Integr. Biol._ 6, e27343 (2013).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Hains, A. B., Yabe, Y. & Arnsten, A. F. Chronic stimulation of alpha-2A-adrenoceptors with guanfacine protects rodent prefrontal
cortex dendritic spines and cognition from the effects of chronic stress. _Neurobiol. Stress_ 2, 1–9 (2015). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Pereira, A. C. _ et al_.
Glutamatergic regulation prevents hippocampal-dependent age-related cognitive decline through dendritic spine clustering. _Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA_ 111, 18733–18738 (2014). Article CAS
PubMed Google Scholar * Brizzee, K. R., Ordy, J. M., Kaack, M. B. & Beavers, T. Effect of prenatal ionizing radiation on the visual cortex and hippocampus of newborn squirrel monkeys.
_J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol._ 39, 523–540 (1980). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Shors, T. J., Anderson, M. L., Curlik, D. M. II & Nokia, M. S. Use it or lose it: how
neurogenesis keeps the brain fit for learning. _Behav. Brain Res._ 227, 450–458 (2012). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kirby, E. D., Kuwahara, A. A., Messer, R. L. & Wyss-Coray,
T. Adult hippocampal neural stem and progenitor cells regulate the neurogenic niche by secreting VEGF. _Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA_ 112, 4128–4133 (2015). Article CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Eriksson, P. S. _ et al_. Neurogenesis in the adult human hippocampus. _Nat. Med._ 4, 1313–1317 (1998). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Seib, D. R. & Martin-Villalba,
A. Neurogenesis in the normal ageing hippocampus: a mini-review. _Gerontology_ 61, 327–335 (2015). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Christian, K. M., Song, H. & Ming, G. L.
Functions and dysfunctions of adult hippocampal neurogenesis. _Annu. Rev. Neurosci._ 37, 243–262 (2014). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Lie, D. C. _ et al_. Wnt
signaling regulates adult hippocampal neurogenesis. _Nature_ 437, 1370–1375 (2005). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Acharya, M. M., Christie, L. A., Hazel, T. G., Johe, K. K. &
Limoli, C. L. Transplantation of human fetal-derived neural stem cells improves cognitive function following cranial irradiation. _Cell Transplant._ 23, 1255–1266 (2014). Article PubMed
Google Scholar * Bostrom, M., Kalm, M., Karlsson, N., Hellstrom Erkenstam, N. & Blomgren, K. Irradiation to the young mouse brain caused long-term, progressive depletion of neurogenesis
but did not disrupt the neurovascular niche. _J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab._ 33, 935–943 (2013). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Snyder, J. S., Kee, N. &
Wojtowicz, J. M. Effects of adult neurogenesis on synaptic plasticity in the rat dentate gyrus. _J. Neurophysiol._ 85, 2423–2431 (2001). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Wong, C. S.
& Van der Kogel, A. J. Mechanisms of radiation injury to the central nervous system: implications for neuroprotection. _Mol. Interv._ 4, 273–284 (2004). Article CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Shiraishi-Yamaguchi, Y. & Furuichi, T. The Homer family proteins. _Genome Biol._ 8, 206 (2007). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Roloff, A. M.,
Anderson, G. R., Martemyanov, K. A. & Thayer, S. A. Homer 1a gates the induction mechanism for endocannabinoid-mediated synaptic plasticity. _J. Neurosci._ 30, 3072–3081 (2010). Article
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Celikel, T. _ et al_. Select overexpression of homer1a in dorsal hippocampus impairs spatial working memory. _Front. Neurosci._ 1, 97–110
(2007). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Tappe-Theodor, A., Fu, Y., Kuner, R. & Neugebauer, V. Homer1a signaling in the amygdala counteracts pain-related synaptic
plasticity, mGluR1 function and pain behaviors. _Mol. Pain_ 7, 38 (2011). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Zhou, F. W. & Roper, S. N. Impaired hippocampal memory
function and synaptic plasticity in experimental cortical dysplasia. _Epilepsia_ 53, 850–859 (2012). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Ehlers, M. D. Activity level controls postsynaptic
composition and signaling via the ubiquitin-proteasome system. _Nat. Neurosci._ 6, 231–242 (2003). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Deisseroth, K. _ et al_. Excitation-neurogenesis
coupling in adult neural stem/progenitor cells. _Neuron_ 42, 535–552 (2004). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Ge, S. _ et al_. GABA regulates synaptic integration of newly generated
neurons in the adult brain. _Nature_ 439, 589–593 (2006). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Prust, M. J. _ et al_. Standard chemoradiation for glioblastoma results in progressive brain
volume loss. _Neurology_ 85, 683–691 (2015). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Karunamuni, R. _ et al_. Dose-dependent cortical thinning after partial brain
irradiation in high-grade glioma. _Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys._ 94, 297–304 (2016). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Seibert, T. M. _ et al_. Selective vulnerability of cerebral
cortex regions to radiation dose-dependent atrophy. [abstract] _Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys._ 96, S177–304 (2016). Article Google Scholar * Karunamuni, R. A. _ et al_. Radiation
sparing of cerebral cortex in brain tumor patients using quantitative neuroimaging. _Radiother. Oncol._ 118, 29–34 (2016). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Olsson, E. _ et
al_. Hippocampal volumes in patients exposed to low-dose radiation to the basal brain. A case–control study in long-term survivors from cancer in the head and neck region. _Radiat. Oncol._
7, 202 (2012). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Nolen, S. C. _ et al_. The effects of sequential treatments on hippocampal volumes in malignant glioma patients. _J.
