Silent cerebral infarcts associated with cardiac disease and procedures
Silent cerebral infarcts associated with cardiac disease and procedures"
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
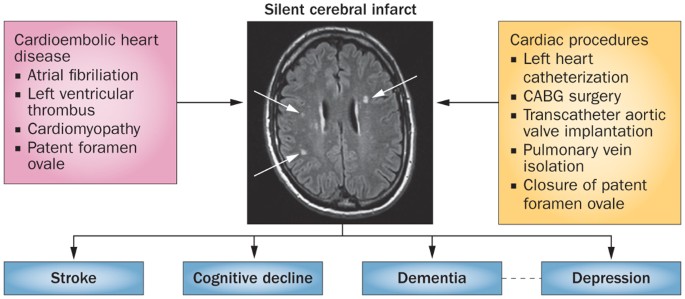
KEY POINTS * Silent cerebral infarcts (SCIs) are increasingly observed in patients with cardiac disease and in individuals who have undergone invasive cardiac procedures * Cardiac diseases
associated with the occurrence of SCIs include atrial fibrillation, cardiomyopathies, and atrial septal abnormalities * Postprocedural SCIs have been detected using MRI after left cardiac
catheterization, transcatheter aortic valve implantation, CABG surgery, pulmonary vein isolation, and closure of patent foramen ovale * SCIs do not always result in acute symptoms, but have
been associated with a threefold increase in the risk of stroke, and can be considered a precursor of ischaemic stroke * Accumulating evidence suggests that SCIs might have a role in the
development of dementia and depression, and in cognitive decline * Increased recognition of SCIs could advance our understanding of their links to cardiac and neurological disorders, and
facilitate the development of preventative therapeutic approaches ABSTRACT The occurrence of clinically silent cerebral infarcts (SCIs) in individuals affected by cardiac disease and after
invasive cardiac procedures is frequently reported. Indeed, atrial fibrillation, left ventricular thrombus formation, cardiomyopathy, and patent foramen ovale have all been associated with
SCIs. Furthermore, postprocedural SCIs have been observed after left cardiac catheterization, transcatheter aortic valve implantation, CABG surgery, pulmonary vein isolation, and closure of
patent foramen ovale. Such SCIs are often described as precursors to symptomatic stroke and are associated with cognitive decline, dementia, and depression. Increased recognition of SCIs
might advance our understanding of their relationship with heart disease and invasive cardiac procedures, facilitate further improvement of therapies or techniques aimed at preventing their
occurrence and, therefore, decrease the risk of adverse neurological outcomes. In this Review, we provide an overview of the occurrence and clinical significance of, and the available
diagnostic modalities for, SCIs related to cardiac disease and associated invasive cardiac procedures. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription
content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print issues and online access $209.00 per year only $17.42 per issue
Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL
ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS CLINICAL AND SUBCLINICAL ACUTE BRAIN
INJURY CAUSED BY INVASIVE CARDIOVASCULAR PROCEDURES Article 11 October 2024 DIFFERENT ASPECTS OF EARLY AND LATE DEVELOPMENT OF ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DURING HOSPITALIZATION IN CRYPTOGENIC
STROKE Article Open access 29 March 2021 LONG-TERM OUTCOMES OF PATIENTS WITH EMBOLIC STROKE OF UNDETERMINED SOURCE ACCORDING TO SUBTYPE Article Open access 23 April 2024 REFERENCES * Hamon,
M., Baron, J. C., Viader, F. & Hamon, M. Periprocedural stroke and cardiac catheterization. _Circulation_ 118, 678–683 (2008). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Arboix, A & Alió, J.
Cardioembolic stroke: clinical features, specific cardiac disorders and prognosis. _Curr. Cardiol. Rev._ 6, 150–161 (2010). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Bendszus, M.
& Stoll, G. Silent cerebral ischaemia: hidden fingerprints of invasive medical procedures. _Lancet Neurol._ 5, 364–372 (2006). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Sacco, R. L. _ et al_.
