Strategies to determine the biological function of micrornas
Strategies to determine the biological function of micrornas"
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
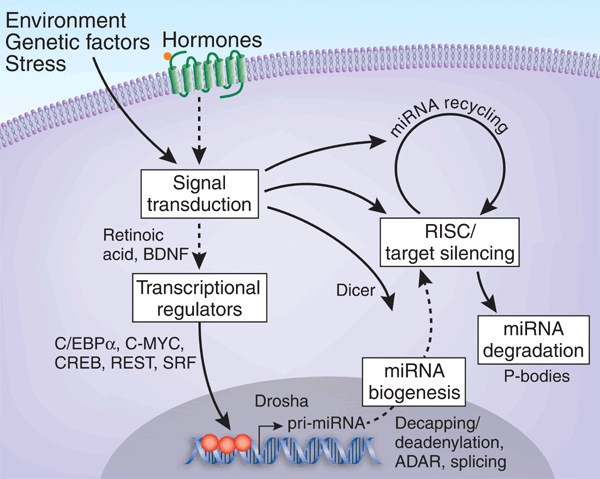
ABSTRACT MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are regulators of gene expression that control many biological processes in development, differentiation, growth and metabolism. Their expression levels, small
size, abundance of repetitive copies in the genome and mode of action pose unique challenges in studies elucidating the function of miRNAs. New technologies for identification, expression
profiling and target gene validation, as well as manipulation of miRNA expression _in vivo_, will facilitate the study of their contribution to biological processes and disease. Such
information will be crucial to exploit the emerging knowledge of miRNAs for the development of new human therapeutic applications. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a
preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print issues and online access $209.00 per
year only $17.42 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated
during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS CHASING
NON-EXISTENT “MICRORNAS” IN CANCER Article Open access 18 April 2025 THE ROLES OF MICRORNAS IN MOUSE DEVELOPMENT Article 15 January 2021 MICRORNA-184 IN THE LANDSCAPE OF HUMAN MALIGNANCIES:
A REVIEW TO ROLES AND CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE Article Open access 24 November 2023 REFERENCES * Lagos-Quintana, M., Rauhut, R., Lendeckel, W. & Tuschl, T. Identification of novel genes
coding for small expressed RNAs. _Science_ 294, 853–858 (2001). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Lau, N.C., Lim, L.P., Weinstein, E.G. & Bartel, D.P. An abundant class of tiny
RNAs with probable regulatory roles in _Caenorhabditis elegans_. _Science_ 294, 858–862 (2001). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Lee, R.C. & Ambros, V. An extensive class of small
RNAs in _Caenorhabditis elegans_. _Science_ 294, 862–864 (2001). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Reinhart, B.J., Weinstein, E.G., Rhoades, M.W., Bartel, B. & Bartel, D.P.
MicroRNAs in plants. _Genes Dev._ 16, 1616–1626 (2002). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Bentwich, I. et al. Identification of hundreds of conserved and nonconserved
human microRNAs. _Nat. Genet._ 37, 766–770 (2005). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Berezikov, E. et al. Phylogenetic shadowing and computational identification of human microRNA
genes. _Cell_ 120, 21–24 (2005). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Lee, Y. et al. MicroRNA genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase II. _EMBO J._ 23, 4051–4060 (2004). Article CAS
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. _Cell_ 116, 281–297 (2004). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kim, V.N.
MicroRNA biogenesis: coordinated cropping and dicing. _Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol._ 6, 376–385 (2005). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Lee, R.C., Feinbaum, R.L. & Ambros, V. The
_C. elegans_ heterochronic gene _lin-4_ encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. _Cell_ 75, 843–854 (1993). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Wightman, B., Ha, I.
