Regulation of immunity and inflammation by hypoxia in immunological niches
Regulation of immunity and inflammation by hypoxia in immunological niches"
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
KEY POINTS * Hypoxia and inflammation are frequently co-incidental microenvironmental features of sites of concentrated physiological or pathological immune activity. * Hypoxia activates
hypoxia-inducible factor, which is a major regulator of multiple aspects of immune cell function. Consequently, hypoxia plays a key role in the regulation of immunity and inflammation. * The
impact of hypoxia on immunity and inflammation is site-specific and cell type-specific. * Pharmacological hydroxylase inhibition, which activates hypoxia-sensitive pathways, is profoundly
protective in multiple models of inflammation. ABSTRACT Immunological niches are focal sites of immune activity that can have varying microenvironmental features. Hypoxia is a feature of
physiological and pathological immunological niches. The impact of hypoxia on immunity and inflammation can vary depending on the microenvironment and immune processes occurring in a given
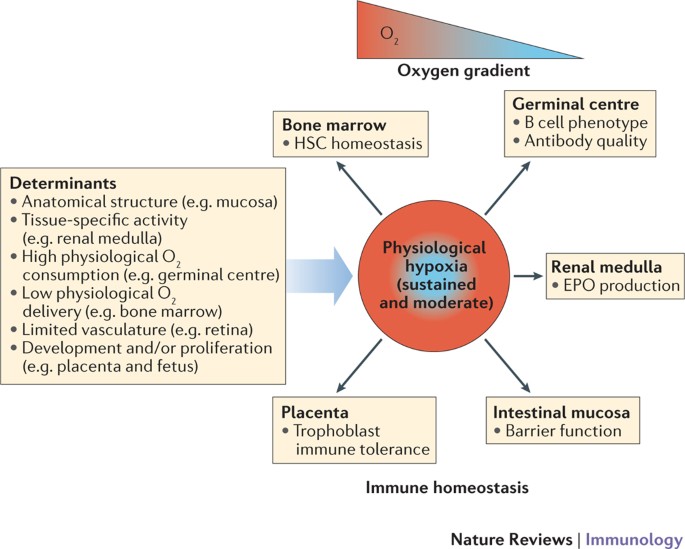
niche. In physiological immunological niches, such as the bone marrow, lymphoid tissue, placenta and intestinal mucosa, physiological hypoxia controls innate and adaptive immunity by
modulating immune cell proliferation, development and effector function, largely via transcriptional changes driven by hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF). By contrast, in pathological
immunological niches, such as tumours and chronically inflamed, infected or ischaemic tissues, pathological hypoxia can drive tissue dysfunction and disease development through immune cell
dysregulation. Here, we differentiate between the effects of physiological and pathological hypoxia on immune cells and the consequences for immunity and inflammation in different
immunological niches. Furthermore, we discuss the possibility of targeting hypoxia-sensitive pathways in immune cells for the treatment of inflammatory disease. Access through your
institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio
journals Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription $29.99 / 30 days cancel any time Learn more Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print issues and online access $209.00 per
year only $17.42 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated
during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS HOW
OXYGENATION SHAPES IMMUNE RESPONSES: EMERGING ROLES FOR PHYSIOXIA AND PATHOLOGICAL HYPOXIA Article 30 September 2024 THE EFFECT OF HIF ON METABOLISM AND IMMUNITY Article 20 June 2022 HYPOXIA
SIGNALING IN HUMAN HEALTH AND DISEASES: IMPLICATIONS AND PROSPECTS FOR THERAPEUTICS Article Open access 07 July 2022 REFERENCES * Beerman, I., Luis, T. C., Singbrant, S., Lo Celso, C. &
Méndez-Ferrer, S. The evolving view of the hematopoietic stem cell niche. _Exp. Hematol._ 50, 22–26 (2017). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Shah, D. K. &
Zúñiga-Pflücker, J. C. An overview of the intrathymic intricacies of T cell development. _J. Immunol._ 192, 4017–4023 (2014). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Campbell, E. L., Kao, D.
J. & Colgan, S. P. Neutrophils and the inflammatory tissue microenvironment in the mucosa. _Immunol. Rev._ 273, 112–120 (2016). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar *
Lin, E. W., Karakasheva, T. A., Hicks, P. D., Bass, A. J. & Rustgi, A. K. The tumor microenvironment in esophageal cancer. _Oncogene_ 35, 5337–5349 (2016). Article CAS PubMed PubMed
Central Google Scholar * Maru, Y. The lung metastatic niche. _J. Mol. Med. (Berl.)_ 93, 1185–1192 (2015). Article CAS Google Scholar * Biswas, S. et al. Microenvironmental control of
stem cell fate in intestinal homeostasis and disease. _J. Pathol._ 237, 135–145 (2015). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Hallenbeck, J. M., Hansson, G. K. & Becker, K.
J. Immunology of ischemic vascular disease: plaque to attack. _Trends Immunol._ 26, 550–556 (2005). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Gobert, A. P. & Wilson, K. T. The immune
battle against _Helicobacter pylori_ infection: NO offense. _Trends Microbiol._ 24, 366–376 (2016). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Quante, M. & Wang, T. C.