An updated definition of stroke for the 21st century: a statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. _Stroke_ 44, 2064–2089 (2013).
Article PubMed Google Scholar * Arboix, A. & Martí-Vilalta, J. L. Lacunar stroke. _Expert Rev. Neurother._ 9, 179–196 (2009). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Vermeer, S. E.,
Koudstaal, P. J., Oudkerk, M., Hofman. A. & Breteler, M. M. Prevalence and risk factors of silent brain infarcts in the population-based Rotterdam Scan Study. _Stroke_ 33, 21–25 (2002).
Article PubMed Google Scholar * Price, T. R. _ et al_. Silent brain infarction on magnetic resonance imaging and neurological abnormalities in community-dwelling older adults: the
Cardiovascular Health Study. _Stroke_ 28, 1158–1164 (1997). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kase, C. S. _ et al_. Prevalence of silent stroke in patients presenting with initial
stroke: the Framingham Study. _Stroke_ 20, 850–852 (1989). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Ricci, S. _ et al_., Silent brain infarctions in patients with first-ever stroke: a
community-based study in Umbria, Italy. _Stroke_ 24, 647–651 (1993). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Das, R. R. _ et al_., Prevalence and correlates of silent cerebral infarcts in
the Framingham Offspring Study. _Stroke_ 39, 2929–2935 (2008). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Wardlaw, J. M. _ et al_. Neuroimaging standards for research into small
vessel disease and its contribution to ageing and neurodegeneration. _Lancet Neurol._ 12, 822–838 (2013). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Kloppenborg, R. P. _ et al_.
Cerebral small-vessel disease and progression of brain atrophy: the SMART-MR study. _Neurology_ 79, 2029–2036 (2012). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Vermeer, S. E. _ et al_., Silent
brain infarcts and the risk of dementia and cognitive decline. _N. Engl. J. Med._ 348, 1215–1222 (2003). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Fujikawa, T., Yamawaki, S. & Touhouda, Y.
Incidence of silent cerebral infarction in patients with major depression. _Stroke_ 24, 1631–1634 (1993). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Yamashita, H. _ et al_. Long-term prognosis
of patients with major depression and silent cerebral infarction. _Neuropsychobiology_ 62, 177–181 (2010). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Debette, S. _ et al_., Association of MRI
markers of vascular brain injury with incident stroke, mild cognitive impairment, dementia, and mortality: the Framingham Offspring Study. _Stroke_ 41, 600–606 (2010). Article PubMed
PubMed Central Google Scholar * Vermeer, S. E. _ et al_. Silent brain infarcts and white matter lesions increase stroke risk in the general population: the Rotterdam Scan Study. _Stroke_
34, 1126–1129 (2003). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Mullins, M. E. _ et al_. CT and conventional and diffusion-weighted MR imaging in acute stroke: study in 691 patients at presentation
to the emergency department. _Radiology_ 224, 353–360 (2002). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Zhu, Y. C., Dufouil, C., Tzourio, C. & Chabriat, H. Silent brain infarcts: a review of
MRI diagnostic criteria. _Stroke_ 42, 1140–1145 (2011). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Marks, M. P. _ et al_. Acute and chronic stroke: navigated spin-echo diffusion-weighted MR imaging.