& Ruvkun, G. Posttranscriptional regulation of the heterochronic gene _lin-14_ by _lin-4_ mediates temporal pattern formation in _C. elegans_. _Cell_ 75, 855–862 (1993). Article CAS
PubMed Google Scholar * Brennecke, J., Hipfner, D.R., Stark, A., Russell, R.B. & Cohen, S.M. _bantam_ encodes a developmentally regulated microRNA that controls cell proliferation and
regulates the proapoptotic gene _hid_ in _Drosophila_. _Cell_ 113, 25–36 (2003). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Xu, P., Vernooy, S.Y., Guo, M. & Hay, B.A. The _Drosophila_
microRNA _Mir-14_ suppresses cell death and is required for normal fat metabolism. _Curr. Biol._ 13, 790–795 (2003). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Giraldez, A.J. et al. MicroRNAs
regulate brain morphogenesis in zebrafish. _Science_ 308, 833–838 (2005). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Lagos-Quintana, M. et al. Identification of tissue-specific microRNAs from
mouse. _Curr. Biol._ 12, 735–739 (2002). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Ambros, V. & Lee, R.C. Identification of microRNAs and other tiny noncoding RNAs by cDNA cloning.
_Methods Mol. Biol._ 265, 131–158 (2004). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Berezikov, E., Cuppen, E. & Plasterk, R.H.A. Approaches to miRNA discovery. _Nat. Genet._ 38, S2–S7 (2006).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Baskerville, S. & Bartel, D.P. Microarray profiling of microRNAs reveals frequent coexpression with neighboring miRNAs and host genes. _RNA_ 11,
241–247 (2005). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Barad, O. et al. MicroRNA expression detected by oligonucleotide microarrays: system establishment and expression
profiling in human tissues. _Genome Res._ 14, 2486–2494 (2004). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Nelson, P.T. et al. Microarray-based, high-throughput gene expression
profiling of microRNAs. _Nat. Methods_ 1, 155–161 (2004). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Thomson, J.M., Parker, J., Perou, C.M. & Hammond, S.M. A custom microarray platform for
analysis of microRNA gene expression. _Nat. Methods_ 1, 47–53 (2004). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Chen, J.F. et al. The role of microRNA-1 and microRNA-133 in skeletal muscle
proliferation and differentiation. _Nat. Genet._ 38, 228–233 (2006). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Zhao, Y., Samal, E. & Srivastava, D. Serum response factor regulates a
muscle-specific microRNA that targets _Hand2_ during cardiogenesis. _Nature_ 436, 214–220 (2005). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Esau, C. et al. MicroRNA-143 regulates adipocyte
differentiation. _J. Biol. Chem._ 279, 52361–52365 (2004). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Calin, G.A. et al. Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro-RNA genes _miR15_ and
_miR16_ at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_ 99, 15524–15529 (2002). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Michael, M.Z. SM, O.C., van
Holst Pellekaan, N.G., Young, G.P. & James, R.J. Reduced accumulation of specific microRNAs in colorectal neoplasia. _Mol. Cancer Res._ 1, 882–891 (2003). CAS PubMed Google Scholar *
Johnson, S.M. et al. _RAS_ is regulated by the _let-7_ microRNA family. _Cell_ 120, 635–647 (2005). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Takamizawa, J. et al. Reduced expression of the
_let-7_ microRNAs in human lung cancers in association with shortened postoperative survival. _Cancer Res._ 64, 3753–3756 (2004). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Eis, P.S. et al.
Accumulation of miR-155 and _BIC_ RNA in human B cell lymphomas. _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_ 102, 3627–3632 (2005). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * He, L. et al. A
microRNA polycistron as a potential human oncogene. _Nature_ 435, 828–833 (2005). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Calin, G.A. et al. Human microRNA genes are
frequently located at fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers. _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_ 101, 2999–3004 (2004). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Lu,
J. et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. _Nature_ 435, 834–838 (2005). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Johnson, S.M., Lin, S.Y. & Slack, F.J. The time of
appearance of the _C. elegans let-7_ microRNA is transcriptionally controlled utilizing a temporal regulatory element in its promoter. _Dev. Biol._ 259, 364–379 (2003). Article CAS PubMed
Google Scholar * Mansfield, J.H. et al. MicroRNA-responsive 'sensor' transgenes uncover Hox-like and other developmentally regulated patterns of vertebrate microRNA expression.