Inflammation and stem cells in gastrointestinal carcinogenesis. _Physiology (Bethesda)_ 23, 350–359 (2008). CAS Google Scholar * Multhoff, G., Molls, M. & Radons, J. Chronic
inflammation in cancer development. _Front. Immunol._ 2, 98 (2012). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Taylor, C. T., Doherty. G., Fallon, P. G. & Cummins, E. P.
Hypoxia-dependent regulation of inflammatory pathways in immune cells. _J. Clin. Invest._ 126, 3716–3724 (2016). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Cummins, E. P., Keogh, C.
E., Crean, D. & Taylor, C. T. The role of HIF in immunity and inflammation. _Mol. Aspects Med._ 47–48, 24–34 (2016). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Scholz, C. C. & Taylor,
C. T. Targeting the HIF pathway in inflammation and immunity. _Curr. Opin. Pharmacol._ 13, 646–653 (2013). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Taylor, C. T. & McElwain, J. C. Ancient
atmospheres and the evolution of oxygen sensing via the hypoxia-inducible factor in metazoans. _Physiology (Bethesda)_ 25, 272–279 (2010). CAS Google Scholar * Colgan, S. P. & Taylor,
C. T. Hypoxia: an alarm signal during intestinal inflammation. _Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol._ 7, 281–287 (2010). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Zheng, L., Kelly, C.
J. & Colgan, S. P. Physiologic hypoxia and oxygen homeostasis in the healthy intestine. A review in the theme: cellular responses to hypoxia. _Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol._ 309,
C350–C360 (2015). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Semenza, G. L. The hypoxic tumor microenvironment: a driving force for breast cancer progression. _Biochim. Biophys.
Acta_ 1863, 382–391 (2016). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Semenza, G. L. Molecular mechanisms mediating metastasis of hypoxic breast cancer cells. _Trends Mol. Med._ 18, 534–543
(2012). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Colgan, S. P., Campbell, E. L. & Kominsky, D. J. Hypoxia and mucosal inflammation. _Annu. Rev. Pathol._ 11, 77–100 (2016).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Eltzschig, H. K. & Carmeliet, P. Hypoxia and inflammation. _N. Engl. J. Med._ 364, 656–665 (2011). Article CAS PubMed PubMed
Central Google Scholar * Loenarz, C. et al. The hypoxia-inducible transcription factor pathway regulates oxygen sensing in the simplest animal, Trichoplax adhaerens. _EMBO Rep._ 12, 63–70
(2011). THIS PAPER IDENTIFIES THE HIGHLY EVOLUTIONARILY CONSERVED NATURE OF THE OXYGEN-SENSING HYDROXYLASE–HIF-DEPENDENT PATHWAY IN ALL METAZOANS. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar *
Cummins, E. P. & Taylor, C. T. Hypoxia-responsive transcription factors. _Pflugers Arch._ 450, 363–371 (2005). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Semenza, G. L. Hypoxia-inducible
factors in physiology and medicine. _Cell_ 148, 399–408 (2012). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Ratcliffe, P. J. Oxygen sensing and hypoxia signalling pathways in
animals: the implications of physiology for cancer. _J. Physiol._ 591, 2027–2042 (2013). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Bunn, H. F. & Poyton, R. O. Oxygen
sensing and molecular adaptation to hypoxia. _Physiol. Rev._ 76, 839–885 (1996). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Taylor, C. T. & Moncada, S. Nitric oxide, cytochrome C oxidase,
and the cellular response to hypoxia. _Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol._ 30, 643–647 (2010). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kaelin, W. G. Jr. The von Hippel-Lindau tumour
suppressor protein: O2 sensing and cancer. _Nat. Rev. Cancer_ 8, 865–873 (2008). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kaelin, W. G. Jr & Ratcliffe, P. J. Oxygen sensing by metazoans:
the central role of the HIF hydroxylase pathway. _Mol. Cell_ 30, 393–402 (2008). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Selfridge, A. C. et al. Hypercapnia suppresses the HIF-dependent
adaptive response to hypoxia. _J. Biol. Chem._ 291, 11800–11808 (2016). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Hubbi, M. E. & Semenza, G. L. An essential role for
chaperone-mediated autophagy in cell cycle progression. _Autophagy_ 11, 850–851 (2015). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Hubbi, M. E., Gilkes, D. M., Hu, H., Kshitiz,
Ahmed, I. & Semenza, G. L. Cyclin-dependent kinases regulate lysosomal degradation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α to promote cell-cycle progression. _Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA_ 111,
E3325–E3334 (2014). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Intlekofer, A. M. et al. L-2-Hydroxyglutarate production arises from noncanonical enzyme function at acidic pH.
_Nat. Chem. Biol._ 13, 494–500 (2017). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Tyrakis, P. A. et al. S-2-hydroxyglutarate regulates CD8+ T-lymphocyte fate. _Nature_ 540,
236–241 (2016). THIS STUDY DEMONSTRATES THAT THE HIF PATHWAY PLAYS A KEY ROLE IN REGULATING ANTITUMOUR ACTIVITY IN CYTOTOXIC T LYMPHOCYTES. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google
Scholar * Koivunen, P. et al. Transformation by the (R)-enantiomer of 2-hydroxyglutarate linked to EGLN activation. _Nature_ 483, 484–488 (2012). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central
Google Scholar * Tannahill, G. M. et al. Succinate is an inflammatory signal that induces IL-1β through HIF-1α. _Nature_ 496, 238–242 (2013). THIS STUDY DEMONSTRATES THAT SUCCINATE IS AN
IMMUNOMETABOLITE THAT REGULATES INNATE IMMUNITY THROUGH THE HIF PATHWAY. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Chandel, N. S. Mitochondrial regulation of oxygen sensing.