_Radiology_ 199, 403–408 (1996). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kucharczyk, J., Mintorovitch, J., Asgari, H. S. & Moseley, M. Diffusion/perfusion MR imaging of acute cerebral
ischemia. _Magn. Reson. Med._ 19, 311–315 (1991). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Burdette, J. H., Ricci, P. E., Petitti, N. & Elster, A. D. Cerebral infarction: time course of
signal intensity changes on diffusion-weighted MR images. _AJR Am. J. Roentgenol._ 171, 791–795 (1998). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kelley, R. E. & Minagar, A. Cardioembolic
stroke: an update. _South. Med. J._ 96, 343–349 (2003). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Friberg, L., Hammar, N. & Rosenqvist, M. Stroke in paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: report from
the Stockholm Cohort of Atrial Fibrillation. _Eur. Heart J._ 31, 967–975 (2010). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Shinkawa, A. _ et al_. Silent cerebral infarction in a community-based
autopsy series in Japan: the Hisayama Study. _Stroke_ 26, 380–385 (1995). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Gaita, F. _ et al_. Prevalence of silent cerebral ischemia in paroxysmal and
persistent atrial fibrillation and correlation with cognitive function. _J. Am. Coll. Cardiol._ http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2013.05.074. * Marfella, R. _ et al_. Brief episodes of
silent atrial fibrillation predict clinical vascular brain disease in type 2 diabetic patients. _J. Am. Coll. Cardiol._ 62, 525–520 (2013). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Kobayashi, A.,
Iguchi, M., Shimizu, S. & Uchiyama, S. Silent cerebral infarcts and cerebral white matter lesions in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. _J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis._ 21,
310–317 (2012). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Neumann, T. _ et al_. MEDAFI-Trial (Micro-Embolization During Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation): comparison of pulmonary vein isolation
using cryoballoon technique vs. radiofrequency energy. _Europace_ 13, 37–44 (2011). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Sato, H. _ et al_. Aspirin attenuates the incidence of silent brain
lesions in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. _Circ. J._ 68, 410–416 (2004). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * EAFT Study Group. Silent brain infarction in nonrheumatic
atrial fibrillation: European Atrial Fibrillation Trial. _Neurology_ 46, 159–165 (1996). * Ezekowitz, M. D. _ et al_. Silent cerebral infarction in patients with nonrheumatic atrial
fibrillation. _Circulation_ 92, 2178–2182 (1995). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Ott, A. _ et al_. Atrial fibrillation and dementia in a population-based study: the Rotterdam Study.
_Stroke_ 28, 316–321 (1997). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Knecht, S. _ et al_. Atrial fibrillation in stroke-free patients is associated with memory impairment and hippocampal
atrophy. _Eur. Heart J._ 29, 2125–2132 (2008). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Mielke, M. M. _ et al_. Vascular factors predict rate of progression in Alzheimer disease. _Neurology_ 69,
1850–1858 (2007). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Santangeli, P. _ et al_. Atrial fibrillation and the risk of incident dementia: a meta-analysis. _Heart Rhythm_ 9, 1761–1768 (2012).
Article PubMed Google Scholar * Miyasaka, Y. _ et al_. Risk of dementia in stroke-free patients diagnosed with atrial fibrillation: data from a community-based cohort. _Eur. Heart J._
28, 1962–1967 (2007). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Vaitkus, P. T. & Barnathan, E. S. Embolic potential, prevention and management of mural thrombus complicating anterior myocardial
infarction: a meta-analysis. _J. Am. Coll. Cardiol._ 22, 1004–1009 (1993). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * US National Library of Medicine. _ClinicalTrials.gov_ [online], (2012). *
Dries, D. L., Rosenberg, Y. D., Waclawiw, M. A. & Domanski, M. J. Ejection fraction and risk of thromboembolic events in patients with systolic dysfunction and sinus rhythm: evidence for
gender differences in the studies of left ventricular dysfunction trials. _J. Am. Coll. Cardiol._ 29, 1074–1080 (1997). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Siachos, T. _ et al_. Silent
strokes in patients with heart failure. _J. Card. Fail._ 11, 485–489 (2005). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Koniaris, L. S. & Goldhaber, S. Z. Anticoagulation in dilated
cardiomyopathy. _J. Am. Coll. Cardiol._ 31, 745–748 (1998). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kozdag, G. _ et al_. Silent cerebral infarction in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy:
