Genetic manipulation of adult mouse neurogenic niches by in vivo electroporation
Genetic manipulation of adult mouse neurogenic niches by in vivo electroporation"
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
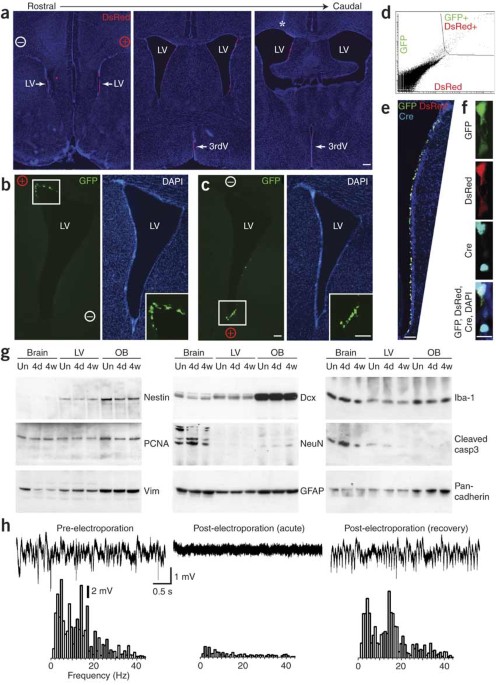
ABSTRACT Targeted ectopic expression of genes in the adult brain is an invaluable approach for studying many biological processes. This can be accomplished by generating transgenic mice or
by virally mediated gene transfer, but these methods are costly and labor intensive. We devised a rapid strategy that allows localized _in vivo_ transfection of plasmid DNA within the adult
neurogenic niches without detectable brain damage. Injection of plasmid DNA into the ventricular system or directly into the hippocampus of adult mice, followed by application of electrical
current via external electrodes, resulted in transfection of neural stem or progenitor cells and mature neurons. We showed that this strategy can be used for both fate mapping and gain- or
loss-of-function experiments. Using this approach, we identified an essential role for cadherins in maintaining the integrity of the lateral ventricle wall. Thus, _in vivo_ electroporation
provides a new approach to study the adult brain. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS
Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print issues and online access $259.00 per year only $21.58 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on
SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about
institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS GLIAL CELL TYPE-SPECIFIC GENE EXPRESSION IN THE MOUSE CEREBRUM USING THE
_PIGGYBAC_ SYSTEM AND IN UTERO ELECTROPORATION Article Open access 01 March 2021 EFFICIENT GENERATION OF FUNCTIONAL NEURONS FROM MOUSE EMBRYONIC STEM CELLS VIA NEUROGENIN-2 EXPRESSION
Article 18 August 2023 DIRECT ANALYSIS OF BRAIN PHENOTYPES VIA NEURAL BLASTOCYST COMPLEMENTATION Article 10 August 2020 REFERENCES * Carlen, M., Meletis, K., Barnabe-Heider, F. & Frisen,
J. Genetic visualization of neurogenesis. _Exp. Cell Res._ 312, 2851–2859 (2006). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Consiglio, A. et al. Robust _in vivo_ gene transfer into adult
mammalian neural stem cells by lentiviral vectors. _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_ 101, 14835–14840 (2004). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Tashiro, A., Zhao, C. & Gage, F.H.
Retrovirus-mediated single-cell gene knockout technique in adult newborn neurons _in vivo_. _Nat. Protoc._ 1, 3049–3055 (2006). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Glover, D.J., Lipps,
H.J. & Jans, D.A. Towards safe, non-viral therapeutic gene expression in humans. _Nat. Rev. Genet._ 6, 299–310 (2005). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Lu, P.Y., Xie, F. &
Woodle, M.C. _In vivo_ application of RNA interference: from functional genomics to therapeutics. _Adv. Genet._ 54, 117–142 (2005). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Falk, A. et al. Gene
delivery to adult neural stem cells. _Exp. Cell Res._ 279, 34–39 (2002). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Mir, L.M., Moller, P.H., Andre, F. & Gehl, J. Electric pulse-mediated
gene delivery to various animal tissues. _Adv. Genet._ 54, 83–114 (2005). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Calegari, F., Haubensak, W., Yang, D., Huttner, W.B. & Buchholz, F.
