Interaction of zinc or vitamin a supplementation and specific parasite infections on mexican infants' growth: a randomized clinical trial
Interaction of zinc or vitamin a supplementation and specific parasite infections on mexican infants' growth: a randomized clinical trial"
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
ABSTRACT BACKGROUND: The efficacy of micronutrient supplementation on growth may be modified by specific gastrointestinal parasite infections METHODS: We carried out a double-blind
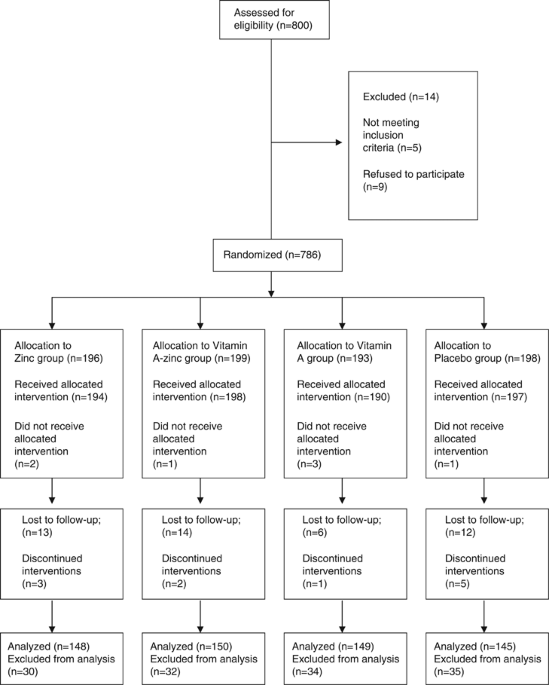
placebo-controlled trial to evaluate the effect of vitamin A and zinc supplementation on gastro-intestinal pathogen infections and growth among 584 infants in Mexico City. Children aged 5–15
months were assigned to receive either a vitamin A supplement every 2 months (20 000 IU of retinol for infants ⩽; 1 year or 45 000 IU for infants >1 year), a daily supplement of 20 mg of
zinc, a combined vitamin A–zinc supplement or a placebo, and were followed up for 1 year. Weight and length were measured once a month and morbidity histories were recorded twice a week for
12 months. Monthly stool samples were screened for _Giardia duodenalis, Ascaris lumbricoides_ and _Entamoeba spp._ Growth velocity slopes, generated from the linear regression of individual
child length, and height-for-age _z_-scores on time were analyzed as end points in regression models, adjusting for the presence of parasite infections RESULTS: The main effect of vitamin A
supplementation was in height improvement (_P_<0.05), and was only found in the model evaluating infants with any parasite. There was an interaction effect of slower growth (_P_<0.05)
found in infants infected with any parasite and supplemented with vitamin A in slower growth (_P_<0.05). In addition, the interaction of zinc supplementation and _Giardia duodenalis_ or
_A. lumbricoides_ was associated with reduced growth (_P_<0.05). CONCLUSION: Gastro-intestinal parasite infections may modify the effect that zinc or vitamin A supplementation has on
childhood growth. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution
Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print issues and online access $259.00 per year only $21.58 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full
article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs *
Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS MICRONUTRIENT SUPPLEMENTS CAN PROMOTE DISRUPTIVE PROTOZOAN AND FUNGAL COMMUNITIES IN THE DEVELOPING INFANT GUT Article Open
access 18 November 2021 EFFECTS OF PROBIOTIC AND SYNBIOTIC SUPPLEMENTATION ON PONDERAL AND LINEAR GROWTH IN SEVERELY MALNOURISHED YOUNG INFANTS IN A RANDOMIZED CLINICAL TRIAL Article Open
access 01 February 2023 _GIARDIA_ HINDERS GROWTH BY DISRUPTING NUTRIENT METABOLISM INDEPENDENT OF INFLAMMATORY ENTEROPATHY Article Open access 18 May 2023 REFERENCES * Allen LH (1993) The
nutrition CRSP: what is marginal malnutrition, and does it affect human function? _Nutr Rev_ 51 255–267 Article CAS Google Scholar * Berkman DS, Lescano AG, Gilman RH, Lopez SL, Black MM
(2002) Effects of stunting, diarrhoeal disease, and parasitic infection during infancy on cognition in late childhood: a follow-up study _Lancet_ 359 564–571 Article Google Scholar *