echocardiographic correlates. _Int. J. Cardiol._ 107, 376–381 (2006). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Kozdag, G. _ et al_. Silent cerebral infarction in chronic heart failure: ischemic
and nonischemic dilated cardiomyopathy. _Vasc. Health Risk Manag._ 4, 463–469 (2008). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Bal, S. _ et al_. High rate of magnetic resonance
imaging stroke recurrence in cryptogenic transient ischemic attack and minor stroke patients. _Stroke_ 43, 3387–3388 (2012). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Foulkes, M. A., Wolf, P. A.,
Price, T. R., Mohr, J. P. & Hier, D. B. The Stroke Data Bank: design, methods, and baseline characteristics. _Stroke_ 19, 547–554 (1988). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Overell,
J. R., Bone, I. & Lees, K. R. Interatrial septal abnormalities and stroke: a meta-analysis of case–control studies. _Neurology_ 55, 1172–1179 (2000). Article CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Cabanes, L. _ et al_. Atrial septal aneurysm and patent foramen ovale as risk factors for cryptogenic stroke in patients less than 55 years of age: a study using transesophageal
echocardiography. _Stroke_ 24, 1865–1873 (1993). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kitsios, G. D., Lasker, A. Singh, J. & Thaler, D. E. Recurrent stroke on imaging and presumed
paradoxical embolism: a cross-sectional analysis. _Neurology_ 78, 993–997 (2012). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Clergeau, M. R. _ et al_. Silent cerebral infarcts in
patients with pulmonary embolism and a patent foramen ovale: a prospective diffusion-weighted MRI study. _Stroke_ 40, 3758–3762 (2009). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Ning, M. _ et al_.
The brain's heart—therapeutic opportunities for patent foramen ovale (PFO) and neurovascular disease. _Pharmacol. Ther._ 139, 111–123 (2013). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central
Google Scholar * Cabanes, L. _ et al_. Atrial septal aneurysm and patent foramen ovale as risk factors for cryptogenic stroke in patients less than 55 years of age. A study using
transesophageal echocardiography. _Stroke_ 24, 1865–1873 (1993). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Mas, J. L. _ et al_. Recurrent cerebrovascular events associated with patent foramen
ovale, atrial septal aneurysm, or both. _N. Engl. J. Med._ 345, 1740–1746 (2001). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Davis, D. _ et al_. Patent foramen ovale, ischemic stroke and
migraine: systematic review and stratified meta-analysis of association studies. _Neuroepidemiology_ 40, 56–67 (2013). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Handke, M., Harloff, A., Bode, C.
& Geibel, A. Patent foramen ovale and cryptogenic stroke: a matter of age? _Semin. Thromb. Hemost._ 35, 505–514 (2009). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Lethen, H. _ et al_. Frequency
of deep vein thrombosis in patients with patent foramen ovale and ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack. _Am. J. Cardiol._ 80, 1066–1069 (1997). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
* Di Tullio, M. R. _ et al_. Patent foramen ovale, subclinical cerebrovascular disease, and ischemic stroke in a population-based cohort. _J. Am. Coll. Cardiol._ 62, 35–41 (2013). Article
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Russell, D. & Brucher, R. Online automatic discrimination between solid and gaseous cerebral microemboli with the first multifrequency
transcranial Doppler. _Stroke_ 33, 1975–1980 (2002). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Fuchs, S. _ et al_. Stroke complicating percutaneous coronary interventions: incidence,
predictors, and prognostic implications. _Circulation_ 106, 86–91 (2002). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Segal, A. Z., Abernethy, W. B., Palacios, I. F., BeLue, R. & Rordorf, G.
Stroke as a complication of cardiac catheterization: risk factors and clinical features. _Neurology_ 56, 975–977 (2001). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Büsing, K. A. _ et al_.
Cerebral infarction: incidence and risk factors after diagnostic and interventional cardiac catheterization—prospective evaluation at diffusion-weighted MR imaging. _Radiology_ 235, 177–183
(2005). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Omran, H. _ et al_. Silent and apparent cerebral embolism after retrograde catheterisation of the aortic valve in valvular stenosis: a prospective,
randomised study. _Lancet_ 361, 1241–1246 (2003). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Lund, C. _ et al_. Cerebral emboli during left heart catheterization may cause acute brain injury. _Eur.