Tissue-specific RNA interference in postimplantation mouse embryos with endoribonuclease-prepared short interfering RNA. _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_ 99, 14236–14240 (2002). Article CAS
PubMed Google Scholar * Inoue, T. & Krumlauf, R. An impulse to the brain–using _in vivo_ electroporation. _Nat. Neurosci._ 4 (Suppl.), 1156–1158 (2001). Article CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Bajocchi, G., Feldman, S.H., Crystal, R.G. & Mastrangeli, A. Direct _in vivo_ gene transfer to ependymal cells in the central nervous system using recombinant adenovirus
vectors. _Nat. Genet._ 3, 229–234 (1993). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Johansson, C.B. et al. Identification of a neural stem cell in the adult mammalian central nervous system.
_Cell_ 96, 25–34 (1999). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Falk, A. & Frisen, J. New neurons in old brains. _Ann. Med._ 37, 480–486 (2005). Article PubMed Google Scholar *
Novak, A., Guo, C., Yang, W., Nagy, A. & Lobe, C.G. Z/EG, a double reporter mouse line that expresses enhanced green fluorescent protein upon Cre-mediated excision. _Genesis_ 28, 147–155
(2000). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Soriano, P. Generalized lacZ expression with the ROSA26 Cre reporter strain. _Nat. Genet._ 21, 70–71 (1999). Article CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Kempermann, G., Jessberger, S., Steiner, B. & Kronenberg, G. Milestones of neuronal development in the adult hippocampus. _Trends Neurosci._ 27, 447–452 (2004). Article CAS
PubMed Google Scholar * Benraiss, A., Chmielnicki, E., Lerner, K., Roh, D. & Goldman, S.A. Adenoviral brain-derived neurotrophic factor induces both neostriatal and olfactory neuronal
recruitment from endogenous progenitor cells in the adult forebrain. _J. Neurosci._ 21, 6718–6731 (2001). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Pencea, V., Bingaman, K.D., Wiegand, S.J.
& Luskin, M.B. Infusion of brain-derived neurotrophic factor into the lateral ventricle of the adult rat leads to new neurons in the parenchyma of the striatum, septum, thalamus, and
hypothalamus. _J. Neurosci._ 21, 6706–6717 (2001). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Gonzalez-Reyes, A. Stem cells, niches and cadherins: a view from _Drosophila_. _J. Cell Sci._ 116,
949–954 (2003). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Zhang, J. et al. Identification of the haematopoietic stem cell niche and control of the niche size. _Nature_ 425, 836–841 (2003).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Lechler, T. & Fuchs, E. Asymmetric cell divisions promote stratification and differentiation of mammalian skin. _Nature_ 437, 275–280 (2005).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Nieman, M.T., Kim, J.B., Johnson, K.R. & Wheelock, M.J. Mechanism of extracellular domain-deleted dominant negative cadherins. _J. Cell Sci._ 112,
1621–1632 (1999). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Matsuda, T. & Cepko, C.L. Controlled expression of transgenes introduced by _in vivo_ electroporation. _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_ 104,
1027–1032 (2007). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Lindvall, O. & Kokaia, Z. Stem cells for the treatment of neurological disorders. _Nature_ 441, 1094–1096 (2006). Article CAS
PubMed Google Scholar * Kondoh, T. et al. _In vivo_ gene transfer into the periventricular region by electroporation. _Neurol. Med. Chir. (Tokyo)_ 40, 618–623 (2000). Article CAS
Google Scholar * Wei, F. et al. Calmodulin regulates synaptic plasticity in the anterior cingulate cortex and behavioral responses: a microelectroporation study in adult rodents. _J.
Neurosci._ 23, 8402–8409 (2003). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kuo, C.T. et al. Postnatal deletion of Numb/Numblike reveals repair and remodeling capacity in the subventricular
neurogenic niche. _Cell_ 127, 1253–1264 (2006). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Rasin, M.R. et al. Numb and Numbl are required for maintenance of cadherin-based adhesion and polarity
of neural progenitors. _Nat. Neurosci._ 10, 819–827 (2007). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Wong, L.F. et al. Lentivirus-mediated gene transfer to the central nervous system:
therapeutic and research applications. _Hum. Gene Ther._ 17, 1–9 (2006). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Bengzon, J., Mohapel, P., Ekdahl, C.T. & Lindvall, O. Neuronal apoptosis
after brief and prolonged seizures. _Prog. Brain Res._ 135, 111–119 (2002). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Hatakeyama, J. et al. Hes genes regulate size, shape and histogenesis of
the nervous system by control of the timing of neural stem cell differentiation. _Development_ 131, 5539–5550 (2004). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Download references
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We thank R. Kageyama (Kyoto University) for the gift of the nestin promoter vector30, C. Ibáñez (Karolinska Institutet) for the gift of a BDNF expression plasmid, M.