Bhandari N, Bahl R, Taneja S (2001) Effect of micronutrient supplementation on linear growth of children _Br J Nutr_ 85 S131–s137 Article CAS Google Scholar * Brown KH, Peerson JM, Rivera
J, Allen LH (2002) Effect of supplemental zinc on the growth and serum zinc concentrations of prepubertal children: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials _Am J Clin Nutr_ 75
1062–1071 Article CAS Google Scholar * Checkley W, Epstein LD, Gilman RH, Black RE, Cabrera L, Sterling CR (1998) Effects of _Cryptosporidium parvum_ infection in Peruvian children:
growth faltering and subsequent catch-up growth _Am J Epidemiol_ 148 497–506 Article CAS Google Scholar * Checkley W, Epstein LD, Gilman RH, Cabrera L, Black RE (2003) Effects of acute
diarrhea on linear growth in Peruvian children _Am J Epidemiol_ 157 166–175 Article Google Scholar * Christian P, West Jr KP (1998) Interactions between zinc and vitamin A: an update _Am J
Clin Nutr_ 68 435S–441S Article CAS Google Scholar * Curtale F, Vaidya Y, Muhilal, Tilden RL (1994) _Ascariasis_, hookworm infection and serum retinol amongst children in Nepal
_Panminerva Med_ 36 19–21 CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Duggan C, MacLeod WB, Krebs NF, Westcott JL, Fawzi WW, Premji ZG _et al_ (2005) Plasma zinc concentrations are depressed during the
acute phase response in children with _falciparum malaria_ _J Nutr_ 135 802–807 Article CAS Google Scholar * Evain-Brion D, Porquet D, Thérond P, Fjellestad-Paulsen A, Grenèche MO,
François L _et al_ (1994) Vitamin A deficiency and nocturnal growth hormone secretion in short children _Lancet_ 343 87–88 Article CAS Google Scholar * Habicht JP, Martorell R, Yarbrough
C, Malina RM, Klein RE (1974) Height and weight standards for preschool children. How relevant are ethnic differences in growth potential? _Lancet_ 7858 611–614 Article Google Scholar *
Hadi H, Stoltzfus RJ, Moulton LH, Dibley MJ, West Jr KP (1999) Respiratory infections reduce the growth response to vitamin A supplementation in a randomized controlled trial _Int J
Epdemiol_ 28 874–881 Article CAS Google Scholar * Hadi H, Dibley MJ, West Jr KP (2004) Complex interactions with infection and diet may explain seasonal growth responses to vitamin A in
preschool aged Indonesian children _Eur J Clin Nutr_ 58 990–999 Article CAS Google Scholar * Kalter H (1992) The validation of interviews for estimating morbidity _Health Policy Plan_ 7
30–39 Article CAS Google Scholar * Houpt E, Barroso L, Lockhart L, Wright R, Cramer C, Lyerly D, Petri WA (2004) Prevention of intestinal amebiasis by vaccination with the _Entamoeba
spp_. Gal/GalNac lectin _Vaccine_ 22 611–617 Article CAS Google Scholar * Kirkwood BR, Ross DA, Arthur P, Morris SS, Dollimore N, Binka FN _et al_ (1996) Effect of vitamin A
supplementation on the growth of young children in northern Ghana _Am J Clin Nutr_ 63 773–781 Article CAS Google Scholar * Kuczmarski RJ, Ogden CL, Guo SS, Grummer-Strawn LM, Flegal KM,
Mei Z _et al_ (2002) 2000 CDC growth charts for the United States: Methods and development. National Center for Health Statistics _Vital Health Stat 11_ 246 1–190 Google Scholar * Lane S,