Heart J._ 26, 1269–1275 (2005). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Ohi, Y. _ et al_. Cerebral microembolism following coronary angiography—a prospective comparative study between left
cardiac catheterization and multidetector computed tomography. _Intern. Med._ 52, 1869–1874 (2013). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Hamon, M. _ et al_. Silent cerebral infarcts after
cardiac catheterization: a randomized comparison of radial and femoral approaches. _Am. Heart J._ 164, 449–454 (2012). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Kim, B. J. _ et al_. Insufficient
platelet inhibition is related to silent embolic cerebral infarctions after coronary angiography. _Stroke_ 43, 727–732 (2012). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kim, I. C. _ et al_.
Incidence and predictors of silent embolic cerebral infarction following diagnostic coronary angiography. _Int. J. Cardiol._ 148, 179–182 (2011). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Murai, M.
_ et al_. Asymptomatic acute ischemic stroke after primary percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with acute coronary syndrome might be caused mainly by manipulating catheters or
devices in the ascending aorta, regardless of the approach to the coronary artery. _Circ. J._ 72, 51–55 (2008). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Hamon, M. _ et al_. Risk of acute brain
injury related to cerebral microembolism during cardiac catheterization performed by right upper limb arterial access. _Stroke_ 38, 2176–2179 (2007). Article PubMed Google Scholar *
Hamon, M. _ et al_., Cerebral microembolism during cardiac catheterization and risk of acute brain injury: a prospective diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging study. _Stroke_ 37,
2035–2038 (2006). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Sun, X., Lindsay, J., Monsein, L. H., Hill, P. C. & Corso, P. J. Silent brain injury after cardiac surgery: a review: cognitive
dysfunction and magnetic resonance imaging diffusion-weighted imaging findings. _J. Am. Coll. Cardiol._ 60, 791–797 (2012). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Keeley, E. C. & Grines, C.
L. Scraping of aortic debris by coronary guiding catheters: a prospective evaluation of 1,000 cases. _J. Am. Coll. Cardiol._ 32, 1861–1865 (1998). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar *
Karalis, D. G. _ et al_. Risk of catheter-related emboli in patients with atherosclerotic debris in the thoracic aorta. _Am. Heart J._ 131, 1149–1155 (1996). Article CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Webb, J. G. _ et al_. Transcatheter aortic valve implantation: impact on clinical and valve-related outcomes. _Circulation_ 119, 3009–3016 (2009). Article PubMed Google Scholar
* Grube, E. _ et al_. Percutaneous aortic valve replacement for severe aortic stenosis in high-risk patients using the second- and current third-generation self-expanding CoreValve
prosthesis: device success and 30-day clinical outcome. _J. Am. Coll. Cardiol._ 50, 69–76 (2007). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Kahlert, P. _ et al_. Silent and apparent cerebral
ischemia after percutaneous transfemoral aortic valve implantation: a diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging study. _Circulation_ 121, 870–878 (2010). Article PubMed Google Scholar
* Rodés-Cabau, J. _ et al_. Cerebral embolism following transcatheter aortic valve implantation: comparison of transfemoral and transapical approaches. _J. Am. Coll. Cardiol._ 57, 18–28
(2011). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Ghanem, A. _ et al_. Prognostic value of cerebral injury following transfemoral aortic valve implantation. _EuroIntervention_ 8, 1296–1306 (2013).
Article PubMed Google Scholar * Fairbairn, T. A. _ et al_. Diffusion-weighted MRI determined cerebral embolic infarction following transcatheter aortic valve implantation: assessment of
predictive risk factors and the relationship to subsequent health status. _Heart_ 98, 18–23 (2012). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Astarci, P. _ et al_. Magnetic resonance imaging
evaluation of cerebral embolization during percutaneous aortic valve implantation: comparison of transfemoral and trans-apical approaches using Edwards Sapiens valve. _Eur. J. Cardiothorac.