_Adv. Exp. Med. Biol._ 661, 339–354 (2010). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Schödel, J., Mole, D. R. & Ratcliffe, P. J. Pan-genomic binding of hypoxia-inducible transcription
factors. _Biol. Chem._ 394, 507–517 (2013). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Mole, D. R. et al. Genome-wide association of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha and HIF-2alpha DNA
binding with expression profiling of hypoxia-inducible transcripts. _J. Biol. Chem._ 284, 16767–16775 (2009). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Duan, C.
Hypoxia-inducible factor 3 biology: complexities and emerging themes. _Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol._ 310, C260–269 (2016). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Palazon, A., Goldrath, A. W.,
Nizet, V. & Johnson, R. S. HIF transcription factors, inflammation, and immunity. _Immunity_ 41, 518–528 (2014). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Lenihan, C. R.
& Taylor, C. T. The impact of hypoxia on cell death pathways. _Biochem. Soc. Trans._ 41, 657–663 (2013). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Haase, V. H. Regulation of erythropoiesis
by hypoxia-inducible factors. _Blood Rev._ 27, 41–53 (2013). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Cummins, E. P. & Crean, D. Hypoxia and inflammatory bowel disease.
_Microbes Infect._ 19, 210–221 (2017). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Glover, L. E. Lee, J. S. & Colgan, S. P. Oxygen metabolism and barrier regulation in the intestinal mucosa.
_J. Clin. Invest._ 126, 3680–3688 (2016). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Ramakrishnan, S. K. & Shah, Y. M. Role of intestinal HIF-2α in health and disease. _Annu.
Rev. Physiol._ 78, 301–325 (2016). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Ivan, M. & Kaelin, W. G. Jr. The EGLN-HIF O2-sensing system: multiple inputs and feedbacks. _Mol. Cell_ 66,
772–779 (2017). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Harris, A. J., Thompson, A. R., Whyte, M. K. & Walmsley, S. R. HIF-mediated innate immune responses: cell
signaling and therapeutic implications. _Hypoxia (Auckl.)_ 2, 47–58 (2014). Google Scholar * Lin, N. & Simon, M. C. Hypoxia-inducible factors: key regulators of myeloid cells during
inflammation. _J. Clin. Invest._ 126, 3661–3671 (2016). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Mills, E. & O'Neill, L. A. Succinate: a metabolic signal in inflammation.
_Trends Cell Biol._ 24, 313–320 (2014). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Hammami, A., Charpentier, T., Smans, M. & Stäger, S. IRF-5-mediated inflammation limits CD8+ T Cell
expansion by inducing HIF-1α and impairing dendritic cell functions during Leishmania infection. _PLoS Pathog._ 11, e1004938 (2015). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar *
Wobben, R. et al. Role of hypoxia inducible factor-1α for interferon synthesis in mouse dendritic cells. _Biol. Chem._ 394, 495–505 (2013). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Cho, S. H.
et al. Germinal centre hypoxia and regulation of antibody qualities by a hypoxia response system. _Nature_ 537, 234–238 (2016). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Ward,
J. B. et al. Hydroxylase inhibition attenuates colonic epithelial secretory function and ameliorates experimental diarrhea. _FASEB J._ 25, 535–543 (2011). Article CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Kelly, C. J. et al. Fundamental role for HIF-1α in constitutive expression of human β defensin-1. _Mucosal Immunol._ 6, 1110–1118 (2013). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central
Google Scholar * Du, J. et al. pVHL negatively regulates antiviral signaling by targeting MAVS for proteasomal degradation. _J. Immunol._ 195, 1782–1790 (2015). Article CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Stehle, F. et al. VHL-dependent alterations in the secretome of renal cell carcinoma: association with immune cell response? _Oncotarget_ 6, 43420–43437 (2015). Article PubMed
PubMed Central Google Scholar * Scholz, C. C. & Taylor, C. T. Hydroxylase-dependent regulation of the NF-κB pathway. _Biol. Chem._ 394, 479–493 (2013). Article CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Corcoran, S. E. & O'Neill, L. A. HIF1α and metabolic reprogramming in inflammation. _J. Clin. Invest._ 126, 3699–3707 (2016). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google
Scholar * Mills, E. L. et al. Succinate dehydrogenase supports metabolic repurposing of mitochondria to drive inflammatory macrophages. _Cell_ 167, 457–470 (2016). Article CAS PubMed
PubMed Central Google Scholar * O'Neill, L. A., Kishton, R. J. & Rathmell, J. A guide to immunometabolism for immunologists. _Nat. Rev. Immunol._ 16553–16565 (2016). * Semenza, G.