Lloyd D (2002) Current trends in research into the waterborne parasite _Giardia_ _Crit Rev Microbiol_ 28 123–147 Article Google Scholar * Langford TD, Housley MP, Boes M, Chen J, Kagnoff
MF, Gillin FD _et al_ (2002) Central importance of immunoglobulin A in host defense against _Giardia_ spp _Infect Immun_ 70 11–18 Article CAS Google Scholar * Linklater JM, Khin-Maung-U,
Bolin TD, Thane-Toe, Pereira SP, Myo-Khin _et al_ (1991) Absorption of carbohydrate from rice in _Ascaris lumbricoides_ infected Burmese village children _J Trop Pediatr_ 38 323–326 Article
Google Scholar * Long KZ, Rosado JL, Montoya Y, Solano ML, Hertzmark E, Santos JI (2007) Impact of vitamin A and zinc supplementation on G lamblia, E spp, and A lumbricoides infections
among Mexican children in a randomized clinical trial _Pediatrics_ 120 e846–e855 Article Google Scholar * Mahalanabis D, Simpson TW, Chakraborty ML, Ganguli C, Bhattacharjee AK, Mukherjee
KL (1979) Malabsorption of water miscible vitamin A in children with giardiasis and ascariasis _Am J Clin Nutr_ 32 313–318 Article CAS Google Scholar * Martin LK, Beaver PC (1968)
Evaluation of Kato thick-smear technique for quantitative diagnosis of helminth infections _Am J Trop Med Hyg_ 17 382–391 Article CAS Google Scholar * Mobarhan S, Greenberg B, Mehta R,
Friedman H, Barch D (1992) Zinc deficiency reduces hepatic cellular retinol-binding protein in rats _Int J Vitam Nutr Res_ 62 148–154 CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Moore SR, Lima AA,
Conaway MR, Schorling JB, Soares AM, Guerrant RL (2001) Early childhood diarrhea and helminthiases associate with long-term linear growth faltering _Intl J Epidemiol_ 30 1457–1464 Article
CAS Google Scholar * Moya-Camarena SY, Sotelo N, Valencia ME (2002) Effects of asymptomatic _Giardia intestinales_ infection on carbohydrate absorption in well-nourished Mexican children
_Am J Trop Med Hyg_ 66 225–259 Article Google Scholar * Muhilal, Permeisih D, Idjradinata YR, Muherdiyantiningsih, Karyadi D (1988) Vitamin A-fortified monosodium glutamate and health
growth and survival of children: a controlled field trial _Am J Clin Nutr_ 48 1271–1276 Article CAS Google Scholar * Ninh NX, Thissen JP, Collette L, Gerard G, Khoi HH, Ketelslegers JM
(1996) Zinc supplementation increases growth and circulating insulin-like growth factor (IGF-I) in growth-retarded Vietnamese children _Am J Clin Nutr_ 63 514–519 Article CAS Google
Scholar * Northrop CA, Lunn PG, Wainwright M, Evans J (1987) Plasma albumin concentrations and intestinal permeability in Bangladeshi children infected with Ascaris lumbricoides _Trans R
Soc Trop Med Hyg_ 81 811–815 Article CAS Google Scholar * Olsen A, Thiong'o FW, Ouma JH, Mwaniki D, Magnussen P, Michaelsen KF, Friis H (2003) Effects of multimicronutrient
supplementation on helminth reinfection: a randomized controlled trial in Kenyan schoolchildren _Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg_ 97 109–114 Article CAS Google Scholar * Ramakrishnan U, Latham
MC, Abel R (1995) Vitamin A supplementation does not improve physical growth of preschool children: A randomized double blind field trial in South India _J Nutr_ 125 202–211 CAS PubMed