Neurooncol._ 129, 433–441 (2016). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Seibert, T. M. _ et al_. Radiation dose-dependent hippocampal atrophy detected with longitudinal
volumetric MRI. _Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys._ http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2016.10.035 (2016). * Walecki, J. _ et al_. Role of short TE 1H-MR spectroscopy in monitoring of
post-operation irradiated patients. _Eur. J. Radiol._ 30, 154–161 (1999). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Sundgren, P. C. _ et al_. Metabolic alterations: a biomarker for
radiation-induced normal brain injury-an MR spectroscopy study. _J. Magn. Reson. Imaging_ 29, 291–297 (2009). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Movsas, B. _ et al_.
Quantifying radiation therapy-induced brain injury with whole-brain proton MR spectroscopy: initial observations. _Radiology_ 221, 327–331 (2001). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar *
Robbins, M. E. _ et al_. Imaging radiation-induced normal tissue injury. _Radiat. Res._ 177, 449–466 (2012). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Wang, S. _ et al_.
Radiation induced brain injury: assessment of white matter tracts in a pre-clinical animal model using diffusion tensor MR imaging. _J. Neurooncol._ 112, 9–15 (2013). Article PubMed Google
Scholar * White, N. S. _ et al_. Diffusion-weighted imaging in cancer: physical foundations and applications of restriction spectrum imaging. _Cancer Res._ 74, 4638–4652 (2014). Article
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Alexander, A. L., Lee, J. E., Lazar, M. & Field, A. S. Diffusion tensor imaging of the brain. _Neurotherapeutics_ 4, 316–329 (2007).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Chan, K. C. _ et al_. MRI of late microstructural and metabolic alterations in radiation-induced brain injuries. _J. Magn. Reson. Imaging_
29, 1013–1020 (2009). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Ravn, S., Holmberg, M., Sorensen, P., Frokjaer, J. B. & Carl, J. Differences in supratentorial white matter diffusion after
radiotherapy — new biomarker of normal brain tissue damage? _Acta Oncol._ 52, 1314–1319 (2013). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Haris, M. _ et al_. Serial diffusion tensor imaging to
characterize radiation-induced changes in normal-appearing white matter following radiotherapy in patients with adult low-grade gliomas. _Radiat. Med._ 26, 140–150 (2008). Article PubMed
Google Scholar * Nagesh, V. _ et al_. Radiation-induced changes in normal-appearing white matter in patients with cerebral tumors: a diffusion tensor imaging study. _Int. J. Radiat. Oncol.
Biol. Phys._ 70, 1002–1010 (2008). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Zhu, T. _ et al_. Effect of the maximum dose on white matter fiber bundles using longitudinal diffusion
tensor imaging. _Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys._ 96, 696–705 (2016). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Qiu, D., Kwong, D. L., Chan, G. C., Leung, L. H. & Khong, P.
L. Diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging finding of discrepant fractional anisotropy between the frontal and parietal lobes after whole-brain irradiation in childhood medulloblastoma
survivors: reflection of regional white matter radiosensitivity? _Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys._ 69, 846–851 (2007). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Chapman, C. H. _ et al_. Regional
variation in brain white matter diffusion index changes following chemoradiotherapy: a prospective study using tract-based spatial statistics. _PLoS ONE_ 8, e57768 (2013). Article CAS
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Chapman, C. H. _ et al_. Diffusion tensor imaging of normal-appearing white matter as biomarker for radiation-induced late delayed cognitive
decline. _Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys._ 82, 2033–2040 (2012). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Khong, P. L. _ et al_. White matter anisotropy in post-treatment childhood cancer
survivors: preliminary evidence of association with neurocognitive function. _J. Clin. Oncol._ 24, 884–890 (2006). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Meyers, C. A., Weitzner, M. A.,
Valentine, A. D. & Levin, V. A. Methylphenidate therapy improves cognition, mood, and function of brain tumor patients. _J. Clin. Oncol._ 16, 2522–2527 (1998). Article CAS PubMed
Google Scholar * Brown, P. D. _ et al_. Memantine for the prevention of cognitive dysfunction in patients receiving whole-brain radiotherapy: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled
trial. _Neuro Oncol._ 15, 1429–1437 (2013). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * McGough, J. J. _ et al_. Once-daily OROS methylphenidate is safe and well tolerated in
adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. _J. Child Adolesc. Psychopharmacol._ 16, 351–356 (2006). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Parsons, C. G., Danysz, W. & Quack,
G. Memantine is a clinically well tolerated N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist — a review of preclinical data. _Neuropharmacology_ 38, 735–767 (1999). Article CAS PubMed
Google Scholar * NRG Oncology. _NRGOncology.org_ [online] NRG-CC001: a randomized phase III Trial of memantine and whole-brain radiotherapy with or without hippocampal avoidance in patients
with brain metastases. https://www.nrgoncology.org/Clinical-Trials/NRG-CC001 (2015). * Howard, R. _ et al_. Donepezil and memantine for moderate-to-severe Alzheimer's disease. _N.
Engl. J. Med._ 366, 893–903 (2012). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kleinberg, L. Neurocognitive challenges in brain tumor survivors: is there anything we can do? _J. Clin. Oncol._
33, 1633–1636 (2015). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Fathpour, P. _ et al_. Bevacizumab treatment for human glioblastoma. Can it induce cognitive impairment? _Neuro
Oncol._ 16, 754–756 (2014). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Calabrese, B. & Halpain, S. Essential role for the PKC target MARCKS in maintaining dendritic spine
morphology. _Neuron_ 48, 77–90 (2005). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Hains, A. B. _ et al_. Inhibition of protein kinase C signaling protects prefrontal cortex dendritic spines and
cognition from the effects of chronic stress. _Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA_ 106, 17957–17962 (2009). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Starr, P. Midostaurin the first targeted therapy
to improve survival in AML: potentially practice-changing. _Am. Health Drug Benefits_ 9, 1–21 (2016). PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Cifelli, J. L., Dozier, L., Chung, T. S.,
Patrick, G. N. & Yang, J. Benzothiazole amphiphiles promote the formation of dendritic spines in primary hippocampal neurons. _J. Biol. Chem._ 291, 11981–11992 (2016). Article CAS
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Williams, C. A. & Lavik, E. B. Engineering the CNS stem cell microenvironment. _Regen. Med._ 4, 865–877 (2009). Article PubMed PubMed Central
Google Scholar * Tysseling-Mattiace, V. M. _ et al_. Self-assembling nanofibers inhibit glial scar formation and promote axon elongation after spinal cord injury. _J. Neurosci._ 28,
3814–3823 (2008). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Wang, H. D., Dunnavant, F. D., Jarman, T. & Deutch, A. Y. Effects of antipsychotic drugs on neurogenesis in the
forebrain of the adult rat. _Neuropsychopharmacology_ 29, 1230–1238 (2004). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Pleasure, D., Soulika, A., Singh, S. K., Gallo, V. & Bannerman, P.
Inflammation in white matter: clinical and pathophysiological aspects. _Ment. Retard. Dev. Disabil. Res. Rev._ 12, 141–146 (2006). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Nunes, M. C. _ et al_.
Identification and isolation of multipotential neural progenitor cells from the subcortical white matter of the adult human brain. _Nat. Med._ 9, 439–447 (2003). Article CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Burger, P. C., Mahley, M. S. Jr, Dudka, L. & Vogel, F. S. The morphologic effects of radiation administered therapeutically for intracranial gliomas: a postmortem study of 25
cases. _Cancer_ 44, 1256–1272 (1979). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Fujii, O. _ et al_. White matter changes on magnetic resonance imaging following whole-brain radiotherapy for
brain metastases. _Radiat. Med._ 24, 345–350 (2006). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Mabbott, D. J., Noseworthy, M. D., Bouffet, E., Rockel, C. & Laughlin, S. Diffusion tensor imaging
of white matter after cranial radiation in children for medulloblastoma: correlation with IQ. _Neuro Oncol._ 8, 244–252 (2006). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Chiang, C.