L., Roth, P. H., Fang, H. M. & Wang, G. L. Transcriptional regulation of genes encoding glycolytic enzymes by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. _J. Biol. Chem._ 269, 23757–23763 (1994). THIS
STUDY IDENTIFIES THE CONTROL OF GLYCOLYTIC METABOLISM BY THE HIF PATHWAY. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Halligan, D. N., Murphy, S. J. & Taylor, C. T. The hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)
couples immunity with metabolism. _Semin. Immunol._ 28, 469–477 (2016). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Michiels, C., Tellier, C. & Feron, O. Cycling hypoxia: a key feature of
the tumor microenvironment. _Biochim. Biophys. Acta_ 1866, 76–86 (2016). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Toffoli, S. & Michiels, C. Intermittent hypoxia is a key regulator of cancer cell
and endothelial cell interplay in tumours. _FEBS J._ 275, 2991–3002 (2008). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Ryan, S., Taylor, C. T. & McNicholas, W. T. Selective activation of
inflammatory pathways by intermittent hypoxia in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. _Circulation_ 112, 2660–2667 (2005). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Taylor, C. T., Kent, B. D.,
Crinion, S. J., McNicholas, W. T. & Ryan, S. Human adipocytes are highly sensitive to intermittent hypoxia induced NF-kappaB activity and subsequent inflammatory gene expression.
_Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun._ 447, 660–665 (2014). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * D'Ignazio, L., Bandarra, D. & Rocha, S. NF-κB and HIF crosstalk in immune responses.
_FEBS J._ 283, 413–424 (2016). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Taylor, C. T. Interdependent roles for hypoxia inducible factor and nuclear factor-kappaB in hypoxic inflammation. _J.
Physiol._ 586, 4055–4059 (2008). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Zhong, Z., Sanchez-Lopez, E. & Karin, M. Autophagy, inflammation, and immunity: a troika
governing cancer and its treatment. _Cell_ 166, 288–298 (2016). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Shalapour, S. & Karin, M. Immunity, inflammation, and cancer: an
eternal fight between good and evil. _J. Clin. Invest._ 125, 3347–3355 (2015). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Frede, S., Stockmann, C., Freitag, P. & Fandrey, J.
Bacterial lipopolysaccharide induces HIF-1 activation in human monocytes via p44/42 MAPK and NF-kappaB. _Biochem. J._ 396, 517–527 (2006). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google
Scholar * Pérez, S., Taléns-Visconti, R., Rius-Pérez, S., Finamor, I. & Sastre, J. Redox signaling in the gastrointestinal tract. _Free Radic. Biol. Med._ 104, 75–103 (2017). Article
CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Chandel, N. S. et al. Reactive oxygen species generated at mitochondrial complex III stabilize hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha during hypoxia: a mechanism of
O2 sensing. _J. Biol. Chem._ 275, 25130–25138 (2000). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Masson, N. et al. The FIH hydroxylase is a cellular peroxide sensor that modulates HIF
transcriptional activity. _EMBO Rep._ 13, 251–257 (2012). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Hagen, T., Taylor, C. T., Lam, F. & Moncada, S. Redistribution of
intracellular oxygen in hypoxia by nitric oxide: effect on HIF1alpha. _Science_ 302, 1975–1978 (2003). THIS STUDY DEMONSTRATES THAT NITRIC OXIDE, A KEY MEDIATOR OF INFLAMMATION, CAN REGULATE
HIF STABILITY THROUGH THE CONTROL OF INTRACELLULAR OXYGEN AVAILABILITY. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Lohninger, L. et al. Hydrogen sulphide induces HIF-1α and Nrf2 in THP-1
macrophages. _Biochimie_ 112, 187–195 (2015). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Flannigan, K. L. et al. Proresolution effects of hydrogen sulfide during colitis are mediated through
hypoxia-inducible factor-1α. _FASEB J._ 29, 1591–1602 (2015). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Wu, B., Teng, H., Yang, G., Wu, L. & Wang, R. Hydrogen sulfide inhibits the
translational expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α. _Br. J. Pharmacol._ 167, 1492–1505 (2012). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Eliasson, P. & Jönsson, J. I.
The hematopoietic stem cell niche: low in oxygen but a nice place to be. _J. Cell. Physiol._ 222, 17–22 (2010). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Parmar, K., Mauch, P., Vergilio, J.
A., Sackstein, R. & Down, J. D. Distribution of hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow according to regional hypoxia. _Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA_ 104, 5431–5436 (2007). Article CAS
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Mortensen, B. T. et al. Changing bone marrow micro-environment during development of acute myeloid leukaemia in rats. _Br. J. Haematol._ 102,
458–464 (1998). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Morikawa, T. & Takubo, K. Hypoxia regulates the hematopoietic stem cell niche. _Pflugers Arch._ 468, 13–22 (2015). Article CAS
PubMed Google Scholar * Forristal, C. E. et al. Pharmacologic stabilization of HIF-1α increases hematopoietic stem cell quiescence _in vivo_ and accelerates blood recovery after severe
irradiation. _Blood_ 121, 759–769 (2013). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Takubo, K. et al. Regulation of the HIF-1alpha level is essential for hematopoietic stem cells. _Cell Stem
Cell._ 7, 391–402 (2010). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Forristal, C. E. & Levesque, J. P. Targeting the hypoxia-sensing pathway in clinical hematology. _Stem Cells Transl
Med._ 3, 135–140 (2014). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Gezer, D., Vukovic, M., Soga, T., Pollard, P. J. & Kranc, K. R. Concise review: genetic dissection of hypoxia signaling
pathways in normal and leukemic stem cells. _Stem Cells_ 32, 1390–1397 (2014). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Annese, V., Navarro-Guerrero, E., Rodríguez-Prieto, I. & Pardal, R.