Wheelock (University of Nebraska Medical Center) for providing the dominant-negative N-cadherin cDNA and K. Fernandes (University of Montreal) for critically reading the manuscript. This
study was supported by grants from the Swedish Research Council, the Swedish Cancer Society, the Foundation for Strategic Research, the Karolinska Institutet, Tobias Stiftelsen and the
European Commission Framework VI Programme, EuroStemCell. F.B.-H. is supported by a postdoctoral fellowship from Canadian Institutes of Health Research. AUTHOR INFORMATION Author notes *
Konstantinos Meletis Present address: Present address: The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 43 Vassar Street, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02139,
USA., AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Department of Cell and Molecular Biology, Medical Nobel Institute, Stockholm, SE-171 77, Sweden Fanie Barnabé-Heider, Konstantinos Meletis, Malin Eriksson,
Olaf Bergmann, Hanna Sabelström, Harald Mikkers & Jonas Frisén * Department of Neuroscience, Box 285, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, SE-171 77, Sweden Michael A Harvey * Department of
Molecular Cell Biology and Regenerative Medicine Program, Leiden University Medical Center, P.O. Box 9600, RC Leiden, 2300, The Netherlands Harald Mikkers Authors * Fanie Barnabé-Heider
View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Konstantinos Meletis View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google
Scholar * Malin Eriksson View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Olaf Bergmann View author publications You can also search for this author
inPubMed Google Scholar * Hanna Sabelström View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Michael A Harvey View author publications You can also
search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Harald Mikkers View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Jonas Frisén View author publications
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CONTRIBUTIONS F.B.-H. designed, performed and analyzed the study and wrote the manuscript; K.M. designed and performed most parts
of the study; M.E. performed and analyzed part of the study (including BAC analysis); O.B. performed part of the study; H.S. performed and analyzed part of the study; M.A.H. performed EEG
analysis; H.M. designed and performed part of the adenoviral study; and J.F. designed the study and wrote the manuscript. CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to Jonas Frisén. SUPPLEMENTARY
INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY TEXT AND FIGURES Supplementary Figures 1–3, Supplementary Methods (PDF 435 kb) RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE
Barnabé-Heider, F., Meletis, K., Eriksson, M. _et al._ Genetic manipulation of adult mouse neurogenic niches by _in vivo_ electroporation. _Nat Methods_ 5, 189–196 (2008).
https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1174 Download citation * Received: 27 September 2007 * Accepted: 13 December 2007 * Published: 20 January 2008 * Issue Date: February 2008 * DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1174 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently
available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Trending News
Today's pickup: digital brokerage app lacking traction, freight markets still volatile(Photo: TruckStockImages) Good day, FreightWaves Chad Prevost is reporting today on the UBS Evidence Lab's finding ...
Induction of breast cancer by oestrogens and methylcholanthrene in high- and low-breast-cancer strain miceAccess through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ...
Old image of farmer’s death revived amid recent protests_(If you feel suicidal or know someone in distress, please reach out to them with kindness and call these_ _numbers_ _of...
15-min pedestrian distance life circle and sustainable community governance in chinese metropolitan cities: a diagnosisABSTRACT Urban planning has shifted from “land-oriented” to “human-oriented” and metropolitan cities start to focus on 1...
Mixed matrix formulations with mof molecular sieving for key energy-intensive separationsABSTRACT Membrane-based separations can improve energy efficiency and reduce the environmental impacts associated with t...
Latests News
Genetic manipulation of adult mouse neurogenic niches by in vivo electroporationABSTRACT Targeted ectopic expression of genes in the adult brain is an invaluable approach for studying many biological ...
Wildlife testing shows decline in harmful chemicalsEnvironmentWildlife testing shows decline in harmful chemicalsByLaura PodgornikJanuary 12, 2011DownloadTesting on eaglet...
Wetherspoon not responsible for harm to man restrained by security, judge rulesJD Wetherspoon was not responsible for injuries sustained by a man whose hip was dislocated when two security guards res...
Harlequins will use new zealand link in search for new director of rugby - ruckTHE_ DAILY MAIL_ HAS REPORTED THAT HARLEQUINS ARE LIKELY TO APPOINT THEIR FIRST KIWI COACH IN 17 YEARS AFTER ZINZAN BROO...
Tencent teams up with taxman on blockchain receiptsFor unscrupulous businesses attempting to take advantage of tax loopholes in China, the sellers of fake receipts on the ...