S., McBride, W. H. & Withers, H. R. Myelin-associated changes in mouse brain following irradiation. _Radiother. Oncol._ 27, 229–236 (1993). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar *
Nakagaki, H., Brunhart, G., Kemper, T. L. & Caveness, W. F. Monkey brain damage from radiation in the therapeutic range. _J. Neurosurg._ 44, 3–11 (1976). Article CAS PubMed Google
Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS J.A.H.-G. has received funding from NIH (grants #1KL2TR001444 and #UL1TR000100), and has received the American Cancer Society Pilot Award
ACS-IRG 70-002. AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Department of Radiation Medicine and Applied Sciences, UC San Diego, 3855 Health Sciences Drive, La Jolla, 92093–0819, CA, USA
Milan T. Makale & Jona A. Hattangadi-Gluth * Department of Psychiatry, 9500 Gilman Drive, UC San Diego, La Jolla, 92093–0841, CA, USA Carrie R. McDonald * Department of Translational
Neuro-Oncology and Neurotherapeutics, John Wayne Cancer Institute at Providence Saint John's Health Center, 2200 Santa Monica Blvd., Santa Monica, 90404, California, USA Santosh Kesari
Authors * Milan T. Makale View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Carrie R. McDonald View author publications You can also search for this
author inPubMed Google Scholar * Jona A. Hattangadi-Gluth View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Santosh Kesari View author publications You
can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CONTRIBUTIONS M.T.M., C.R.M., and J.A.H.-G. contributed to researching the data, writing and reviewing of the manuscript. S.K.
provided substantial contributions to the discussion of the content and revising of the manuscript. CORRESPONDING AUTHORS Correspondence to Milan T. Makale or Santosh Kesari. ETHICS
DECLARATIONS COMPETING INTERESTS The authors declare no competing financial interests. RELATED LINKS FURTHER INFORMATION WHO description of health POWERPOINT SLIDES POWERPOINT SLIDE FOR FIG.
1 POWERPOINT SLIDE FOR FIG. 2 POWERPOINT SLIDE FOR FIG. 3 POWERPOINT SLIDE FOR FIG. 4 POWERPOINT SLIDE FOR FIG. 5 POWERPOINT SLIDE FOR FIG. 6 POWERPOINT SLIDE FOR FIG. 7 POWERPOINT SLIDE
FOR TABLE 1 GLOSSARY * Whole-brain radiotherapy Entire brain and brainstem are irradiated to treat a tumour. * Partial-brain radiotherapy Irradiation treatment of the tumour or tumour bed
and surrounding margin; moreover, some healthy brain tissue is subject to incidental irradiation. * Diffusion tensor imaging Models the motion of water as an ellipse, with derived metrics
allowing the study of white matter integrity. * Delayed Match-to-Sample A test used to assess non-verbal elements of short-term memory in humans and primates: the participant must recall
whether a stimulus matches a previously presented 'sample' stimulus. * Homer1a Homer1a is a protein expressed by neurons that selectively inhibits the binding of family 1
metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR) to the synapse. * Diffusion-weighted imaging Measures and models the diffusion of water at the cellular level. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and
permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Makale, M., McDonald, C., Hattangadi-Gluth, J. _et al._ Mechanisms of radiotherapy-associated cognitive disability in patients with brain
tumours. _Nat Rev Neurol_ 13, 52–64 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2016.185 Download citation * Published: 16 December 2016 * Issue Date: January 2017 * DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2016.185 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not
currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Trending News
Exchange on democracy in america | thearticleFirst {{register.errors.names}} Last Gender What's this for? Age bracket What's this for? This is to help us s...
Iran says enemies used lizards to spyIran's Western enemies used lizards that "attract atomic waves" to spy on the country's nuclear prog...
Fifa suspends 2026 world cup bidding amid scandalBidding for the 2026 FIFA soccer World Cup has been suspended as corruption allegations engulf the organization. The dec...
One-pot wonders: the best warm and comfort food for winterRun the frozen spinach under cold water in a colander to thaw and get rid of the excess ice. Squeeze as much water as yo...
'jupiter's legacy' decodes the superhero genre without subverting itYou'd be forgiven for wondering how Netflix's _Jupiter's Legacy_ compares to other recent entries in the ...
Latests News
Mechanisms of radiotherapy-associated cognitive disability in patients with brain tumoursKEY POINTS * Intracranial radiotherapy leads to permanent and substantial cognitive disability in 50–90% of patients * T...
Eastenders spoilers: linda carter loses custody of ollie?Executive producer Jon Sen told Digital Spy: ”This autumn the Carters will face one of their biggest crises to date when...
Boy, 16, arrested after 'dangerous driving' leaves 3 injuredA boy aged 16 has been arrested after three people were hurt in a crash on a Leicestershire road yesterday (Saturday, Ma...
Mortgage rates: how to get best mortgage rates & avoid paying too muchMortgages can make the expenditure you face on a property more manageable. Although, that’s not to say that everyone wil...
How to live longer - best exercise to add years onto your lifespanThe key to living longer could be to eat a healthy, balanced diet - including at least five portions of fruit and vegeta...