Physiological plasticity of neural-crest-derived stem cells in the adult mammalian carotid body. _Cell Rep._ 19, 471–478 (2017). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar *
Mazumdar, J. et al. O2 regulates stem cells through Wnt/β-catenin signalling. _Nat. Cell Biol._ 12, 1007–1013 (2010). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Simsek, T. et
al. The distinct metabolic profile of hematopoietic stem cells reflects their location in a hypoxic niche. _Cell Stem Cell._ 7, 380–390 (2010). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google
Scholar * Krock, B. L. et al. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator is an essential regulator of murine hematopoietic stem cell viability. _Blood_ 125, 3263–3272 (2015).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Guitart, A. V. et al. Hif-2α is not essential for cell-autonomous hematopoietic stem cell maintenance. _Blood_ 122, 1741–1745 (2013).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Abbott, R. K. et al. Germinal center hypoxia potentiates immunoglobulin class switch recombination. _J. Immunol._ 197, 4014–4020 (2016). REFERENCES 52
AND 92 DEMONSTRATE THAT PHYSIOLOGICAL HYPOXIA IN GCS PLAYS A KEY ROLE IN B CELL DEVELOPMENT. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kumpel, B. M. & Manoussaka, M. S. Placental
immunology and maternal alloimmune responses. _Vox Sang._ 102, 2–12 (2012). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Fryer, B. H. & Simon, M. C. Hypoxia, HIF and the placenta. _Cell
Cycle_ 5, 495–498 (2006). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Macklin, P. S., McAuliffe, J., Pugh, C. W. & Yamamoto, A. Hypoxia and HIF pathway in cancer and the placenta. _Placenta_
56, 8–13 (2017). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Yaghi, L. et al. Hypoxia inducible factor-1 mediates the expression of the immune checkpoint HLA-G in glioma cells through hypoxia
response element located in exon 2. _Oncotarget_ 7, 63690–63707 (2016). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Barsoum, I. B., Smallwood, C. A., Siemens, D. R. & Graham, C.
H. A mechanism of hypoxia-mediated escape from adaptive immunity in cancer cells. _Cancer Res._ 74, 665–674 (2014). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Webster, W. S. & Abela, D. The
effect of hypoxia in development. _Birth Defects Res. C Embryo Today_ 81, 215–228 (2007). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Filiano, A. J., Gadani, S. P. & Kipnis, J. Interactions
of innate and adaptive immunity in brain development and function. _Brain Res._ 1617, 18–27 (2015). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Dowling, D. J. & Levy, O. Ontogeny of early
life immunity. _Trends Immunol._ 35, 299–310 (2014). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Shepherd, A. P. Metabolic control of intestinal oxygenation and blood flow. _Fed.
Proc._ 41, 2084–2089 (1982). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Karhausen, J. et al. Epithelial hypoxia-inducible factor-1 is protective in murine experimental colitis. _J. Clin. Invest._ 114,
1098–1106 (2004). THIS STUDY IDENTIFIES A PROTECTIVE ROLE FOR THE HIF PATHWAY IN INTESTINAL INFLAMMATION. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Evans, S. M. et al.
Detection of hypoxia in human squamous cell carcinoma by EF5 binding. _Cancer Res._ 60, 2018–2024 (2000). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Albenberg, L. et al. Correlation between intraluminal
oxygen gradient and radial partitioning of intestinal microbiota. _Gastroenterology_ 147, 1055–1063 (2014). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Goda, F. et al. _In vivo_ oximetry using EPR
and India ink. _Magn. Reson. Med._ 33, 237–245 (1995). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * He, G. et al. Noninvasive measurement of anatomic structure and intraluminal oxygenation in the
gastrointestinal tract of living mice with spatial and spectral EPR imaging. _Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA_ 96, 4586–4591 (1999). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar *
Labiano, S., Palazon, A. & Melero, I. Immune response regulation in the tumor microenvironment by hypoxia. _Semin. Oncol._ 42, 378–386 (2015). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar *
Unwith, S., Zhao, H., Hennah, L. & Ma, D. The potential role of HIF on tumour progression and dissemination. _Int. J. Cancer._ 136, 2491–2503 (2015). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
* Courtnay, R. et al. Cancer metabolism and the Warburg effect: the role of HIF-1 and PI3K. _Mol. Biol. Rep._ 42, 841–851 (2015). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Miller, J. F.