Google Scholar * Ramakrishnan U, Aburto N, McCabe G, Martorell R (2004) Micronutrient interventions but not vitamin A or iron interventions alone improve child growth: Results of 3
meta-analyses _J Nutr_ 134 2592–2602 Article CAS Google Scholar * Rivera Dommarco J, Shama-Levy T, Villalpando-Hernandez S, González-de Cossío T, Hernández-Prado B, Sepúlveda J (2001
_Encuesta Nacional de Nutricion 1999_ Estado nutrocio de ninos y mujeres en Mexico, Cuernavaca, Morelos: Instituto Nacional de Salud Pública. Google Scholar * Rosado JL, López P, Muñoz E,
Martinez H, Allen LH (1997) Zinc supplementation reduced morbidity, but neither zinc nor iron supplementation affected growth or body composition of Mexican preschoolers _Am J Clin Nutr_ 65
13–19 Article CAS Google Scholar * Rosado JL (1998) Zinc deficiency and its functional implications _Salud Pública Mex_ 40 181–188 Article CAS Google Scholar * Rosado JL (1999)
Separate and joint effects of micronutrient deficiencies on linear growth _J Nutr_ 129 531S–533S Article CAS Google Scholar * Schorling JB, McAuliffe JF, de Souza MA, Guerrant RL (1990)
Malnutrition is associated with increased diarrhoea incidence and duration among children in an urban Brazilian slum _Int J Epidemiol_ 19 728–735 Article CAS Google Scholar * Scott ME,
Koski KG (2000) Zinc deficiency impairs immune responses against parasitic nematode infections at intestinal and systemic sites _J Nutr_ 130 1412S–1420S Article CAS Google Scholar *
Shankar AH, Genton B, Semba RD, Baisor M, Paino J, Tamja S _et al_ (1999) Effect of vitamin A supplementation on morbidity due to _Plasmodium falciparum_ in young children in Papua New
Guinea: a randomized trial _Lancet_ 354 203–209 Article CAS Google Scholar * Shankar AH, Genton B, Baisor M, Paino J, Tamja S, Adiguma T _et al_ (2000) The influence of zinc
supplementation on morbidity due to _Plasmodium falciparum_: a randomized trial in preschool children in Papua New Guinea _Am J Trop Med Hyg_ 62 663–669 Article CAS Google Scholar *
Solomons NW (1982) Giardiasis: nutritional implications _Rev Infect Dis_ 4 859–869 Article CAS Google Scholar * Sommers A, West KP (1996 _Vitamin A Deficiency: Health, Survival, and
Vision_ Oxford University Press: New York Google Scholar * Stanley SL (2003) Amoebiasis _Lancet_ 361 1025–1034 Article CAS Google Scholar * Turner JD, Faulkner H, Kamgno J, Cormont F,
Van Snick J, Else KJ _et al_ (2003) Th2 cytokines are associated with reduced worm burdens in a human intestinal helminth infection _J Infect Dis_ 188 1768–1775 Article CAS Google Scholar
* Underwood BA, Arthur P (1996) The contribution of vitamin A to public health _FASEB J_ 10 1040–1048 Article CAS Google Scholar * Valencia ME, McNeill G, Haggarty P, Moya SY, Pinelli
A, Quihui L _et al_ (1995) Energetic consequences of mild Giardia intestinalis infestation in Mexican children _Am J Clin Nutr_ 61 860–865 Article CAS Google Scholar * Viteri FE, Gonzalez
H (2002) Adverse outcomes of poor micronutrient status in childhood and adolescence _Nutr Rev_ 60 (5 Part 2) S77–S83 Article Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This
project was supported by the Instituto de Nutricion Danone, CONACYT (National Council of Science and Technology of Mexico) and by the National Institutes of Health Grant no. K01 DK06142-02.