Surg._ 40, 475–479 (2011). PubMed Google Scholar * Ghanem, A. _ et al_. Risk and fate of cerebral embolism after transfemoral aortic valve implantation: a prospective pilot study with
diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. _J. Am. Coll. Cardiol._ 55, 1427–1432 (2010). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Arnold, M. _ et al_. Embolic cerebral insults after
transapical aortic valve implantation detected by magnetic resonance imaging. _JACC Cardiovasc. Interv._ 3, 1126–1132 (2010). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Erdoes, G. _ et al_.
Transcranial Doppler-detected cerebral embolic load during transcatheter aortic valve implantation. _Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg._ 41, 778–783 (2012). Article PubMed Google Scholar *
Reinsfelt, B. _ et al_. Transcranial Doppler microembolic signals and serum marker evidence of brain injury during transcatheter aortic valve implantation. _Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand._ 56,
240–247 (2012). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kahlert, P. _ et al_. Cerebral embolization during transcatheter aortic valve implantation: a transcranial Doppler study.
_Circulation_ 126, 1245–1255 (2012). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Hynes, B. G. & Rodés-Cabau, J. Transcatheter aortic valve implantation and cerebrovascular events: the current
state of the art. _Ann. NY Acad. Sci._ 1254, 151–163 (2012). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Knipp, S. C. _ et al_. Cognitive outcomes three years after coronary artery bypass surgery:
relation to diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. _Ann. Thorac. Surg._ 85, 872–879 (2008). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Ito, A. _ et al_. Postoperative neurological
complications and risk factors for pre-existing silent brain infarction in elderly patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting. _J. Anesth._ 26, 405–411 (2012). Article PubMed
Google Scholar * Gerriets, T. _ et al_. Evaluation of methods to predict early long-term neurobehavioral outcome after coronary artery bypass grafting. _Am. J. Cardiol._ 105, 1095–1101
(2010). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Bendszus, M. _ et al_. Brain damage after coronary artery bypass grafting. _Arch. Neurol._ 59, 1090–1095 (2002). Article PubMed Google Scholar *
Lund, C. _ et al_. Cerebral ischemic injury and cognitive impairmentafter off-pump and on-pump coronary artery bypass grafting surgery. _Ann. Thorac. Surg._ 80, 2126–2131 (2005). Article
PubMed Google Scholar * Wimo, A. _ et al_. The economic impact of dementia in Europe in 2008-cost estimates from the Eurocode project. _Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry_ 26, 825–832 (2011).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Blum, S. _ et al_. Memory after silent stroke: hippocampus and infarcts both matter. _Neurology_ 78, 38–46 (2012). Article CAS PubMed PubMed
Central Google Scholar * Arvanitakis, Z., Leurgans, S. E., Barnes, L. L., Bennett, D. A. & Schneider, J. A. Microinfarct pathology, dementia, and cognitive systems. _Stroke_ 42,
722–727 (2011). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Gerriets, T. _ et al_. Protecting the brain from gaseous and solid micro-emboli during coronary artery bypass grafting: a
randomized controlled trial. _Eur. Heart J._ 31, 260–268 (2010). Article Google Scholar * Djaiani, G. _ et al_. Mild to moderate atheromatous disease of the thoracic aorta and new ischemic
brain lesions after conventional coronary artery bypass graft surgery. _Stroke_ 35, e356–e358 (2004). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Floyd, T. F. _ et al_. Clinically silent cerebral
ischemic events after cardiac surgery: their incidence, regional vascular occurrence, and procedural dependence. _Ann. Thorac. Surg._ 81, 2160–2166 (2006). Article PubMed Google Scholar *
Selnes, O. A. & McKhann, G. M. Neurocognitive complications after coronary artery bypass surgery. _Ann. Neurol._ 57, 615–621 (2005). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Van Dijk, D. _ et
al_. Cognitive outcome after off-pump and on-pump coronary artery bypass graft surgery: a randomized trial. _JAMA_ 287, 1405–1412 (2002). Article PubMed Google Scholar * European Heart
Rhythm Association. Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation: the Task Force for the Management of Atrial Fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). _Eur. Heart
J._ 31, 2369–2429 (2010). * Haeusler, K. G. _ et al_. 3 Tesla MRI-detected brain lesions after pulmonary vein isolation for atrial fibrillation: results of the MACPAF study. _J. Cardiovasc.