& Sadelain, M. The journey from discoveries in fundamental immunology to cancer immunotherapy. _Cancer Cell_ 27, 439–449 (2015). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Maus, M. V. et
al. Adoptive immunotherapy for cancer or viruses. _Annu. Rev. Immunol._ 32, 189–225 (2014). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Corzo, C. A. et al. HIF-1α regulates
function and differentiation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in the tumor microenvironment. _J. Exp. Med._ 207, 2439–2453 (2010). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar *
Williams, A. E. & Chambers, R. C. The mercurial nature of neutrophils: still an enigma in ARDS? _Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol._ 306, L217–L230 (2014). Article CAS PubMed
Google Scholar * Liu, Z. et al. AMP-activated protein kinase and Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3β modulate the severity of sepsis-induced lung injury. _Mol. Med._ 21, 937–950 (2015). Article
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Campbell, E. L. et al. Transmigrating neutrophils shape the mucosal microenvironment through localized oxygen depletion to influence resolution
of inflammation. _Immunity_ 40, 66–77 (2014). THIS STUDY IDENTIFIES THAT THE NEUTROPHIL OXIDATIVE BURST IS A KEY CAUSE OF MUCOSAL HYPOXIA IN INFLAMMATORY DISEASE OF THE INTESTINE. Article
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Huang, J. S. et al. Chronic granulomatous disease caused by a deficiency in p47(phox) mimicking Crohn's disease. _Clin. Gastroenterol.
Hepatol._ 2, 690–695 (2004). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Manresa, M. C., Godson, C. & Taylor, C. T. Hypoxia-sensitive pathways in inflammation-driven fibrosis. _Am. J.
Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol._ 307, R1369–R1380 (2014). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Devraj, G., Beerlage, C., Brüne, B. & Kempf, V. A. Hypoxia and HIF-1 activation
in bacterial infections. _Microbes Infect._ 19, 144–156 (2017). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Werth, N. et al. Activation of hypoxia inducible factor 1 is a general phenomenon in
infections with human pathogens. _PLoS ONE._ 5, e11576 (2010). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Schaffer, K. & Taylor, C. T. The impact of hypoxia on bacterial
infection. _FEBS J._ 282, 2260–2266 (2015). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Worlitzsch, D. et al. Effects of reduced mucus oxygen concentration in airway Pseudomonas infections of
cystic fibrosis patients. _J. Clin. Invest._ 109, 317–325 (2002). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Schaible, B., Schaffer, K. & Taylor, C. T. Hypoxia, innate
immunity and infection in the lung. _Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol._ 174, 235–243 (2010). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Schaible, B. et al. Hypoxia modulates infection of epithelial
cells by _Pseudomonas aeruginosa_. _PLoS ONE._ 8, e56491 (2013). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Schaible, B., Taylor, C. T. & Schaffer, K. Hypoxia increases
antibiotic resistance in _Pseudomonas aeruginosa_ through altering the composition of multidrug efflux pumps. _Antimicrob. Agents Chemother._ 56, 2114–2118 (2012). Article CAS PubMed
PubMed Central Google Scholar * Schaible, B. et al. Hypoxia reduces the pathogenicity of _Pseudomonas aeruginosa_ by decreasing the expression of multiple virulence factors. _J. Infect.
Dis._ 215, 1459–1467 (2017). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Koh, H. S. et al. The HIF-1/glial TIM-3 axis controls inflammation-associated brain damage under hypoxia. _Nat. Commun._
6, 6340 (2015). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Zhang, J. et al. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-2α limits natural killer T cell cytotoxicity in renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. _J. Am.
Soc. Nephrol._ 27, 92–106 (2016). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Luo, L. et al. The role of HIF-1 in up-regulating MICA expression on human renal proximal tubular epithelial cells
during hypoxia/reoxygenation. _BMC Cell Biol._ 11, 91 (2010). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Chan, M. C., Holt-Martyn, J. P., Schofield, C. J. & Ratcliffe, P. J.
Pharmacological targeting of the HIF hydroxylases—a new field in medicine 1development. _Mol. Aspects Med._ 47–48, 54–75 (2016). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Muchnik, E. &
Kaplan, J. HIF prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors for anemia. _Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs_ 20, 645–656 (2011). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Maxwell, P. H. & Eckardt, K. U. HIF
prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors for the treatment of renal anaemia and beyond. _Nat. Rev. Nephrol._ 12, 157–168 (2016). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Cho, H. et al. On-target
efficacy of a HIF-2α antagonist in preclinical kidney cancer models. _Nature._ 539, 107–111 (2016). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Chen, W. et al. Targeting renal
cell carcinoma with a HIF-2 antagonist. _Nature_ 539, 112–117 (2016). REFERENCES 132 AND 133 DEMONSTRATE THAT SELECTIVE TARGETING OF THE HIF2 PATHWAY MAY BE OF CLINICAL BENEFIT IN KIDNEY
CANCER. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Cummins, E. P., Doherty, G. A. & Taylor, C. T. Hydroxylases as therapeutic targets in inflammatory bowel disease. _Lab.