_Nat. Genet._ 36, 1079–1083 (2004). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kloosterman, W.P., Wienholds, E., de Bruijn, E., Kauppinen, S. & Plasterk, R.H. _In situ_ detection of miRNAs
in animal embryos using LNA-modified oligonucleotide probes. _Nat. Methods_ 3, 27–29 (2006). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * John, B. et al. Human MicroRNA targets. _PLoS Biol._ 2,
1862–1879 (2004). Article CAS Google Scholar * Kiriakidou, M. et al. A combined computational-experimental approach predicts human microRNA targets. _Genes Dev._ 18, 1165–1178 (2004).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Krek, A. et al. Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. _Nat. Genet._ 37, 495–500 (2005). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar *
Rajewsky, N. microRNA target predictions in animals. _Nat. Genet._ 38, S8–S13 (2006). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Lewis, B.P., Shih, I.H., Jones-Rhoades, M.W., Bartel, D.P. &
Burge, C.B. Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets. _Cell_ 115, 787–798 (2003). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Krutzfeldt, J. et al. Silencing of microRNAs _in vivo_ with
'antagomirs'. _Nature_ 438, 685–689 (2005). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Farh, K.K. et al. The widespread impact of mammalian MicroRNAs on mRNA repression and evolution.
_Science_ 310, 1817–1821 (2005). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Poy, M.N. et al. A pancreatic islet-specific microRNA regulates insulin secretion. _Nature_ 432, 226–230 (2004).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Schratt, G.M. et al. A brain-specific microRNA regulates dendritic spine development. _Nature_ 439, 283–289 (2006). Article CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Lim, L.P. et al. Microarray analysis shows that some microRNAs downregulate large numbers of target mRNAs. _Nature_ 433, 769–773 (2005). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar *
Chen, C.Z., Li, L., Lodish, H.F. & Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs modulate hematopoietic lineage differentiation. _Science_ 303, 83–86 (2004). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Hayashita,
Y. et al. A polycistronic microRNA cluster, _miR-17–92_, is overexpressed in human lung cancers and enhances cell proliferation. _Cancer Res._ 65, 9628–9632 (2005). Article CAS PubMed
Google Scholar * Kanellopoulou, C. et al. Dicer-deficient mouse embryonic stem cells are defective in differentiation and centromeric silencing. _Genes Dev._ 19, 489–501 (2005). Article
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Harfe, B.D., McManus, M.T., Mansfield, J.H., Hornstein, E. & Tabin, C.J. The RNaseIII enzyme Dicer is required for morphogenesis but not
patterning of the vertebrate limb. _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_ 102, 10898–10903 (2005). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Harris, K.S., Zhang, Z., McManus, M.T.,
Harfe, B.D. & Sun, X. Dicer function is essential for lung epithelium morphogenesis. _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_ 103, 2208–2213 (2006). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google
Scholar * Ying, S.Y. & Lin, S.L. MicroRNA: fine-tunes the function of genes in zebrafish. _Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun._ 335, 1–4 (2005). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google
Scholar * Meister, G., Landthaler, M., Dorsett, Y. & Tuschl, T. Sequence-specific inhibition of microRNA- and siRNA-induced RNA silencing. _RNA_ 10, 544–550 (2004). Article CAS PubMed
PubMed Central Google Scholar * Hutvagner, G., Simard, M.J., Mello, C.C. & Zamore, P.D. Sequence-specific inhibition of small RNA function. _PLoS Biol._ 2, E98 (2004). Article
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Leaman, D. et al. Antisense-mediated depletion reveals essential and specific functions of microRNAs in _Drosophila_ development. _Cell_ 121,
1097–1108 (2005). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Esau, C. et al. _miR-122_ regulation of lipid metabolism revealed by _in vivo_ antisense targeting. _Cell Metab._ 3, 87–98 (2006).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Bagga, S. et al. Regulation by _let-7_ and _lin-4_ miRNAs results in target mRNA degradation. _Cell_ 122, 553–563 (2005). Article CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Soutschek, J. et al. Therapeutic silencing of an endogenous gene by systemic administration of modified siRNAs. _Nature_ 432, 173–178 (2004). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
* Fazi, F. et al. A minicircuitry comprised of microRNA-223 and transcription factors NFI-A and C/EBPalpha regulates human granulopoiesis. _Cell_ 123, 819–831 (2005). Article CAS PubMed
Google Scholar * O'Donnell, K.A., Wentzel, E.A., Zeller, K.I., Dang, C.V. & Mendell, J.T. c-Myc-regulated microRNAs modulate E2F1 expression. _Nature_ 435, 839–843 (2005).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Vo, N. et al. A cAMP-response element binding protein-induced microRNA regulates neuronal morphogenesis. _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_ 102, 16426–16431
(2005). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Conaco, C., Otto, S., Han, J.J. & Mandel, G. Reciprocal actions of REST and a microRNA promote neuronal identity. _Proc.
Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_ 103, 2422–2427 (2006). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Liu, J. et al. A role for the P-body component GW182 in microRNA function. _Nat. Cell
Biol._ 7, 1161–1166 (2005). Article CAS Google Scholar * Liu, J., Valencia-Sanchez, M.A., Hannon, G.J. & Parker, R. MicroRNA-dependent localization of targeted mRNAs to mammalian
P-bodies. _Nat. Cell Biol._ 7, 719–723 (2005). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Yang, W. et al. Modulation of microRNA processing and expression through RNA editing by
ADAR deaminases. _Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol._ 13, 13–21 (2006). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Download references AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Laboratory of Metabolic
Diseases, The Rockefeller University, 1230 York Avenue, New York, 10021, New York, USA Jan Krützfeldt, Matthew N Poy & Markus Stoffel Authors * Jan Krützfeldt View author publications
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Matthew N Poy View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Markus Stoffel View author
publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar ETHICS DECLARATIONS COMPETING INTERESTS M.S. is a member of the Scientific Advisory Board of Aluylam Pharmaceuticals.
RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Krützfeldt, J., Poy, M. & Stoffel, M. Strategies to determine the biological function of microRNAs.
_Nat Genet_ 38 (Suppl 6), S14–S19 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1799 Download citation * Published: 30 May 2006 * Issue Date: June 2006 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1799 SHARE THIS
ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Trending News
A new school in kyiv is training women to pilot dronesRACHEL MARTIN, HOST: Women have played a big role in Ukraine's resistance to Russia's invasion. Now a new scho...
48 thousand uc graduate student workers go on strikeAILSA CHANG, HOST: It is day two of a UAW strike in California. Some 48,000 academic workers, like teaching assistants a...
Fresh air weekend: 'weird al' yankovic; to retire, or not to retire?_Fresh Air Weekend highlights some of the best interviews and reviews from past weeks, and new program elements speciall...
Brazil's president has finally broken his silence about the presidential election | WFAE 90.7 - Charlotte's NPR News SourceBrazil's president has finally broken his silence about the presidential election By Carrie Kahn Published November 1, 2...
Photos: what do reparations mean to me?When photographer Dee Dwyer attended the Rally 4 Reparations in Washington, D.C., she heard from people across the count...
Latests News
Strategies to determine the biological function of micrornasABSTRACT MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are regulators of gene expression that control many biological processes in development, dif...
Taylor Swift breaks a record and sweeps Billboard's top ten spots | WFAE 90.7 - Charlotte's NPR News SourceTaylor Swift breaks a record and sweeps Billboard's top ten spots Published November 1, 2022 at 5:02 AM EDT Facebook Twi...
Movie Review: 'Wakanda Forever' | WFAE 90.7 - Charlotte's NPR News SourceMovie Review: 'Wakanda Forever' Published November 12, 2022 at 5:09 PM EST Facebook Twitter LinkedIn Email Listen • 3:44...
Michigan voters reelect Gov. Whitmer, safeguard abortion rights in the state | WFAE 90.7 - Charlotte's NPR News SourceUnited States & World Michigan voters reelect Gov. Whitmer, safeguard abortion rights in the state Michigan Public | By ...
FTX investors fear they lost everything, and wonder if there's anything they can do | WFAE 90.7 - Charlotte's NPR News SourceFTX investors fear they lost everything, and wonder if there's anything they can do By Chris Arnold Published November 1...