Electrophysiol._ 24, 14–21 (2013). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Herrera Siklódy, C. _ et al_. Incidence of asymptomatic intracranial embolic events after pulmonary vein isolation:
comparison of different atrial fibrillation ablation technologies in a multicenter study. _J. Am. Coll. Cardiol._ 58, 681–688 (2011). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Schwarz, N. _ et al_.
Neuropsychological decline after catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. _Heart Rhythm._ 7, 1761–1767 (2010). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Gaita, F. _ et al_., Radiofrequency
catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: a cause of silent thromboembolism? Magnetic resonance imaging assessment of cerebral thromboembolism in patients undergoing ablation of atrial
fibrillation. _Circulation_ 122, 1667–1673 (2010). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Schrickel, J. W. _ et al_. Incidence and predictors of silent cerebral embolism during pulmonary vein
catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation. _Europace_ 12, 52–57 (2010). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Meier, B. _ et al_. Percutaneous closure of patent foramen ovale in cryptogenic
embolism. _N. Engl. J. Med._ 368, 1083–1091 (2013). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Carroll, J. D. _ et al_. Closure of patent foramen ovale versus medical therapy after cryptogenic
stroke. _N. Engl. J. Med._ 368, 1092–1100 (2013). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Skowasch, D. _ et al_. Silent and apparent cerebral embolism after interventional closure of
symptomatic patent foramen ovale. _Int. J. Cardiol._ 145, 401–402 (2010). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Dorenbeck, U. _ et al_. Cerebral embolism with interventional closure of
symptomatic patent foramen ovale: an MRI-based study using diffusion-weighted imaging. _Eur. J. Neurol._ 14, 451–454 (2007). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Bernick, C. _ et al_.
Silent MRI infarcts and the risk of future stroke: the Cardiovascular Health Study. _Neurology_ 57, 1222–1229 (2001). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Choi, S. H. _ et al_.
Diffusion-weighted MRI in vascular dementia. _Neurology_ 54, 83–89 (2000). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Vermeer, S. E., Longstreth, W. T. Jr & Koudstaal, P. J. Silent brain
infarcts: a systematic review. _Lancet Neurol._ 6, 611–619 (2007). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Fujikawa, T., Yanai, I. & Yamawaki, S. Psychosocial stressors in patients with major
depression and silent cerebral infarction. _Stroke_ 28, 1123–1125 (1997). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Fujikawa, T., Yamawaki, S. & Touhouda, Y. Incidence of silent cerebral
infarction in patients with major depression. _Stroke_ 24, 1631–1634 (1993). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Yanai, I., Fujikawa, T., Horiguchi, J., Yamawaki, S. & Touhouda, Y.