Invest._ 93, 378–383 (2013). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Hams, E. et al. The hydroxylase inhibitor dimethyloxallyl glycine attenuates endotoxic shock via alternative activation
of macrophages and IL-10 production by B1 cells. _Shock_ 36, 295–302 (2011). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Provenzano, R. et al. Oral hypoxia-inducible factor
prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor roxadustat (FG-4592) for the treatment of anemia in patients with CKD. _Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol._ 11, 982–991 (2016). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central
Google Scholar * Brigandi, R. A. et al. A novel hypoxia-inducible factor-prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor (GSK1278863) for anemia in CKD: 28 day, phase 2A randomized trial. _Am. J. Kidney Dis._
67, 861–871 (2016). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Pergola, P. E., Spinowitz, B. S., Hartman, C. S., Maroni, B. J. & Haase, V. H. Vadadustat, a novel oral HIF stabilizer,
provides effective anemia treatment in nondialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease. _Kidney Int._ 90, 1115–1122 (2016). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Tambuwala, M. M. et al.
Targeted delivery of the hydroxylase inhibitor DMOG provides enhanced efficacy with reduced systemic exposure in a murine model of colitis. _J. Control. Release_ 217, 221–227 (2015). Article
CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Maxwell, P. H. et al. Sites of erythropoietin production. _Kidney Int._ 51, 393–401 (1997). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Spencer, J. A. et al.
Direct measurement of local oxygen concentration in the bone marrow of live animals. _Nature_ 508, 269–273 (2014). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Grimm, C. &
Willmann, G. Hypoxia in the eye: a two-sided coin. _High Alt. Med. Biol._ 13169–13175 (2012). * Cummins, E. P. et al. Prolyl hydroxylase-1 negatively regulates IkappaB kinase-beta, giving
insight into hypoxia-induced NFkappaB activity. _Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA_ 103, 18154–18159 (2006). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Cockman, M. E. et al.
Posttranslational hydroxylation of ankyrin repeats in IkappaB proteins by the hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) asparaginyl hydroxylase, factor inhibiting HIF (FIH). _Proc. Natl Acad. Sci.
USA_; 103, 14767–1 4772. REFERENCES 143 AND 144 DEMONSTRATE THAT COMPONENTS OF THE NF-ΚB PATHWAY ARE TARGETS FOR HYDROXYLATION. Article CAS Google Scholar * Ghosh, S., Paul, A. & Sen,
E. Tumor necrosis factor α-induced hypoxia-inducible factor 1α-β-catenin axis regulates major histocompatibility complex class I gene activation through chromatin remodeling. _Mol. Cell.
Biol._ 33, 2718–2731 (2013). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Dang, E. V. et al. Control of T(H)17/T(reg) balance by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. _Cell_ 146, 772–784
(2011). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Clambey, E. T. et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha-dependent induction of FoxP3 drives regulatory T-cell abundance and
function during inflammatory hypoxia of the mucosa. _Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA_ 109, E2784–E2793 (2012). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Cummins, E. P. et al. The
hydroxylase inhibitor dimethyloxalylglycine is protective in a murine model of colitis. _Gastroenterology_ 134, 156–165 (2008). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Hindryckx, P. et al.
Longitudinal quantification of inflammation in the murine dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis model using muPET/CT. _Inflamm. Bowel Dis._ 17, 2058–2064 (2011). Article CAS PubMed
Google Scholar * Cosin-Roger, J. et al. Hypoxia ameliorates intestinal inflammation through NLRP3/mTOR downregulation and autophagy activation. _Nat. Commun._ 8, 98 (2017). Article CAS
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Robinson, A. et al. Mucosal protection by hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibition. _Gastroenterology_ 134, 145–155 (2008). REFERENCES
148 AND 151 DEMONSTRATE THAT PHARMACOLOGICAL HYDROXYLASE INHIBITION IS PROTECTIVE IN COLITIS. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Hindryckx, P. et al. Hydroxylase inhibition abrogates
TNF-alpha-induced intestinal epithelial damage by hypoxia-inducible factor-1-dependent repression of FADD. _J. Immunol._ 185, 6306–6316 (2010). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar *
Hirota, S. A. et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor signaling provides protection in _Clostridium difficile_-induced intestinal injury. _Gastroenterology_ 139, 259–269 (2010). Article CAS PubMed
Google Scholar * Hart, M. L. et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha dependent protection from intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury involves ecto-5′-nucleotidase (CD73) and the A2B
adenosine receptor. _J. Immunol._ 186, 4367–4374 (2011). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Marchbank, T., Mahmood, A., Harten, S., Maxwell, P. H. & Playford, R. J.
Dimethyloxalyglycine stimulates the early stages of gastrointestinal repair processes through VEGF-dependent mechanisms. _Lab. Invest._ 91, 1684–1694 (2011). Article CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Keely, S. et al. Contribution of epithelial innate immunity to systemic protection afforded by prolyl hydroxylase inhibition in murine colitis. _Mucosal Immunol._ 7, 114–123
(2014). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Marks, E. et al. Oral delivery of prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor: AKB-4924 promotes localized mucosal healing in a mouse model of colitis.
_Inflamm. Bowel Dis._ 21, 267–275 (2015). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Taniguchi, C. M. et al. PHD inhibition mitigates and protects against radiation-induced gastrointestinal toxicity
via HIF2. _Sci. Transl Med._ 6, 236ra64 (2014). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Jeong, S. et al. Lipophilic modification enhances anti-colitic properties of
rosmarinic acid by potentiating its HIF-prolyl hydroxylases inhibitory activity. _Eur. J. Pharmacol._ 747, 114–122 (2015). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Gupta, R. et al.