We thank Cristina Barrgan and Matilde Juárez of the Clinical Microbiological Laboratory, Hospital La Perla, Cda Netzahuaycoytl, México for their assistance in the laboratory. AUTHOR
INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * School of Natural Sciences, Universidad Autónoma de Querétaro, Mexico J L Rosado & M C Caamaño * Centro de Salud para Infancia y Adolescencia,
Secretaría de Salud, Mexico City, Mexico Y A Montoya * Instituto Nacional de Ciencias Médicas y Nutrición 'Salvador Zubiran, Mexico City, México M de Lourdes Solano * Department of
Experimental Medicine, School of Medicine, Universidad Nacional Autonoma de Mexico, Mexico City, Mexico J I Santos * Nutrition, Disease Control and Injury Unit, School of Population Health,
University of Queensland, Australia K Z Long * Nutrition, CINDETEC, Queretaro, Mexico K Z Long Authors * J L Rosado View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed
Google Scholar * M C Caamaño View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Y A Montoya View author publications You can also search for this author
inPubMed Google Scholar * M de Lourdes Solano View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * J I Santos View author publications You can also search
for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * K Z Long View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to J L Rosado.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION Presented in part: Impact of vitamin A and zinc supplementation on growth among Mexican infants. Rosado JL, Caamaño MC, Montoya YA, Frongillo E, Santos JI, Long KZ.
Experimental Biology Meetings, San Franciso CA 2006. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Rosado, J., Caamaño, M., Montoya, Y. _et al._
Interaction of zinc or vitamin A supplementation and specific parasite infections on Mexican infants' growth: a randomized clinical trial. _Eur J Clin Nutr_ 63, 1176–1184 (2009).
https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2009.53 Download citation * Received: 12 June 2008 * Revised: 03 March 2009 * Accepted: 15 April 2009 * Published: 22 July 2009 * Issue Date: October 2009 * DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2009.53 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not
currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative KEYWORDS * vitamin A * zinc * parasites * growth * infants
Trending News
The best (nontoxic) pesticides and insecticides, according to gardenersEven though it’s easier than ever to buy plants online, keeping them alive is still a challenge. So we’re digging up eve...
The aarp minute: july 22, 2020Memorial Day Sale! Join AARP for just $11 per year with a 5-year membership Join now and get a FREE gift. Expires 6/4 G...
Baba vanga 2019 predictions: shock claims of cataclysmVILLAGERS VISIT BULGARIAN MYSTIC BABA VANGA The Bulgarian mystic, dubbed by her followers the Balkan Nostradamus, is sa...
How to recognise french road signs for recommended, not obligatory, behaviourTHE SIGNS ARE BECOMING INCREASINGLY USED IN SOME AREAS Some road signs in France signal ‘recommended’ behaviour for moto...
Bandra boy kidnappers who took `5 lakh held1978 Blockbuster _Inqaar_ reportedly inspired a kidnapping 23 years later, with four accused forcing a minor victim’s fa...
Latests News
Interaction of zinc or vitamin a supplementation and specific parasite infections on mexican infants' growth: a randomized clinical trialABSTRACT BACKGROUND: The efficacy of micronutrient supplementation on growth may be modified by specific gastrointestina...
Ipl 2023: list of players who will arrive late due to international commitmentsFEW INTERNATIONAL SERIES ARE SET TO OVERLAP WITH THE 16TH EDITION OF THE INDIAN PREMIER LEAGUE (IPL) AND HENCE, FEW TEAM...
Martin bayfield's acting career: films, tv and cameos - ruckWE TAKE A LOOK AT MARTIN BAYFIELD’S ACTING CAREER SINCE RETIRING FROM RUGBY WITH A NUMBER OF BIG ROLES INCLUDED. As well...
Vic news - 9news - latest updates and breaking headlines victoriaThis is a collection page for Victoria news. Check this page for breaking headlines from Melbourne plus surrounding regi...
Standard deviation price channel strategyData cycle: about 30 minutes Support: Digital Currency Spot, Digital currency Futures Support: Commodity futures Digital...