The 3-year course and outcome of patients with major depression and silent cerebral infarction. _J. Affect. Disord._ 47, 25–30 (1998). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Fujikawa, T.,
Yamawaki, S. & Touhouda, Y. Background factors and clinical symptoms of major depression with silent cerebral infarction. _Stroke_ 25, 798–801 (1994). Article CAS PubMed Google
Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This work was supported by grants from the Dutch Heart Foundation (2011 T022) and National Health Insurance Board/ZonMw, Netherlands
(40-00703-98-11629) to R. Delewi. AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Department of Cardiology, Academic Medical Center, University of Amsterdam, Meibergdreef 9, Amsterdam, 1105
AZ, Netherlands Mariëlla E. C. Hassell, Jan J. Piek & Ronak Delewi * Department of Neurology, Academic Medical Center, University of Amsterdam, Meibergdreef 9, Amsterdam, 1105 AZ,
Netherlands Yvo B. W. Roos * Department of Neuroradiology, Academic Medical Center, University of Amsterdam, Meibergdreef 9, Amsterdam, 1105 AZ, Netherlands Charles B. L. Majoie * Department
of Cardiology, VU University Medical Center Amsterdam, De Boelelaan 1117, Amsterdam, 1081 HV, Netherlands Robin Nijveldt * Clinical Research Department, University Hospital of Caen, Avenue
Côte de Nacre, Caen, Normandy, France Martial Hamon Authors * Mariëlla E. C. Hassell View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Robin Nijveldt
View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Yvo B. W. Roos View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar *
Charles B. L. Majoie View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Martial Hamon View author publications You can also search for this author
inPubMed Google Scholar * Jan J. Piek View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Ronak Delewi View author publications You can also search for
this author inPubMed Google Scholar CONTRIBUTIONS M. E. C. Hassell researched the data for the article. M. E. C. Hassell, R. Delewi, and R. Nijveldt contributed substantially to discussion
of the content. M. E. C. Hassell and R. Delewi contributed substantially to writing the article. All the authors reviewed/edited the manuscript before submission. CORRESPONDING AUTHOR
Correspondence to Ronak Delewi. ETHICS DECLARATIONS COMPETING INTERESTS The authors declare no competing financial interests. POWERPOINT SLIDES POWERPOINT SLIDE FOR FIG. 1 POWERPOINT SLIDE
FOR FIG. 2 POWERPOINT SLIDE FOR TABLE 1 POWERPOINT SLIDE FOR TABLE 2 RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Hassell, M., Nijveldt, R., Roos, Y.
_et al._ Silent cerebral infarcts associated with cardiac disease and procedures. _Nat Rev Cardiol_ 10, 696–706 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrcardio.2013.162 Download citation *
Published: 29 October 2013 * Issue Date: December 2013 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrcardio.2013.162 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this
content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Trending News
Ryanair passengers praise 'perfect' cabin bag with 'lots of pockets' - YorkshireLiveWhat's OnRyanair passengers praise 'perfect' cabin bag with 'lots of pockets'The VANKEV Backpack is the ideal travel com...
Dwp change for people on benefits born within three-year period rolled outThe Department for Work and Pensions is launching a new initiative to support benefits claimants born in specific years....
Moyes in tribute to victims and emergency services after liverpool parade crashTHE EVERTON BOSS BECAME THE LATEST FIGUREHEAD TO EXPRESS SOLIDARITY WITH THOSE AFFECTED BY THE CITY CENTRE INCIDENT 11:3...
Foreign office issues fresh warnings to brits heading to turkeyThe UK Foreign Office has today issued a fresh caution to Brits planning to visit Turkey, advising extra care when using...
Karine jean-pierre roasted over ‘orwellian’ tweet touting ‘0% inflation’EXPLORE MORE President Biden’s truth-averse top spokesperson was ridiculed after she touted “0% inflation in July” follo...
Latests News
Silent cerebral infarcts associated with cardiac disease and proceduresKEY POINTS * Silent cerebral infarcts (SCIs) are increasingly observed in patients with cardiac disease and in individua...
The page you were looking for doesn't exist.You may have mistyped the address or the page may have moved.By proceeding, you agree to our Terms & Conditions and our ...
Celtic's 69-match unbeaten run ends with hearts thrashingCeltic's unbeaten run of 69 domestic matches, stretching back to May 2016, is over after a 4-0 thrashing at Hearts ...
Thierry henry sends psg stars neymar and kylian mbappe messageBayern also have Serge Gnabry, Thiago Alcantara and Canadian sensation Alphonso Davies among their ranks. European footb...
Death by 1,900 cuts: will quality journalism thrive under fairfax’s new model?It was less than ten years ago that Fairfax Media’s The Age opened its shiny, new printing presses at Tullamarine. Bille...