Therapeutic treatment with a novel hypoxia-inducible factor hydroxylase inhibitor (TRC160334) ameliorates murine colitis. _Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol._ 7, 13–23 (2014). Article CAS PubMed
PubMed Central Google Scholar * Jamadarkhana, P. et al. Treatment with a novel hypoxia-inducible factor hydroxylase inhibitor (TRC160334) ameliorates ischemic acute kidney injury. _Am. J.
Nephrol._ 36, 208–218 (2012). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Bernhardt, W. M. et al. Donor treatment with a PHD-inhibitor activating HIFs prevents graft injury and prolongs survival
in an allogenic kidney transplant model. _Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA_ 106, 21276–21281 (2009). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Manresa, M. C. et al. Hydroxylase
inhibition regulates inflammation-induced intestinal fibrosis through the suppression of ERK-mediated TGF-β1 signaling [corrected]. _Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol._ 311,
G1076–G1090 (2016). Article PubMed Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Work from the authors' laboratories is funded through research grants from Science Foundation
Ireland, the European Union and the US National Institutes of Health. AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * UCD Conway Institute, Systems Biology Ireland and the School of Medicine,
University College Dublin, Belfield, 4, Dublin, Ireland Cormac T. Taylor * Department of Medicine and the Mucosal Inflammation Program, University of Colorado School of Medicine, Aurora,
80045, Colorado, USA Sean P. Colgan Authors * Cormac T. Taylor View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Sean P. Colgan View author publications
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CONTRIBUTIONS C.T.T. and S.P.C. both contributed to discussions of the content and the writing, review and editing of this
manuscript CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to Cormac T. Taylor. ETHICS DECLARATIONS COMPETING INTERESTS C.T.T. and S.P.C. are members of the Scientific Advisory Board of Akebia
Therapeutics. POWERPOINT SLIDES POWERPOINT SLIDE FOR FIG. 1 POWERPOINT SLIDE FOR FIG. 2 POWERPOINT SLIDE FOR FIG. 3 POWERPOINT SLIDE FOR TABLE 1 GLOSSARY * Microenvironmental features
Physiochemical conditions found within a specific niche or tissue. * Hypoxia The condition that arises when cellular oxygen demand exceeds supply. * Electron transport chain (ETC). Primary
eukaryotic system for the reduction of molecular oxygen and the generation of ATP. Located within mitochondria. * Oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS). The generation of cellular ATP using
energy derived from electron transport during aerobic respiration. * Lysosomal degradation pathway A mechanism of intracellular protein degradation that involves proteolysis in lysosomal
compartments. * Glycolysis The utilization of glucose to generate ATP. * Physiological angiogenesis The normal growth of blood vessels in healthy tissues. * Carotid body Small organelle
situated at the bifurcation of the carotid artery responsible for sensing blood oxygen levels and regulating the respiratory rate. * Semi-allogeneic trophoblasts Fetal cells that express
both maternal and paternal surface antigens. * Crypt–villus axis Structure at the mucosal surface of the small intestine. * Erythropoiesis The process by which red blood cell production is
controlled. Involves the release of erythropoietin from cells of the kidney and liver. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Taylor, C.,
Colgan, S. Regulation of immunity and inflammation by hypoxia in immunological niches. _Nat Rev Immunol_ 17, 774–785 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/nri.2017.103 Download citation *
Published: 03 October 2017 * Issue Date: December 2017 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nri.2017.103 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this
content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Trending News
🎯 dart (dartlang) introduction: getting started with dart/flutterDART TUTORIALS: BASICS FLUTTER IS A FRAMEWORK WRITTEN IN DART LANGUAGE FOR BUILDING NATIVE APPLICATIONS FOR IOS AND ANDR...
Your key to success in 2023, says attention expert: the difference between 'habits' and 'routines'Your New Year's resolution this year might never become a true "habit" — but that's probably OK, acc...
Cbo reports health care bill unaffordable for older americansA new analysis of the American Health Care Act passed by the House of Representatives estimates that 23 million people w...
In their own words: americans depend on social securityMemorial Day Sale! Join AARP for just $11 per year with a 5-year membership Join now and get a FREE gift. Expires 6/4 G...
Boris johnson battles to keep boosterism at bayIt feels like a very long time since I’ve been able to start this email with anything which could be described as good n...
Latests News
Regulation of immunity and inflammation by hypoxia in immunological nichesKEY POINTS * Hypoxia and inflammation are frequently co-incidental microenvironmental features of sites of concentrated ...
Microsoft No Longer Sees Cortana as a Competitor to Alexa or Google AssistantMicrosoft seems to be giving up on its ambitions to dominate the voice-powered virtual assistant arena and will reported...
Vital signs: nbn’s new price plans are too little, too lateThis week NBN Co announced pricing changes for the National Broadband Network. It includes a new plan boasting a downloa...
Two jhqvamc use cases win in robots with benefits competition | va mountain home health care | veterans affairsMountain Home , TN — Two JHQVAMC robotic use case submissions won separate categories in the Robots with Benefits virtua...
FICTION - Los Angeles TimesNEXT OF KIN _ by Marianne Langer Zeitlin (Zephyr Press: $18.95; 188 pp.)_ . After the death of her sister Esther by a dr...